Your Star: _____________________ Write down the wavelength at which the one
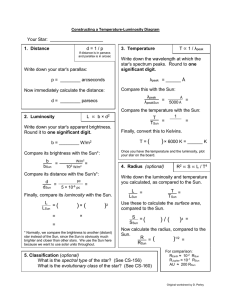
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
... of some of the well-known stars to calculate, using the formulas and methods discussed in class, their intrinsic properties (temperature, luminosity, and radius.) We will then look for patterns in these properties by way of the H-R (temperature-luminosity) diagram. Your group will be in charge of a ...
lecture25
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
... Radar ranging - good for measuring distances in the solar system (up to about 0.0001 light years) Parallax - good for measuring distances to a few hundred light years ...
Kepler-452b is not a new Earth A twin of the Sun
... the planet's surface taken by LORRI during the flyby. Among the features that most attracted the researchers’ attention there are some flat plains extending towards the left lobe of the “heart” (informally named “Tombaugh Regio”, after Clyde Tombaugh who discovered Pluto in 1930), which appear fract ...
... the planet's surface taken by LORRI during the flyby. Among the features that most attracted the researchers’ attention there are some flat plains extending towards the left lobe of the “heart” (informally named “Tombaugh Regio”, after Clyde Tombaugh who discovered Pluto in 1930), which appear fract ...
Fulltext PDF
... star clusters are widely used as ideal samples to study stellar evolution as all other parameters are fixed, and the mass of stars defines it’s evolution. In the present times, they are also very useful in understanding star and planet formation as these are very closely linked processes, planet for ...
... star clusters are widely used as ideal samples to study stellar evolution as all other parameters are fixed, and the mass of stars defines it’s evolution. In the present times, they are also very useful in understanding star and planet formation as these are very closely linked processes, planet for ...
Evolved Stellar Populations
... and bluer than younger and foreground objects. C-rich are redder than O-rich AGB stars Both criteria exclude upper-RGB stars. ...
... and bluer than younger and foreground objects. C-rich are redder than O-rich AGB stars Both criteria exclude upper-RGB stars. ...
Star Location, Constellations and Intro to Solar System 1
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the East-West location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the East-West location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
Time From the Perspective of a Particle Physicist
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the East-West location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
... What to Remember - EW • What time during the day a star rises, is overhead, and sets changes with the seasons • look up on Star Chart (right ascension is the East-West location) • Changes 2 hours/month • Only on the Equator can all stars be viewed from a single location Hawaii or northern Chile a ...
PSF - ESO
... Once a provisional list of common stars is identified, it can be used to obtain a provisional geometric transformation matrix. The program starts off by considering the first input list as a "master" list. Taking each star in turn from the second input list, it applies the provisional transformation ...
... Once a provisional list of common stars is identified, it can be used to obtain a provisional geometric transformation matrix. The program starts off by considering the first input list as a "master" list. Taking each star in turn from the second input list, it applies the provisional transformation ...
what`s up this month – april 2017
... the middle ages the Virgin was often associated with the Virgin Mary. Spica is the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo and the 16 th brightest star in the night sky. Analysis of its parallax shows that it is located 250 light years from the Sun. It is a spectroscopic binary and rotating ell ...
... the middle ages the Virgin was often associated with the Virgin Mary. Spica is the brightest star in the constellation of Virgo and the 16 th brightest star in the night sky. Analysis of its parallax shows that it is located 250 light years from the Sun. It is a spectroscopic binary and rotating ell ...
12.748 Lecture 2 Cosmic Abundances, Nucleosynthesis and
... outer shell of the star, and blow it away. The explosion, a Type II supernova, is pushed from behind by neutrinos. The outer 90% of the star is blown away in a rapidly expanding shell of gas in a matter of seconds. Not bad for something with no mass, no charge and very little interaction, mister neu ...
... outer shell of the star, and blow it away. The explosion, a Type II supernova, is pushed from behind by neutrinos. The outer 90% of the star is blown away in a rapidly expanding shell of gas in a matter of seconds. Not bad for something with no mass, no charge and very little interaction, mister neu ...
Word Document - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... length. Comment on properties such as the relative brightness and color of the two components. Describe it verbally here, and draw a sketch (if you feel so moved) in blank parts of the form……………………………………………………………………………… ...
