Test - Scioly.org
... 41. What is the sub-luminous type of supernova that may not destroy a what dwarf called? A. Type Iab B. Type Ib C. Type Ix D. Type Iax E. Type II 42. A star with a surface temperature hotter than the Sun will live a(n): A. Longer life on the main sequence B. Shorter life on the main sequence C. Equ ...
... 41. What is the sub-luminous type of supernova that may not destroy a what dwarf called? A. Type Iab B. Type Ib C. Type Ix D. Type Iax E. Type II 42. A star with a surface temperature hotter than the Sun will live a(n): A. Longer life on the main sequence B. Shorter life on the main sequence C. Equ ...
white dwarf supernova
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
... When the white dwarf hits the mass limit, it gets hot enough for carbon fusion to start. It undergoes carbon fusion everywhere at once, so it’s a HUGE release of energy. This is called a “light curve” It plots luminosity as a function of time ...
IND 6 - 1 Stars and Stellar Evolution In order to better understand
... layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( > 8 Msun), will eventually explode as a massive star supernova (often known as a “Type II” sup ...
... layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( > 8 Msun), will eventually explode as a massive star supernova (often known as a “Type II” sup ...
Stars - cayugascience
... extremely long. All stars form inside a collapsing nebula, a cloud of dust and gases. A nebula’s collapse can be triggered by a disturbance such as the gravitational attraction of a nearby star or the shockwave from an exploding star. Inside a collapsing nebula, the region with the greatest amount o ...
... extremely long. All stars form inside a collapsing nebula, a cloud of dust and gases. A nebula’s collapse can be triggered by a disturbance such as the gravitational attraction of a nearby star or the shockwave from an exploding star. Inside a collapsing nebula, the region with the greatest amount o ...
Here
... resolving the disk of any star (apart from the Sun). The stars are very far away, so their angular size as seen from Earth is extremely small. • The light we receive from a star comes from the entire hemisphere that is facing us. That is, we see the “disk-integrated” light. ...
... resolving the disk of any star (apart from the Sun). The stars are very far away, so their angular size as seen from Earth is extremely small. • The light we receive from a star comes from the entire hemisphere that is facing us. That is, we see the “disk-integrated” light. ...
visual photometry - El Camino College
... see much fainter than 4th or 6th magnitudes. This magnitude system, despite its antiquity and obvious problems, has persisted and been adapted to become more numerically rigorous. The standard star used when calibrating the magnitude system was declared to be a fairly bright summer star – Vega. Vega ...
... see much fainter than 4th or 6th magnitudes. This magnitude system, despite its antiquity and obvious problems, has persisted and been adapted to become more numerically rigorous. The standard star used when calibrating the magnitude system was declared to be a fairly bright summer star – Vega. Vega ...
Visual Photometry - El Camino College
... see much fainter than 4th or 6th magnitudes. This magnitude system, despite its antiquity and obvious problems, has persisted and been adapted to become more numerically rigorous. The standard star used when calibrating the magnitude system was declared to be a fairly bright summer star – Vega. Vega ...
... see much fainter than 4th or 6th magnitudes. This magnitude system, despite its antiquity and obvious problems, has persisted and been adapted to become more numerically rigorous. The standard star used when calibrating the magnitude system was declared to be a fairly bright summer star – Vega. Vega ...
Killer Skies
... luminosity and temperature. Also enables astronomers to sort the stars by their sizes. The diagram is named after its originators:Ejnar Hertzsprung in the Netherlands, and Henry Norris Russell in the United States. Note, temperature decreases to the right (unlike most graphs)!!! Historical now, so w ...
... luminosity and temperature. Also enables astronomers to sort the stars by their sizes. The diagram is named after its originators:Ejnar Hertzsprung in the Netherlands, and Henry Norris Russell in the United States. Note, temperature decreases to the right (unlike most graphs)!!! Historical now, so w ...
Galaxies - Indiana University Astronomy
... Using the same website as above, click on “spectrum” for the two galaxies whose distances you measured. The optical spectrum of the galaxy is shown at the top of the spectrum page. Shown are many different spectral features, including absorption lines and emission lines, superimposed on continuum em ...
... Using the same website as above, click on “spectrum” for the two galaxies whose distances you measured. The optical spectrum of the galaxy is shown at the top of the spectrum page. Shown are many different spectral features, including absorption lines and emission lines, superimposed on continuum em ...
For stars
... • Even though Polaris is currently the North star, it doesn’t lie due North –and eventually will move and Vega will be our North Star, Why do you think this is happening? Discuss with your elbow partner, write down your thoughts on your white board, be ready to defend them. ...
