CHP 13
... b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can grow hot through friction. b. neutron stars of more than 3 solar masses are not ...
... b. produced by a supernova explosion. c. produced by a nova explosion. d. a nebula within which planets are forming. e. a cloud of hot gas surround a planet 3. The Chandrasekhar limit tells us that a. accretion disks can grow hot through friction. b. neutron stars of more than 3 solar masses are not ...
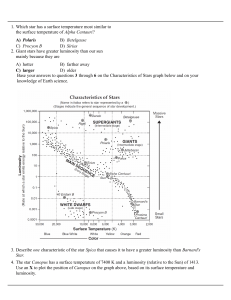
Project 8 : Stellar Spectra: Classification
... The spectra shown at Fig. 6 come from stars with the same temperature T but pressure P increasing downwards in the plot. Because the collision rate between atoms is higher for denser gas. When an atom collides with another particle, its energy levels are temporarily shifted making ...
... The spectra shown at Fig. 6 come from stars with the same temperature T but pressure P increasing downwards in the plot. Because the collision rate between atoms is higher for denser gas. When an atom collides with another particle, its energy levels are temporarily shifted making ...
Stellar Evolution – Cosmic Cycles of Formation and Destruction
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
... becomes depleted and the fusion of hydrogen nuclei to helium nuclei stops. The massluminosity relationship for main sequence stars is defined as: L/L (Sun) ~ [M/M (Sun)]4. All main sequence stars with a mass less than ~8 solar masses are sometimes referred to as dwarf stars, with the coolest, least ...
Document
... tremendous shock wave that blows apart the entire shell of the star in an explosion called a Supernova (Type II) ...
... tremendous shock wave that blows apart the entire shell of the star in an explosion called a Supernova (Type II) ...
The Cosmic Perspective Star Stuff
... a) They recycle material from stars that have died. b) They create new elements and blow them out into space so that new generations of stars can be made from them. c) They destroy elements, letting each new generation of stars begin anew. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... a) They recycle material from stars that have died. b) They create new elements and blow them out into space so that new generations of stars can be made from them. c) They destroy elements, letting each new generation of stars begin anew. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
FREE Sample Here
... and set the magnitude limit to -30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
... and set the magnitude limit to -30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
chapter 2 - Test Bank 1
... and set the magnitude limit to -30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
... and set the magnitude limit to -30.0 to 5.0 and turn off the display of all objects except stars, planets, moon, and sun. For now turn off all reference lines, including the constellation reference lines. Now you’re ready to begin the demonstration. Press Alt+> and the program will display the daily ...
We Are Made of Stardust
... For stars, there is a price to be paid for creativity: The more kinds of atoms created, the shorter-lived the star. Only the chemically laconic are long-lived. The reason pertains to gravity and how gravity determines the extent and pace of nuclear fusion. The more mass (more hydrogen) that a star b ...
... For stars, there is a price to be paid for creativity: The more kinds of atoms created, the shorter-lived the star. Only the chemically laconic are long-lived. The reason pertains to gravity and how gravity determines the extent and pace of nuclear fusion. The more mass (more hydrogen) that a star b ...
STELLAR FORMATION AND EVOLUTION
... region of young stars. As time goes on, stars change or evolve as the physics in their cores change. But for most of the lifetime of a star, it sits somewhere on the main sequence. We will begin by looking at what happens to most stars in the universe. These are the low mass stars. In space, there a ...
... region of young stars. As time goes on, stars change or evolve as the physics in their cores change. But for most of the lifetime of a star, it sits somewhere on the main sequence. We will begin by looking at what happens to most stars in the universe. These are the low mass stars. In space, there a ...
Constellation Catalog
... 1.) Cassiopeia has three stars with known planets and contains two Messier objects (objects similar yet not classified as comets) 2.) Cassiopeia is the 25th largest constellation in the night sky occupying 598 square degrees. 3.) The Perseids meteor shower is associated with Cassiopeia ...
... 1.) Cassiopeia has three stars with known planets and contains two Messier objects (objects similar yet not classified as comets) 2.) Cassiopeia is the 25th largest constellation in the night sky occupying 598 square degrees. 3.) The Perseids meteor shower is associated with Cassiopeia ...
3.2 Spectra and Spectral Classification
... (a) absolute magnitude or luminosity and (b) spectral type or effective temperature (sometimes also color index) That means there exist different forms of this diagram, usually ● log L versus spectral type ● log L versus log T ● M versus B-V ...
... (a) absolute magnitude or luminosity and (b) spectral type or effective temperature (sometimes also color index) That means there exist different forms of this diagram, usually ● log L versus spectral type ● log L versus log T ● M versus B-V ...
So, what`s the problem for high
... finished accretion from its parent cloud core. Radiation pressure should stop accretion before a star can reach its final mass. High-mass stars only form in clusters, so isolating individuals is difficult: Almost no HMPOs have been unambiguously identified at specific star-like points on the sky tha ...
... finished accretion from its parent cloud core. Radiation pressure should stop accretion before a star can reach its final mass. High-mass stars only form in clusters, so isolating individuals is difficult: Almost no HMPOs have been unambiguously identified at specific star-like points on the sky tha ...
LAB #5 - GEOCITIES.ws
... A, F, G, K, and M, and though the letter designations have no meaning other than that imposed on them by history, the names have stuck to this day. Each spectral class is divided into tenths, so that a B0 star follows an O9, and an A0, a B9. The early spectral classification system was based on the ...
... A, F, G, K, and M, and though the letter designations have no meaning other than that imposed on them by history, the names have stuck to this day. Each spectral class is divided into tenths, so that a B0 star follows an O9, and an A0, a B9. The early spectral classification system was based on the ...
Fulltext PDF
... star clusters are widely used as ideal samples to study stellar evolution as all other parameters are fixed, and the mass of stars defines it’s evolution. In the present times, they are also very useful in understanding star and planet formation as these are very closely linked processes, planet for ...
... star clusters are widely used as ideal samples to study stellar evolution as all other parameters are fixed, and the mass of stars defines it’s evolution. In the present times, they are also very useful in understanding star and planet formation as these are very closely linked processes, planet for ...