Night Sky Course Stars and Star Clusters within the
... shine. The method was developed by Henrietta Leavitt: See Cepheid Variables – short History ...
... shine. The method was developed by Henrietta Leavitt: See Cepheid Variables – short History ...
SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF A NEWLY DISCOVERED HgMn STAR
... mercury abundance. New observations at high resolution including 3500 to 4500 Å region may also help to improve the Hg overabundance value. A noticeable radial velocity shift (36.4 ± 5 km s-1) was detected among the spectra of HD 318126 taken on two different days that were separated by 5 days (Fig. ...
... mercury abundance. New observations at high resolution including 3500 to 4500 Å region may also help to improve the Hg overabundance value. A noticeable radial velocity shift (36.4 ± 5 km s-1) was detected among the spectra of HD 318126 taken on two different days that were separated by 5 days (Fig. ...
What we can measure
... the sun – since we have the planets orbiting the sun. We are only now being able to “see” other planets orbit other stars since those stars are so far away. However, we notice that there are lots of stars that orbit each other – and we can use that to get the mass of the bigger (central) star. ...
... the sun – since we have the planets orbiting the sun. We are only now being able to “see” other planets orbit other stars since those stars are so far away. However, we notice that there are lots of stars that orbit each other – and we can use that to get the mass of the bigger (central) star. ...
The Great Debate - The Story Behind The Science
... The significance of this rotational period requires understanding Shapley's size of the Milky Way. Shapley had been a supporter of the island universe idea until he determined the Milky Way to be 300,000 light-years in diameter (10x larger than the consensus estimate). He concluded this by measuring ...
... The significance of this rotational period requires understanding Shapley's size of the Milky Way. Shapley had been a supporter of the island universe idea until he determined the Milky Way to be 300,000 light-years in diameter (10x larger than the consensus estimate). He concluded this by measuring ...
March 2016 BRAS Addendum Newsletter
... M 41 (NGC 2287), mag. 4.5 (photo), 06 46.0 -20 44, 38’ in size, is an open cluster of 100 stars; detached, weak concentration of stars; large range in brightness; very large, bright. M 41contains contrasting blue, yellow, and orange stars with a giant reddish star (12 CMa) at mag. 6.93 in its center ...
... M 41 (NGC 2287), mag. 4.5 (photo), 06 46.0 -20 44, 38’ in size, is an open cluster of 100 stars; detached, weak concentration of stars; large range in brightness; very large, bright. M 41contains contrasting blue, yellow, and orange stars with a giant reddish star (12 CMa) at mag. 6.93 in its center ...
The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog
... On "the first day of the New Year" sometime "early in the twentieth century", 3 different observatories simultaneously announced having noticed unexplainable perturbations in the motion of planet Neptune. It will be soon be found that this is due to a foreign star - a "strange wanderer ... a great ...
... On "the first day of the New Year" sometime "early in the twentieth century", 3 different observatories simultaneously announced having noticed unexplainable perturbations in the motion of planet Neptune. It will be soon be found that this is due to a foreign star - a "strange wanderer ... a great ...
Lecture Eight (Powerpoint format) - Flash
... Globular clusters are distributed in a sphere around the galaxy. Other disk galaxies have been observed to have their own system of globular clusters surrounding them. Some globulars may pass through the plane of the galactic disk from time to time, stripping away some stars in a “disk shockin ...
... Globular clusters are distributed in a sphere around the galaxy. Other disk galaxies have been observed to have their own system of globular clusters surrounding them. Some globulars may pass through the plane of the galactic disk from time to time, stripping away some stars in a “disk shockin ...
1.3 Lifecycle of stars
... Evolution of a Sun-Like Star The helium flash: The pressure within the helium core is almost totally due to “electron degeneracy”—two electrons cannot be in the same quantum state, so the core cannot contract beyond a certain point. This pressure is almost independent of temperature— when the heliu ...
... Evolution of a Sun-Like Star The helium flash: The pressure within the helium core is almost totally due to “electron degeneracy”—two electrons cannot be in the same quantum state, so the core cannot contract beyond a certain point. This pressure is almost independent of temperature— when the heliu ...