... • Even though Polaris is currently the North star, it doesn’t lie due North –and eventually will move and Vega will be our North Star, Why do you think this is happening? Discuss with your elbow partner, write down your thoughts on your white board, be ready to defend them. ...
Modified True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true or false
... 8. HS-ESS1-1 In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a a. Red supergiant. c. White dwarf. b. Black dwarf. d. Black hole. ...
... 8. HS-ESS1-1 In the last stage of stellar evolution following a supernova, stars too massive to form neutron stars may form a a. Red supergiant. c. White dwarf. b. Black dwarf. d. Black hole. ...
Accretion Disk
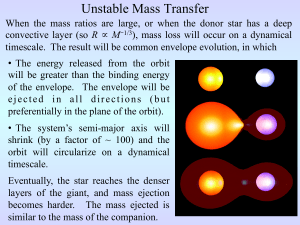
... still be two stars: a low mass star still burning hydrogen, and a helium proto-white dwarf. The separation will be very small, and the hot core will ionize the ejected envelope, producing a planetary nebula. ...
... still be two stars: a low mass star still burning hydrogen, and a helium proto-white dwarf. The separation will be very small, and the hot core will ionize the ejected envelope, producing a planetary nebula. ...
Studying Variable stars using Small Telescopes Observational
... Advantages of having Small Telescopes – 1. Convenient access to a telescope. 2. For sufficiently bright stars, small telescopes achieve same photometric accuracy as that of large telescopes. 3. With advanced increasing sophistications in optics and electronics it is possible for smaller telescopes t ...
... Advantages of having Small Telescopes – 1. Convenient access to a telescope. 2. For sufficiently bright stars, small telescopes achieve same photometric accuracy as that of large telescopes. 3. With advanced increasing sophistications in optics and electronics it is possible for smaller telescopes t ...
Lab 6
... Determining distances using a different standard candle – the Cepheid variable star Henrietta Leavitt at Harvard University, in the early part of the 20th century, studied a class of variable stars called the Cepheids. These stars vary in brightness in a cyclical pattern, and are bright enough to be ...
... Determining distances using a different standard candle – the Cepheid variable star Henrietta Leavitt at Harvard University, in the early part of the 20th century, studied a class of variable stars called the Cepheids. These stars vary in brightness in a cyclical pattern, and are bright enough to be ...
The Evening Sky Map
... Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances from Earth (optical double). Apparent separation of stars is given in seconds of arc ("). Ecliptic – The path of the Sun’s center o ...
... Double Star – Two stars that appear close to each other in the sky; either linked by gravity so that they orbit each other (binary star) or lying at different distances from Earth (optical double). Apparent separation of stars is given in seconds of arc ("). Ecliptic – The path of the Sun’s center o ...
Climbing the Distance Ladder
... 1) Distances within the Solar System can be measured using radar. 2) Distances of nearby stars can be measured using parallax. 3) Greater distances can be measured ...
... 1) Distances within the Solar System can be measured using radar. 2) Distances of nearby stars can be measured using parallax. 3) Greater distances can be measured ...
Unit 1
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
supplemental educational materials PDF
... composition, history, location, and motion. Many of the scientists at the Space Telescope Science Institute are astronomers. Astronomers from all over the world use the Hubble Space Telescope. ...
... composition, history, location, and motion. Many of the scientists at the Space Telescope Science Institute are astronomers. Astronomers from all over the world use the Hubble Space Telescope. ...
Color-Magnitude Diagram Lab Manual
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
... on a particular cluster, its CMD will be loaded onto the same graph used in the lab. For each of the following clusters, use the Zero-Age Main Sequence and Isochrones to determine the distance modulus and age of each cluster. (Note, if the clusters data does not load when selected, try opening the Z ...
doc - Pocket Stars
... chart if currently visible and Done is chosen. An image of the object is displayed if available. Choose "Info" to show a text description of the object. Messier and Caldwell images can be downloaded automatically if you have an internet connection to your Smartphone (either phone network or ActiveSy ...
... chart if currently visible and Done is chosen. An image of the object is displayed if available. Choose "Info" to show a text description of the object. Messier and Caldwell images can be downloaded automatically if you have an internet connection to your Smartphone (either phone network or ActiveSy ...
Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... The Spectral Sequence is a Temperature Sequence • Gross differences among the spectral types are due to differences in Temperature. • ComposiZon differences are minor at best. – Demonstrated by Cecilia Payne‐Gaposhkin in 1920’s ...
... The Spectral Sequence is a Temperature Sequence • Gross differences among the spectral types are due to differences in Temperature. • ComposiZon differences are minor at best. – Demonstrated by Cecilia Payne‐Gaposhkin in 1920’s ...