11 Stellar Remnants - Journigan-wiki
... When stars that are more massive than 10 solar masses reach the end of their lives, they can compress their cores with so much pressure that they rift the fabric of space-time. To understand black holes you have to understand escape velocity! ...
... When stars that are more massive than 10 solar masses reach the end of their lives, they can compress their cores with so much pressure that they rift the fabric of space-time. To understand black holes you have to understand escape velocity! ...
Lecture 15
... B. It will be near the end of its life and doesn’t have time C. It will not be massive enough to make it hot enough for further reactions D. The heavier elements will all go into a planetary nebula E. A and B ...
... B. It will be near the end of its life and doesn’t have time C. It will not be massive enough to make it hot enough for further reactions D. The heavier elements will all go into a planetary nebula E. A and B ...
Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli) Chapter 33
... 6) Many supernovas are thought to result in A) neutron stars. B) red giant stars. C) regular stars like our sun. D) white dwarfs. Answer: A Var: 1 7) Black holes A) are gaps in space, containing no matter. B) are predicted by Einstein's special theory of relativity. C) are the collapsed remnant of ...
... 6) Many supernovas are thought to result in A) neutron stars. B) red giant stars. C) regular stars like our sun. D) white dwarfs. Answer: A Var: 1 7) Black holes A) are gaps in space, containing no matter. B) are predicted by Einstein's special theory of relativity. C) are the collapsed remnant of ...
CP2: KUPKA et al.: Observational signatures of atmospheric velocity
... profile synthesis with microturbulence, and search for line profiles which deviate from this model in ways that provide further information about the atmospheric velocity fields. This poster gives a progress report on this ...
... profile synthesis with microturbulence, and search for line profiles which deviate from this model in ways that provide further information about the atmospheric velocity fields. This poster gives a progress report on this ...
EXAM II REVIEW - University of Maryland: Department of
... motion _______ you • redshift (longer wavelength) motion AWAY from you • greater shift greater speed ...
... motion _______ you • redshift (longer wavelength) motion AWAY from you • greater shift greater speed ...
CS3_Ch 3 - Leon County Schools
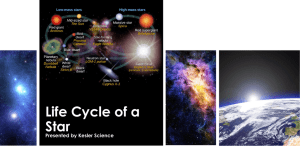
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Stars III - Indiana University Astronomy
... • Sun-like stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbon nuclei, and end as white dwarfs • Intermediate mass stars can make elements heavier than carbon but end as white dwarfs ...
... • Sun-like stars with <2MSun have long lives, never become hot enough to fuse carbon nuclei, and end as white dwarfs • Intermediate mass stars can make elements heavier than carbon but end as white dwarfs ...
Document
... • High Mass stars often times explode! • This spreads all of the elements Hydrogen through Iron (which makes up our planets and other new stars) and forms all elements after Iron (up to element 92). ...
... • High Mass stars often times explode! • This spreads all of the elements Hydrogen through Iron (which makes up our planets and other new stars) and forms all elements after Iron (up to element 92). ...
PHY111 Stellar Evolution
... However, note that lifetime does not equal age: the lower-mainsequence stars in the Pleiades are much younger than the Sun, even though their lifetimes are much longer. ...
... However, note that lifetime does not equal age: the lower-mainsequence stars in the Pleiades are much younger than the Sun, even though their lifetimes are much longer. ...
Why are Binary Stars so Important for the Theory
... 1I1 and the masses ('= 2.30 Mol are very nearly equal and known to an accuracy of 1 %. The primary minimum is a total eclipse and the luminosity ratio of the components is known very precisely. The photometric elements are derived by the classical Russell-Merrill method and by the modern model-simul ...
... 1I1 and the masses ('= 2.30 Mol are very nearly equal and known to an accuracy of 1 %. The primary minimum is a total eclipse and the luminosity ratio of the components is known very precisely. The photometric elements are derived by the classical Russell-Merrill method and by the modern model-simul ...
5-E Galaxy T - McDonald Observatory
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
... Galaxies, compared to their size, are closer together than stars. They are also much more massive, having the combined mass of billions of stars. So, even over a large distance the force of gravity between galaxies can accelerate them toward each other. Think of bowling balls (galaxies) on a trampol ...
Lecture Nine (Powerpoint format) - Flash
... Globular clusters are distributed in a sphere around the galaxy. Other disk galaxies have been observed to have their own system of globular clusters surrounding them. Some globulars may pass through the plane of the galactic disk from time to time, stripping away some stars in a “disk shockin ...