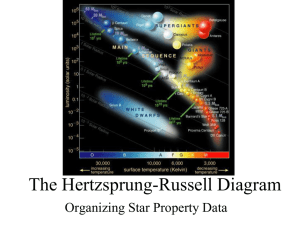
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... Equal Radius Lines In general the hotter the star is the brighter it will be. Thus you would expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
HighRedshiftGalaxies
... in galaxies observed at high redshift. However, stellar evolution is baselined in physical time (the conventional unit is the Gyr: 109 yr), whereas we observe distant sources in redshift units. The mapping of time and redshift depends on the world model. Broadly speaking there is less time for the n ...
... in galaxies observed at high redshift. However, stellar evolution is baselined in physical time (the conventional unit is the Gyr: 109 yr), whereas we observe distant sources in redshift units. The mapping of time and redshift depends on the world model. Broadly speaking there is less time for the n ...
The Sky - HiSPARC
... At roughly the same time Charles Messier was also taking a closer look at the skies. He made the now famous list of 110 Messier objects.4 Messier was a comet hunter, he became frustrated by objects strongly resembling comets but which were in fact not comets. In modern catalogues the original Messie ...
... At roughly the same time Charles Messier was also taking a closer look at the skies. He made the now famous list of 110 Messier objects.4 Messier was a comet hunter, he became frustrated by objects strongly resembling comets but which were in fact not comets. In modern catalogues the original Messie ...
S1-4-03 - Celestial Navigation
... Part C: Movement of the Stars Northern Circumpolar Constellations Show students the northern circumpolar constellations. Note that depending on where you live, some constellations are visible all year round and some constellations are seasonal. If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, the constellati ...
... Part C: Movement of the Stars Northern Circumpolar Constellations Show students the northern circumpolar constellations. Note that depending on where you live, some constellations are visible all year round and some constellations are seasonal. If you live in the Northern Hemisphere, the constellati ...
Mass and the Properties of Main Sequence Stars
... will balance the gravitational pressure (if the star is not too massive) to form a neutron star. The estimated of the neutron stars are about 10 km in diameter, with a mass of about 1 M⊙ Too small to be directly observed! However, the strong gravity of the neutron stars pull surrounding materials ...
... will balance the gravitational pressure (if the star is not too massive) to form a neutron star. The estimated of the neutron stars are about 10 km in diameter, with a mass of about 1 M⊙ Too small to be directly observed! However, the strong gravity of the neutron stars pull surrounding materials ...
DP11 Foundations of Astronomy
... know its distance, we can determine its luminosity, from the socalled inverse square law: b = L/4 d2 ...
... know its distance, we can determine its luminosity, from the socalled inverse square law: b = L/4 d2 ...
Star
... entirely of subatomic particles called neutrons; or even smaller and more dense black holes, objects that have such immense gravity that light cannot escape their surface. ...
... entirely of subatomic particles called neutrons; or even smaller and more dense black holes, objects that have such immense gravity that light cannot escape their surface. ...
Sakurai`s Object - Department of Physics, HKU
... shell flash before it dies and joins the rank of white dwarfs. • This star is currently evolving at a timescale of a few 10s to at most 100 years --- a very rare situation in stellar evolution indeed. • Besides Sakurai’s object, V605 Aql (outburst around 1919-1921) and FG Sge (outburst around 1900-1 ...
... shell flash before it dies and joins the rank of white dwarfs. • This star is currently evolving at a timescale of a few 10s to at most 100 years --- a very rare situation in stellar evolution indeed. • Besides Sakurai’s object, V605 Aql (outburst around 1919-1921) and FG Sge (outburst around 1900-1 ...
ph507lecnote06
... Because stellar colours and spectral types are roughly correlated, we may construct a plot of absolute magnitude versus colour - called a colour-magnitude diagram. The relative ease and convenience with which colour indices (such as B - V) may be determined for vast numbers of stars dictates the pop ...
... Because stellar colours and spectral types are roughly correlated, we may construct a plot of absolute magnitude versus colour - called a colour-magnitude diagram. The relative ease and convenience with which colour indices (such as B - V) may be determined for vast numbers of stars dictates the pop ...
1 pracovni list HR diagram I EN
... Note: You can find the needed values in the catalogues of stars. Calculate values marked by an asterisk using the formulas provided in exercise 3. What types of stars did you find? What are the characteristic features of each type? ...
... Note: You can find the needed values in the catalogues of stars. Calculate values marked by an asterisk using the formulas provided in exercise 3. What types of stars did you find? What are the characteristic features of each type? ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.