Westerlund 1 : A Super-Star Cluster within the Milky Way
... We present optical and IR photometric and spectroscopic observations of the young open cluster Westerlund 1 that indicate it is the first Super Star Cluster identified in the Milky Way. Wd1 hosts a rich population of OB supergiants, Wolf-Rayet stars, Luminous Blue Variables, Yellow Hypergiants and R ...
... We present optical and IR photometric and spectroscopic observations of the young open cluster Westerlund 1 that indicate it is the first Super Star Cluster identified in the Milky Way. Wd1 hosts a rich population of OB supergiants, Wolf-Rayet stars, Luminous Blue Variables, Yellow Hypergiants and R ...
DTU_9e_ch12
... can initially be isolated but, as they age, grow and exchange mass. Such mass exchange leads to different fates than if the same stars had evolved in isolation. ...
... can initially be isolated but, as they age, grow and exchange mass. Such mass exchange leads to different fates than if the same stars had evolved in isolation. ...
AAVSO: Mu Cephei, October 2002 Variable Star Of The Month
... Mu Cephei has not quite reached the point of a supernova explosion, although it may be close. Mu Cep has expanded and cooled and is currently in its red supergiant phase of life. Like other red giants and supergiants, it is unstable and it pulsates. Right now the radial (in-and-out) pulsations are o ...
... Mu Cephei has not quite reached the point of a supernova explosion, although it may be close. Mu Cep has expanded and cooled and is currently in its red supergiant phase of life. Like other red giants and supergiants, it is unstable and it pulsates. Right now the radial (in-and-out) pulsations are o ...
Lesson Plan G2 The Stars
... the other properties of the star. Some stars look bright because they are very near the Sun. Others look equally bright but are many times further away from the Sun. These more distant stars are extraordinarily bright. Without knowing the distance it’s impossible to distinguish between the two. ...
... the other properties of the star. Some stars look bright because they are very near the Sun. Others look equally bright but are many times further away from the Sun. These more distant stars are extraordinarily bright. Without knowing the distance it’s impossible to distinguish between the two. ...
Variable Star Spectroscopy 2008
... spectra of classical and dwarf novae in outburst for example are quite different. The rather pretty spectrum of Nova Cyg 08 taken by Alain Lopez using an unmodified Cannon DSLR shows clear emission lines from Hydrogen and Iron whereas the spectrum of dwarf nova And 08 is very blue but virtually feat ...
... spectra of classical and dwarf novae in outburst for example are quite different. The rather pretty spectrum of Nova Cyg 08 taken by Alain Lopez using an unmodified Cannon DSLR shows clear emission lines from Hydrogen and Iron whereas the spectrum of dwarf nova And 08 is very blue but virtually feat ...
The Significance of Mega Stars
... letters to the brightest stars visible in each constellation, usually in descending order of apparent brightness (but Bayer was not always consistent in this). In the early 1700s John Flamsteed assigned numbers to the bright stars in each constellation, in order of right ascension. The Flamsteed num ...
... letters to the brightest stars visible in each constellation, usually in descending order of apparent brightness (but Bayer was not always consistent in this). In the early 1700s John Flamsteed assigned numbers to the bright stars in each constellation, in order of right ascension. The Flamsteed num ...
Continuous Spectrum Absorption Line Spectrum Emission Line
... to the relative position in the spectral sequence. For example, O1 is earlier than O8; and B3 is later than O8. Stars come in a wide range of sizes and temperatures. The hottest stars in the sky have temperatures in excess of 40,000 K, whereas the coolest stars that we can detect optically have temp ...
... to the relative position in the spectral sequence. For example, O1 is earlier than O8; and B3 is later than O8. Stars come in a wide range of sizes and temperatures. The hottest stars in the sky have temperatures in excess of 40,000 K, whereas the coolest stars that we can detect optically have temp ...
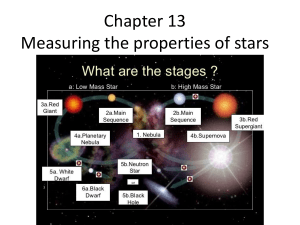
CHAPTER 12—STELLAR EVOLUTION
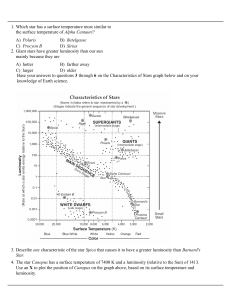
... 1. The main sequence has a limit at the lower end because a. low mass stars form from the interstellar medium very rarely. b. hydrogen fusion combined 4 hydrogen nuclei to form 1 helium nucleus. c. pressure does not depend on temperature in degenerate matter. d. the lower limit represents when the r ...
... 1. The main sequence has a limit at the lower end because a. low mass stars form from the interstellar medium very rarely. b. hydrogen fusion combined 4 hydrogen nuclei to form 1 helium nucleus. c. pressure does not depend on temperature in degenerate matter. d. the lower limit represents when the r ...
Understanding Stars
... In this exercise, your group will calculate the temperature, luminosity, and radius of a number of stars, and add these values to the temperature-luminosity diagram on the board. The accompanying handout gives recipes for calculating, in physical units, the properties of any star based only on its s ...
... In this exercise, your group will calculate the temperature, luminosity, and radius of a number of stars, and add these values to the temperature-luminosity diagram on the board. The accompanying handout gives recipes for calculating, in physical units, the properties of any star based only on its s ...
Encyclopedia of Optical Engineering Stellar Evolution
... In this configuration, the electrons become closely ‘‘stacked’’ in space, separated by the Pauli exclusion principle: No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers relating to energy and motion in a very tiny volume. Basically, the electrons can only be pushed so close together. The electr ...
... In this configuration, the electrons become closely ‘‘stacked’’ in space, separated by the Pauli exclusion principle: No two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers relating to energy and motion in a very tiny volume. Basically, the electrons can only be pushed so close together. The electr ...