What is a Hertzsprung
... – Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram – A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high-mass: luminous and blue; low-mass: faint and red) ...
... – Normal stars that fuse H to He in their cores fall on the main sequence of an H-R diagram – A star’s mass determines its position along the main sequence (high-mass: luminous and blue; low-mass: faint and red) ...
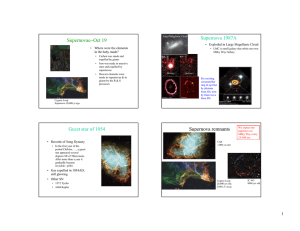
Supernovae Oct 19 − Supernova 1987A
... Sirius A, a main-sequence star Sirius B, an earth-sized white dwarf ...
... Sirius A, a main-sequence star Sirius B, an earth-sized white dwarf ...
Nature of Stars 2
... Earth is on the other side of its orbit. As seen from the Earth, the nearby star appears to sweep through the angle shown. Half of this angle, is the parallax, p. ...
... Earth is on the other side of its orbit. As seen from the Earth, the nearby star appears to sweep through the angle shown. Half of this angle, is the parallax, p. ...
ASTR 1101-001 Spring 2008 - Louisiana State University
... Gustav’s Effect on this Course • Fall Holiday has been cancelled, which means our class will meet on Thursday, 9 October. (This makes up for one class day lost to Gustav last week.) • We will hold an additional makeup class on Saturday, 20 September! (This will account for the second class day lost ...
... Gustav’s Effect on this Course • Fall Holiday has been cancelled, which means our class will meet on Thursday, 9 October. (This makes up for one class day lost to Gustav last week.) • We will hold an additional makeup class on Saturday, 20 September! (This will account for the second class day lost ...
We Are Stardust: Synthesis of the Elements Essential for Life Aparna
... • Thus, a general pattern emerges: when the star exhausts one fuel, it can no longer support itself against gravity, so it contracts until it reaches a core temperature that can ignite the product of the previous fuel. Since this product is a heavier element than the initial fuel, this process requi ...
... • Thus, a general pattern emerges: when the star exhausts one fuel, it can no longer support itself against gravity, so it contracts until it reaches a core temperature that can ignite the product of the previous fuel. Since this product is a heavier element than the initial fuel, this process requi ...
Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... Hulse were able to show that the orbital period of this binary pair was getting shorter. This is because the system is radiating gravitational waves. For this work Hulse and Taylor were awarded the 1993 Nobel Prize in physics. ...
... Hulse were able to show that the orbital period of this binary pair was getting shorter. This is because the system is radiating gravitational waves. For this work Hulse and Taylor were awarded the 1993 Nobel Prize in physics. ...
Chapter 11 Surveying the Stars How do we measure stellar
... Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and ...
... Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and ...
1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... The surface temperature of Barnard’s star is about 3 500 K. Using this information and information about its luminosity, explain why Barnard’s star cannot be (i) ...
... The surface temperature of Barnard’s star is about 3 500 K. Using this information and information about its luminosity, explain why Barnard’s star cannot be (i) ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Which of the following is true about a binary pulsar system? A: It will last forever. B: They can only be found in star forming regions C: The total mass of the two pulsars must be more than 10 solar masses. D: Each of the pulsars was produced by a massive star that exploded in a Supernova event. ...
... Which of the following is true about a binary pulsar system? A: It will last forever. B: They can only be found in star forming regions C: The total mass of the two pulsars must be more than 10 solar masses. D: Each of the pulsars was produced by a massive star that exploded in a Supernova event. ...
Student Exploration Sheet: Growing Plants
... Light from the Andromeda galaxy is blueshifted because Andromeda is moving toward our galaxy, the Milky Way. Cepheid variable – a star that expands and contracts in a regularly repeating cycle. ...
... Light from the Andromeda galaxy is blueshifted because Andromeda is moving toward our galaxy, the Milky Way. Cepheid variable – a star that expands and contracts in a regularly repeating cycle. ...
