Bluffer`s Guide to Sirius
... that the star was moving slightly in a predictable manner. It was clear that Sirius was being tugged by the gravitational pull of another object, so there was something else orbiting Sirius, too faint to be seen. However, telescopes were increasing in size and in 1862 the companion was seen for the ...
... that the star was moving slightly in a predictable manner. It was clear that Sirius was being tugged by the gravitational pull of another object, so there was something else orbiting Sirius, too faint to be seen. However, telescopes were increasing in size and in 1862 the companion was seen for the ...
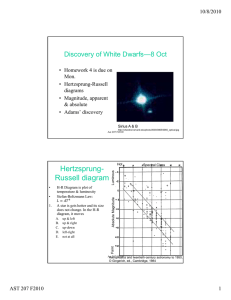
Discovery of White Dwarfs—8 Oct
... temperatures and approximately the same size. Dwarfs are most common. Giants are large. White dwarfs are small. ...
... temperatures and approximately the same size. Dwarfs are most common. Giants are large. White dwarfs are small. ...
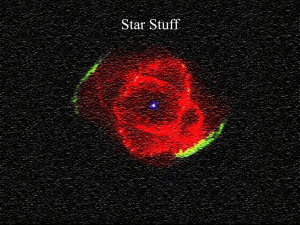
Stars
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
VLT/FORS Surveys of Wolf-Rayet Stars beyond the
... suggestions that early-type WC stars are richer in carbon than late-type WC stars. However, quantitative analysis of WC subtypes allowing for radiative transfer effects do not support a subtype dependence of elemental abundances in WC stars. In contrast, Crowther et al. (2002) proposed that late spe ...
... suggestions that early-type WC stars are richer in carbon than late-type WC stars. However, quantitative analysis of WC subtypes allowing for radiative transfer effects do not support a subtype dependence of elemental abundances in WC stars. In contrast, Crowther et al. (2002) proposed that late spe ...
How we found about BLACK HOLES
... old. These stories are science-facts, but just as readable as science fiction. “Black Holes” in space – what are they? How did they come to be found? There is something almost frightening about the possibility of “Black Holes” Do they really exist? Isaac Asimov explains step by step how astronomers ...
... old. These stories are science-facts, but just as readable as science fiction. “Black Holes” in space – what are they? How did they come to be found? There is something almost frightening about the possibility of “Black Holes” Do they really exist? Isaac Asimov explains step by step how astronomers ...
Measuring the Stars Section 29.2
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
... emitted per second, or watts. The Sun’s luminosity is about 3.85 × 1026 W. The values for other stars vary widely, from about 0.0001 to more than 1 million times the Sun’s luminosity. No other stellar property varies as much. ...
Document
... – two stars in a binary system can be close enough to transfer mass from one to the other – gaining or losing mass will change the life path of a star ...
... – two stars in a binary system can be close enough to transfer mass from one to the other – gaining or losing mass will change the life path of a star ...
The Official Magazine of the University Of St Andrews Astronomical Society 1
... about 18 stellar radii from the star. In comparison, the sun’s flares are about only 1 solar radius in length. Most of the flares, however, were much shorter and like the sun’s. At this stage in the stars’ lives the stars are surrounded by a disk of material within which the cores of gas giants are ...
... about 18 stellar radii from the star. In comparison, the sun’s flares are about only 1 solar radius in length. Most of the flares, however, were much shorter and like the sun’s. At this stage in the stars’ lives the stars are surrounded by a disk of material within which the cores of gas giants are ...
sections 12-15 instructor notes
... functions of some sort. In a way the most basic of such functions is the general luminosity function (GLF), which gives us the distribution function of absolute magnitude, M, for the average unit volume in the vicinity of the Sun. We require that basic distribution function to describe not only the ...
... functions of some sort. In a way the most basic of such functions is the general luminosity function (GLF), which gives us the distribution function of absolute magnitude, M, for the average unit volume in the vicinity of the Sun. We require that basic distribution function to describe not only the ...
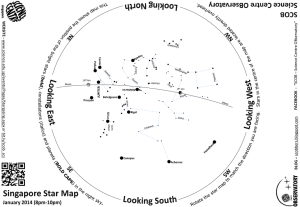
Star Map - Science Centre
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
... The Big Dipper is one of the most famous asterisms (star patterns) throughout history. In some places of the Northern Hemisphere, its seven brightest stars can be seen all year round. Further South near the equator, it is only visible for a few months. Merak and Dubhe are known as The Pointers, poin ...
Visual Measurements of the Multiple Star
... pattern of (1) calibration of the eyepiece, (2) collecting Pulkowa. The principle instrument was an equatorial separation and position angle measurements on a refractor with a 15-inch objective lens. This was the “known “ double star (a system that has been exten- largest refractor in the world at t ...
... pattern of (1) calibration of the eyepiece, (2) collecting Pulkowa. The principle instrument was an equatorial separation and position angle measurements on a refractor with a 15-inch objective lens. This was the “known “ double star (a system that has been exten- largest refractor in the world at t ...
Part I: Shining a Light on Visual Magnitude
... Systems Tool Kit (STK) with the Electro-Optical Infrared (EOIR) plugin tool can model the behaviors of sensors and measure various characteristics of stars. STK and EOIR have a plethora of capabilities and we will cover a sliver of them for this analysis, specifically features related to measuring t ...
... Systems Tool Kit (STK) with the Electro-Optical Infrared (EOIR) plugin tool can model the behaviors of sensors and measure various characteristics of stars. STK and EOIR have a plethora of capabilities and we will cover a sliver of them for this analysis, specifically features related to measuring t ...
December - Rose City Astronomers
... and open cluster combo is a remarkable stroke of cosmic serendipity in an area nearly devoid of other major deep-sky objects. The refractor at 44x shows the 12' diameter star cluster as six stars (9th to 11thmagnitude) embedded in a background haze of a half dozen more fainter suns. The Triangulum o ...
... and open cluster combo is a remarkable stroke of cosmic serendipity in an area nearly devoid of other major deep-sky objects. The refractor at 44x shows the 12' diameter star cluster as six stars (9th to 11thmagnitude) embedded in a background haze of a half dozen more fainter suns. The Triangulum o ...
Review 3 (11-18-10)
... size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Noth ...
... size of Earth. Atoms stop further collapse. M less than 1.4 solar masses • Neutron Stars: even denser, about mass of Sun in size of Orlando. Neutrons stop further collapse. M between 1.4 and 3 solar masses. Some neutron stars can be detected as pulsars • Black Holes: M more than 3 solar masses. Noth ...
The Sky
... • The ancient astronomers divided the stars into six classes. – The brightest were called first-magnitude stars and those that were fainter, second-magnitude. The scale continued downward to sixth-magnitude stars, the faintest visible to the human eye. – Thus, the larger the magnitude number, the fa ...
... • The ancient astronomers divided the stars into six classes. – The brightest were called first-magnitude stars and those that were fainter, second-magnitude. The scale continued downward to sixth-magnitude stars, the faintest visible to the human eye. – Thus, the larger the magnitude number, the fa ...