... Globular clusters are distributed in a sphere around the galaxy. Other disk galaxies have been observed to have their own system of globular clusters surrounding them. Some globulars may pass through the plane of the galactic disk from time to time, stripping away some stars in a “disk shockin ...
a to z of astronomy
... DARK CLOUD A relatively dense cloud of interstellar material containing dust particles. The dust particles absorb light from the more distant stars etc, so that the region appears dark compared with its surroundings. The clouds are often of low temperature and contain many molecules. DARK MATTER Mat ...
... DARK CLOUD A relatively dense cloud of interstellar material containing dust particles. The dust particles absorb light from the more distant stars etc, so that the region appears dark compared with its surroundings. The clouds are often of low temperature and contain many molecules. DARK MATTER Mat ...
astronomy webquest…… explore the universe
... A teaspoon of material from a neuron star can weigh about _____________________. Stars are made mainly from the gases _____________ and ______________. Describe the stages of a star’s life cycle in the correct order. ...
... A teaspoon of material from a neuron star can weigh about _____________________. Stars are made mainly from the gases _____________ and ______________. Describe the stages of a star’s life cycle in the correct order. ...
2014 State Test
... A. Hydrogen C. Carbon B. Helium D. Neon B12. The electron capture required for turning a proton into a neutron (needed to burn hydrogen into helium) releases a very light particle that interacts extremely weakly with matter. What is the name of that particle? A. Charm quark C. Exciton B. Neutrino D. ...
... A. Hydrogen C. Carbon B. Helium D. Neon B12. The electron capture required for turning a proton into a neutron (needed to burn hydrogen into helium) releases a very light particle that interacts extremely weakly with matter. What is the name of that particle? A. Charm quark C. Exciton B. Neutrino D. ...
Astronomy 15 - Problem Set Number 4 1) Suppose one were to
... 2) Astronomers build big telescopes because the objects they deal with are so faint. For visible wavelengths and shorter, the amount of information an astronomer gets from an object is ultimately limited by the inherent ‘graininess’ of the signal – by the fact that the photon energy E = hν. This qu ...
... 2) Astronomers build big telescopes because the objects they deal with are so faint. For visible wavelengths and shorter, the amount of information an astronomer gets from an object is ultimately limited by the inherent ‘graininess’ of the signal – by the fact that the photon energy E = hν. This qu ...
A-level Physics A Question paper Unit 05 - Section 2A
... 3 (b) (ii) Give reasons for your answer to part (b)(i). ...
... 3 (b) (ii) Give reasons for your answer to part (b)(i). ...
The Milky Way - University of North Texas
... 20. The period of a Cepheid variable star and the time of one recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has ...
... 20. The period of a Cepheid variable star and the time of one recent maximum can be used to predict the time of a future maximum. Suppose that you calculate the time of future maximum brightness and then make measurements to observe this maximum. After the correction for Earth's orbital position has ...
12/08/14-- Student ID ______ TA Name
... Use Fig. 4 to answer the next 5 questions. 9. (1 pt) Contains the coolest region where absorption lines form. B 10. (1 pt) Energy gets through this region via the “random walk.” D 11. (1 pt) Magnetic fields from Sun’s interior poke out in these photospheric dark regions. A 12. (1 pt) The “boiling” m ...
... Use Fig. 4 to answer the next 5 questions. 9. (1 pt) Contains the coolest region where absorption lines form. B 10. (1 pt) Energy gets through this region via the “random walk.” D 11. (1 pt) Magnetic fields from Sun’s interior poke out in these photospheric dark regions. A 12. (1 pt) The “boiling” m ...
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... • Gravity is 2 billion times that of the gravity on Earth. • Gravity presses the material in on itself so tightly that protons and electrons combine to make neutrons, yielding the name "neutron star”. ...
... • Gravity is 2 billion times that of the gravity on Earth. • Gravity presses the material in on itself so tightly that protons and electrons combine to make neutrons, yielding the name "neutron star”. ...
Phase Analysis of RV Tauri and Semi-regular Variables Abstract
... with alternating deep and shallow minima, a period range of 30-150 days, and a spectral class that ranges from G to K. Semi-Regular variable stars are a type of long period variable star. Semi-Regular stars are usually giants or supergiants that have noticeable periods with intervals of semiregular ...
... with alternating deep and shallow minima, a period range of 30-150 days, and a spectral class that ranges from G to K. Semi-Regular variable stars are a type of long period variable star. Semi-Regular stars are usually giants or supergiants that have noticeable periods with intervals of semiregular ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.