Background Science - Faulkes Telescope Project
... Supernova remnants are studied at many different wavelengths from optical light to Xrays. Different things are happening in different wavelengths; when we observe in, say the X-ray, we are looking at the parts of the shell that are much hotter than the areas shining in the optical. The X-rays come f ...
... Supernova remnants are studied at many different wavelengths from optical light to Xrays. Different things are happening in different wavelengths; when we observe in, say the X-ray, we are looking at the parts of the shell that are much hotter than the areas shining in the optical. The X-rays come f ...
Chapter 13 Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... massive than that, nothing will stop its collapse, and it will become smaller and smaller and denser and denser. Eventually the gravitational force is so intense that even light cannot escape. The remnant has become a black hole. ...
... massive than that, nothing will stop its collapse, and it will become smaller and smaller and denser and denser. Eventually the gravitational force is so intense that even light cannot escape. The remnant has become a black hole. ...
How Old is the Universe?
... other stars because the lines are too weak. But in CS 22892-052 the thorium lines can be seen because the iron lines are very weak. The Th/Eu (Europium) ratio in this star is 0.219 compared to 0.369 in the Solar System now. Thorium decays with a half-life of 14.05 Gyr, so the Solar System formed wit ...
... other stars because the lines are too weak. But in CS 22892-052 the thorium lines can be seen because the iron lines are very weak. The Th/Eu (Europium) ratio in this star is 0.219 compared to 0.369 in the Solar System now. Thorium decays with a half-life of 14.05 Gyr, so the Solar System formed wit ...
Chapter 6 Stars
... the star expands into space. This material may become part of a nebula. This nebula can then contract to form a new, partly recycled star. Astronomers think the sun began as a nebula that contained material from a supernova. Neutron Stars After a supergiant explodes, some of the material from the st ...
... the star expands into space. This material may become part of a nebula. This nebula can then contract to form a new, partly recycled star. Astronomers think the sun began as a nebula that contained material from a supernova. Neutron Stars After a supergiant explodes, some of the material from the st ...
A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... Nebulae absorb light from nearby stars and radiate it back into space. Most nebulae glow red, the color of hydrogen gas. The brightest nebula is the Orion Nebula (see slide #60) which can be seen with the unaided eye in a dark sky. Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to ...
... Nebulae absorb light from nearby stars and radiate it back into space. Most nebulae glow red, the color of hydrogen gas. The brightest nebula is the Orion Nebula (see slide #60) which can be seen with the unaided eye in a dark sky. Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to ...
Star Types - College of Engineering and Computer Science
... property in how a star’s life and death will proceed. The mass of a star can only be measured directly by observing the effect of its gravity on another object This is most easily done for two stars which orbit one another --- a binary star! ...
... property in how a star’s life and death will proceed. The mass of a star can only be measured directly by observing the effect of its gravity on another object This is most easily done for two stars which orbit one another --- a binary star! ...
Compa ring between Spectroscopic and Photometric Method for
... and their proximity on the night sky is not just the effect of projection. When both stars are visible, sequence of observations would indicate that the stars move around a common center of gravity. Observations indicate that majority of stars have a companion, thus that stars are in more than 50% o ...
... and their proximity on the night sky is not just the effect of projection. When both stars are visible, sequence of observations would indicate that the stars move around a common center of gravity. Observations indicate that majority of stars have a companion, thus that stars are in more than 50% o ...
Star Clusters and their stars
... If the cluster is massive and dense enough to hold its stars together, then they will stay together – and age together. We have therefore a globular cluster. In our Galaxy, all globular clusters (i.e., the clusters where the stars are bound) have very old stars. You can tell by their color – all blu ...
... If the cluster is massive and dense enough to hold its stars together, then they will stay together – and age together. We have therefore a globular cluster. In our Galaxy, all globular clusters (i.e., the clusters where the stars are bound) have very old stars. You can tell by their color – all blu ...
Planets and Stars Key Vocabulary: Comparing and Contrasting
... in the sky. Telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the moon and the planets. The number of stars that can be seen through telescopes is dramatically greater than can be seen by the unaided eye. ...
... in the sky. Telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the moon and the planets. The number of stars that can be seen through telescopes is dramatically greater than can be seen by the unaided eye. ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.