... length. Comment on properties such as the relative brightness and color of the two components. Describe it verbally here, and draw a sketch (if you feel so moved) in blank parts of the form……………………………………………………………………………… ...
galaxy.
... • The zone of avoidance must be an artifact of something in our galaxyperhaps dust extinction- blocking our view of galaxies in the Milky Way. • S Andromeda was not a normal nova. It was something else, something much brighter. • Slipher’s observations of several spiral nebulae showed that they had ...
... • The zone of avoidance must be an artifact of something in our galaxyperhaps dust extinction- blocking our view of galaxies in the Milky Way. • S Andromeda was not a normal nova. It was something else, something much brighter. • Slipher’s observations of several spiral nebulae showed that they had ...
absolute brightness: The apparent brightness a star would have if it
... emission nebula: A glowing cloud of hot interstellar gas. The gas glows as a result of a nearby young star which is ionizing the gas. Since this gas is mostly hydrogen, the emitted radiation falls predominantly in the red region of a spectrum, because of a dominant hydrogen emission. emission spectr ...
... emission nebula: A glowing cloud of hot interstellar gas. The gas glows as a result of a nearby young star which is ionizing the gas. Since this gas is mostly hydrogen, the emitted radiation falls predominantly in the red region of a spectrum, because of a dominant hydrogen emission. emission spectr ...
stars - acpsd
... luminosity and surface temperature place it in sequence on a Hertzsprung- Russell diagram. A fundamental property of all main sequence stars is thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium is the liberation of energy from the interior of the star balanced by the energy released at the surface of the sta ...
... luminosity and surface temperature place it in sequence on a Hertzsprung- Russell diagram. A fundamental property of all main sequence stars is thermal equilibrium. Thermal equilibrium is the liberation of energy from the interior of the star balanced by the energy released at the surface of the sta ...
Ch12&13 Life and Death of Stars
... • The core is inert He, but outside the core, in the radiation-zone, there is still plenty of H. • As the core contracts it, of course, brings some of the rest of the star with it. A layer of H in the radiation-zone gets sufficiently hot to start ...
... • The core is inert He, but outside the core, in the radiation-zone, there is still plenty of H. • As the core contracts it, of course, brings some of the rest of the star with it. A layer of H in the radiation-zone gets sufficiently hot to start ...
PODEX – PhOtometric Data EXtractor
... curve. A light curve with a high D–value and/or a high variance has low weight for the reference light curve. Clicking the Calc Va-Cp button, the reference light curve is determined and subtracted from the light curve of star #1. The resulting relative (or absolute, if the offset cor. option is used ...
... curve. A light curve with a high D–value and/or a high variance has low weight for the reference light curve. Clicking the Calc Va-Cp button, the reference light curve is determined and subtracted from the light curve of star #1. The resulting relative (or absolute, if the offset cor. option is used ...
J: Chapter 4: Stars and Galaxies
... its parallax—the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. Extend your arm and look at your thumb first with your left eye closed and then with your right eye closed, as the girl in Figure 3A is doing. Your thumb appears to change position with respect to ...
... its parallax—the apparent shift in the position of an object when viewed from two different positions. Extend your arm and look at your thumb first with your left eye closed and then with your right eye closed, as the girl in Figure 3A is doing. Your thumb appears to change position with respect to ...
ppt
... Find an object whose luminosity you know. Measure the energy (flux) that you observe. Use the inverse square law to figure the distance to the object… ...
... Find an object whose luminosity you know. Measure the energy (flux) that you observe. Use the inverse square law to figure the distance to the object… ...
Lecture 3
... Hydrogen lines in the visible part of the spectrum (known as the Balmer Series) are created when a photon is absorbed by bouncing an electron from the 1st excited level to a higher excited level. • Photons with just the right energy to move an electron from the 1st excited state to the 2nd excited s ...
... Hydrogen lines in the visible part of the spectrum (known as the Balmer Series) are created when a photon is absorbed by bouncing an electron from the 1st excited level to a higher excited level. • Photons with just the right energy to move an electron from the 1st excited state to the 2nd excited s ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.























