Stellar Remnants - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... If a black hole has a close binary companion, material may be pulled from the companion to form an accretion disk around the black hole. The accretion disk radiates x-rays and gamma rays as the gas is heated to very high temperatures as it approaches the event horizon. From their x-ray emissions ...
... If a black hole has a close binary companion, material may be pulled from the companion to form an accretion disk around the black hole. The accretion disk radiates x-rays and gamma rays as the gas is heated to very high temperatures as it approaches the event horizon. From their x-ray emissions ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Distances to Stars
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
Scientific Results Summary
... A lot of telescope time at Subaru is dedicated to looking at stars to assess their different stages of formation and evolution. Scientists at Subaru have pierced through a dusty stellar nursery of a Class O protostar located 500 light years away and captured the earliest and most detailed view of a ...
... A lot of telescope time at Subaru is dedicated to looking at stars to assess their different stages of formation and evolution. Scientists at Subaru have pierced through a dusty stellar nursery of a Class O protostar located 500 light years away and captured the earliest and most detailed view of a ...
Luminosity - U of L Class Index
... Which of these stars can be no more than 10 million years old? ...
... Which of these stars can be no more than 10 million years old? ...
Star Stuff
... - divides the light up into its colors (wavelengths) - use a smaller range of wavelengths than entire EM spectrum because instrumentation is different ...
... - divides the light up into its colors (wavelengths) - use a smaller range of wavelengths than entire EM spectrum because instrumentation is different ...
The Night Sky This Month - Usk Astronomical Society
... The Moon is at apogee (most distant from Earth) on the 18th and at perigee (nearest Earth) on the 6th, at around the time of the new Moon. A syzygy is when three interacting celestial bodies form a straight line, and is used to define either of the two positions (conjunction or opposition) of a cel ...
... The Moon is at apogee (most distant from Earth) on the 18th and at perigee (nearest Earth) on the 6th, at around the time of the new Moon. A syzygy is when three interacting celestial bodies form a straight line, and is used to define either of the two positions (conjunction or opposition) of a cel ...
Shows` Detail - Nejoum Planetarium
... Shapes of the Moon Adventure ride to Moon day by day in our sky. KG to II KG to II This is called the phases of the Moon. Each shape of the Moon also has a becomes the first dog to be on the Moon and as an name. The show covers shapes of the Moon and related astronaut dog explores the barren Moonlan ...
... Shapes of the Moon Adventure ride to Moon day by day in our sky. KG to II KG to II This is called the phases of the Moon. Each shape of the Moon also has a becomes the first dog to be on the Moon and as an name. The show covers shapes of the Moon and related astronaut dog explores the barren Moonlan ...
stars-notes
... Classifying Stars • Stars are now classified by how hot they are. • Temperature differences between stars result in color differences that can be seen. For example, class O stars are blue—the hottest stars. ...
... Classifying Stars • Stars are now classified by how hot they are. • Temperature differences between stars result in color differences that can be seen. For example, class O stars are blue—the hottest stars. ...
X-ray output should be time variable
... •Nearly 30% of the O stars in the sample are variable •No dramatic variability (e.g. no flares) ...
... •Nearly 30% of the O stars in the sample are variable •No dramatic variability (e.g. no flares) ...
Part I Light, Telescopes, Atoms and Stars
... Stars range typically from 2,000K to 40,000K 2000K = red , 40000K = white/blue The Balmer series is a better thermometer Cool stars = weak Balmer series lines (less ionizations) Hot stars = weak lines (everything ionized), Medium stars = strong lines (correct amount of energy for these lines i ...
... Stars range typically from 2,000K to 40,000K 2000K = red , 40000K = white/blue The Balmer series is a better thermometer Cool stars = weak Balmer series lines (less ionizations) Hot stars = weak lines (everything ionized), Medium stars = strong lines (correct amount of energy for these lines i ...
Lecture 15, PPT version
... At their maximum brightness, supernovae are as bright as an entire galaxy. ...
... At their maximum brightness, supernovae are as bright as an entire galaxy. ...
holiday lights - Denver Astronomical Society
... border of Corona Australis and Telescopium on February 1st before beginning a rapid northward and was used by Isaac Newton to verify Kepler’s Laws. Its orbit was similar to that of ISON, sugrise. On March 10th, when at its brightest (pre- gesting that it may be similarly bright if all goes well. dic ...
... border of Corona Australis and Telescopium on February 1st before beginning a rapid northward and was used by Isaac Newton to verify Kepler’s Laws. Its orbit was similar to that of ISON, sugrise. On March 10th, when at its brightest (pre- gesting that it may be similarly bright if all goes well. dic ...
Lecture 31: The Properties of Stars
... This lecture describes the basic observed properties of stars. The color of a star depends on its temperature: cooler stars are redder, hotter stars are blue. Luminosity, the total energy output expressed in Watts or Solar Luminosities, depends on the radius and temperature. The absorption spectra o ...
... This lecture describes the basic observed properties of stars. The color of a star depends on its temperature: cooler stars are redder, hotter stars are blue. Luminosity, the total energy output expressed in Watts or Solar Luminosities, depends on the radius and temperature. The absorption spectra o ...
Stars and Galaxies - La Salle Elementary Public Schools No 122
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Contents ISP 205 Section 2 Study Guide for Test 3 28 March 2007
... forever. 15. Why are elements with 12, 16, 20, 24, 28 nuclei more abundant in the universe? They are made by adding helium4 to the parent nucleus. 16. When will the earth be too hot for humans? In 1-4Byr, when sun is still a MS star. ...
... forever. 15. Why are elements with 12, 16, 20, 24, 28 nuclei more abundant in the universe? They are made by adding helium4 to the parent nucleus. 16. When will the earth be too hot for humans? In 1-4Byr, when sun is still a MS star. ...
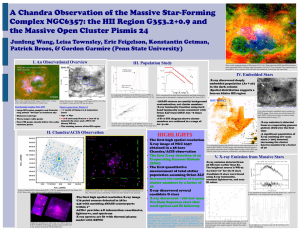
A Chandra Observation of the Massive Star-Forming
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
... XLFs constructed from hard band luminosities and total luminosities the ACIS-I FOV compared to those (449) detected in X-ray (uncorrected for absorption) compared with Orion XLF from COUP Three color composite MSX image of NGC 6357. Central cavity and bright nebulosities are clearly seen. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.