15_Testbank
... 6) Two stars, Tom and Jerry, have the same spectral type. Tom is luminosity class V and Jerry is luminosity class I. Which star is bigger? Which star is more luminous? Which star has a hotter surface temperature? Explain your answers. Answer: Tom is on the main sequence, while Jerry is a supergiant ...
... 6) Two stars, Tom and Jerry, have the same spectral type. Tom is luminosity class V and Jerry is luminosity class I. Which star is bigger? Which star is more luminous? Which star has a hotter surface temperature? Explain your answers. Answer: Tom is on the main sequence, while Jerry is a supergiant ...
Summary Of the Structure of the Milky Way
... RR Lyrae variables are periodic variable stars, commonly found in globular clusters, and often used as standard candles to measure galactic distances. • This type of variable is named after the prototype, the variable star RR Lyrae in the constellation Lyra. • RR Lyraes are pulsating horizontal bra ...
... RR Lyrae variables are periodic variable stars, commonly found in globular clusters, and often used as standard candles to measure galactic distances. • This type of variable is named after the prototype, the variable star RR Lyrae in the constellation Lyra. • RR Lyraes are pulsating horizontal bra ...
Constituents of the Milky Way
... Measuring Ages of Individual Stars For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen ...
... Measuring Ages of Individual Stars For individual stars that aren’t in clusters (like the Sun), we can’t use the cluster turnoff method to measure an age. For instance, a lone G star might be young, or it might be 10 billion years old. How do we measure its age? The universe contained only hydrogen ...
Document
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
PRESS 2001 Project Report - Hong Kong University of Science and
... 1. Introduction [1] Half or more of all stars in the universe are in orbit around another star or stars. In most of these multiple-star systems, there is a type of system which consists of two stars only, known as a binary star system, whose components may be separated by a large fraction of a light ...
... 1. Introduction [1] Half or more of all stars in the universe are in orbit around another star or stars. In most of these multiple-star systems, there is a type of system which consists of two stars only, known as a binary star system, whose components may be separated by a large fraction of a light ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Letter to the Editor Low
... masses. Because of ≈ 10 magnitudes range in luminosities in the crowded core region our sensitivity limits of Js ≈ 21m , H ≈ 20m and Ks ≈ 19m don’t appear to be exceedingly faint (and are about 3 magnitudes above ISAAC’s detection limit for isolated sources). However, only VLT/ISAAC’s high angular r ...
... masses. Because of ≈ 10 magnitudes range in luminosities in the crowded core region our sensitivity limits of Js ≈ 21m , H ≈ 20m and Ks ≈ 19m don’t appear to be exceedingly faint (and are about 3 magnitudes above ISAAC’s detection limit for isolated sources). However, only VLT/ISAAC’s high angular r ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... Open the HR Diagram Explorer. Begin by familiarizing yourself with the capabilities of the HertzsprungRussell Diagram Explorer through experimentation. An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around ...
... Open the HR Diagram Explorer. Begin by familiarizing yourself with the capabilities of the HertzsprungRussell Diagram Explorer through experimentation. An actual HR Diagram is provided in the upper right panel with an active location indicated by a red x. This active location can be dragged around ...
Observational properties of stars
... spectrum, “B” corresponds to blue light, “V” is green, “R” is red and “I” is infrared. There are actually hundreds of different types of filters, some are telescope specific, or are used only by particular observatories. However, the filters given here are the most commonly used in stellar astronomy ...
... spectrum, “B” corresponds to blue light, “V” is green, “R” is red and “I” is infrared. There are actually hundreds of different types of filters, some are telescope specific, or are used only by particular observatories. However, the filters given here are the most commonly used in stellar astronomy ...
Star-S_Teacher_Guide - The University of Texas at Dallas
... o If your students have already done the Scale Model Solar System Activity, discuss the usefulness of the scale factor. Ask your students what the advantage would be of modeling stars on the same scale. By using the same scale factor of 1:10 billion, the students will more easily be able to make com ...
... o If your students have already done the Scale Model Solar System Activity, discuss the usefulness of the scale factor. Ask your students what the advantage would be of modeling stars on the same scale. By using the same scale factor of 1:10 billion, the students will more easily be able to make com ...
Globular Clusters
... are stars that have passed the red giant phase, lost much of their outer shell, and are now small, hot, blue stars, fusing helium. They are considerably dimmer than the brightest red giants, but they can still be visible in photographs or with large telescopes. Blue Stragglers Dimmer yet, but still ...
... are stars that have passed the red giant phase, lost much of their outer shell, and are now small, hot, blue stars, fusing helium. They are considerably dimmer than the brightest red giants, but they can still be visible in photographs or with large telescopes. Blue Stragglers Dimmer yet, but still ...
Summary: Modes of Star Formation
... properties of binaries are largely preserved from their time of formation, and this allows binary statistics to be used to infer something about the typical sites of star formation. The field population contains a mix of contributions from starforming regions of all types, and since the frequency of ...
... properties of binaries are largely preserved from their time of formation, and this allows binary statistics to be used to infer something about the typical sites of star formation. The field population contains a mix of contributions from starforming regions of all types, and since the frequency of ...
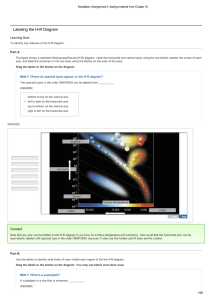
Labeling the HR Diagram - Mastering Physics Answers
... Spectral type is related to surface temperature, with stars of spectral type O having the highest surface temperature and stars of spectral type M having the lowest surface temperature. In other words, spectral type increases to the left on the HR diagram. Now proceed to Part E to determine how the ...
... Spectral type is related to surface temperature, with stars of spectral type O having the highest surface temperature and stars of spectral type M having the lowest surface temperature. In other words, spectral type increases to the left on the HR diagram. Now proceed to Part E to determine how the ...
A Stars
... • B Stars (15-30,000 K): Most of H is ionized, so only very weak H lines. • A Stars (10,000 K): Ideal excitation conditions, strongest H lines. • G Stars (6000 K): Too cool, little excited H, so only weak H lines. ...
... • B Stars (15-30,000 K): Most of H is ionized, so only very weak H lines. • A Stars (10,000 K): Ideal excitation conditions, strongest H lines. • G Stars (6000 K): Too cool, little excited H, so only weak H lines. ...
Table of Contents - Imiloa Astronomy Center
... - This is a pulsating giant that has become the prototype of a class of variable stars called Bayer Stars. - The Bayer stars are quite bright. - Their brightness ranges from –1.5 to fifth magnitude. - There are a dozen stars of third magnitude or better. ...
... - This is a pulsating giant that has become the prototype of a class of variable stars called Bayer Stars. - The Bayer stars are quite bright. - Their brightness ranges from –1.5 to fifth magnitude. - There are a dozen stars of third magnitude or better. ...
Lec09_ch11_lifecycleofstars
... unstable and variable – but often in predictable ways--Cepheid variables ...
... unstable and variable – but often in predictable ways--Cepheid variables ...