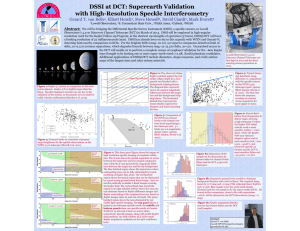
2-GW_MEPhI_2016_bisnovatyi
... Discovery of pulsars: A.Hewish, J.Bell et al., 1968, Nature, 217, 709 1973: all pulsars are single (more than 100) more than half massive stars (predesessors of pulsars) are in binaries. ...
... Discovery of pulsars: A.Hewish, J.Bell et al., 1968, Nature, 217, 709 1973: all pulsars are single (more than 100) more than half massive stars (predesessors of pulsars) are in binaries. ...
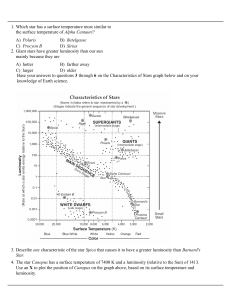
Warm-Up Monday, July 23, 2012
... • A. The stars of Orion are closer together in space. • B. The stars in Orion orbit the Sun, just like the planets. • C. The brightest stars in Orion are the ones that are closest to us. • D. You can’t tell if the brightest stars in Orion are really brighter than the others, or if they are just clos ...
... • A. The stars of Orion are closer together in space. • B. The stars in Orion orbit the Sun, just like the planets. • C. The brightest stars in Orion are the ones that are closest to us. • D. You can’t tell if the brightest stars in Orion are really brighter than the others, or if they are just clos ...
Relation Between the Luminosity of the Star at Different
... When examined for the best suitable equation that defines the curve, a sinusoidal curve showed a promising result with RMSE value 0.00183680. However, when we see the graph as a whole, we see that the curve increases and decreases periodically. This does not support any theory unless it is a Cepheid ...
... When examined for the best suitable equation that defines the curve, a sinusoidal curve showed a promising result with RMSE value 0.00183680. However, when we see the graph as a whole, we see that the curve increases and decreases periodically. This does not support any theory unless it is a Cepheid ...
Opakování z minulého cvičení
... HR diagram – star formation Star formation Stars form when cool, relatively dense clouds of gas and dust in space shrink in upon themselves as a result of gravitational collapse. This mainly happens in giant molecular clouds, where the density is about 1 billion or 10 billion atoms per cubic metre. ...
... HR diagram – star formation Star formation Stars form when cool, relatively dense clouds of gas and dust in space shrink in upon themselves as a result of gravitational collapse. This mainly happens in giant molecular clouds, where the density is about 1 billion or 10 billion atoms per cubic metre. ...
The Sun
... – Summer, fall, winter, and spring constellations can be seen only at certain times of the year because of Earth’s changing position in its orbit around the Sun. ...
... – Summer, fall, winter, and spring constellations can be seen only at certain times of the year because of Earth’s changing position in its orbit around the Sun. ...
November 2015 - Denver Astronomical Society
... NASA Space Place. . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 about 14° above the horizon, and slightly closer; at ...
... NASA Space Place. . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 about 14° above the horizon, and slightly closer; at ...
ES Chapter 30
... – Summer, fall, winter, and spring constellations can be seen only at certain times of the year because of Earth’s changing position in its orbit around the Sun. ...
... – Summer, fall, winter, and spring constellations can be seen only at certain times of the year because of Earth’s changing position in its orbit around the Sun. ...
chapter 26 instructor notes
... galaxies are bright at infrared wavelengths, however. Although the starburst activity was initially discovered in the galaxy nuclei, some spiral galaxies also exhibit diskwide starburst activity. The star formation is assumed to have been induced by shock waves generated by the gravitational interac ...
... galaxies are bright at infrared wavelengths, however. Although the starburst activity was initially discovered in the galaxy nuclei, some spiral galaxies also exhibit diskwide starburst activity. The star formation is assumed to have been induced by shock waves generated by the gravitational interac ...
Astronomy - Career Account Web Pages
... the deepest infrared image taken of the universe. Based on the object's color, astronomers believe it is 13.2 billion light-years away. The most distant objects in the universe appear extremely red because their light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths by the expansion of the universe. This ...
... the deepest infrared image taken of the universe. Based on the object's color, astronomers believe it is 13.2 billion light-years away. The most distant objects in the universe appear extremely red because their light is stretched to longer, redder wavelengths by the expansion of the universe. This ...
The Interstellar Medium
... an emission nebula, but is enough to give sufficient scattering to make the dust visible. Thus, the spectrum shown by reflection nebulae is similar to that of the illuminating stars, but bluer due to the efficiency with which blue light is scattered. ...
... an emission nebula, but is enough to give sufficient scattering to make the dust visible. Thus, the spectrum shown by reflection nebulae is similar to that of the illuminating stars, but bluer due to the efficiency with which blue light is scattered. ...
Distance Between Stars - cK-12
... As Figure 1.1 shows, astronomers use this same principle to measure the distance to stars. Instead of a finger, they focus on a star, and instead of switching back and forth between eyes, they switch between the biggest possible differences in observing position. To do this, an astronomer first look ...
... As Figure 1.1 shows, astronomers use this same principle to measure the distance to stars. Instead of a finger, they focus on a star, and instead of switching back and forth between eyes, they switch between the biggest possible differences in observing position. To do this, an astronomer first look ...
2-star-life-cycle-and-star-classification
... A) in the Sun by fusion B) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere C) from the movement of crustal plates D) during nuclear decay 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud ...
... A) in the Sun by fusion B) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere C) from the movement of crustal plates D) during nuclear decay 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud ...
Article Reference - Archive ouverte UNIGE
... 12.8) km s−1 . Those values are well away from any of the known young moving groups reported in Zuckerman & Song (2004). This means the gyrochronological age is not reliable. ...
... 12.8) km s−1 . Those values are well away from any of the known young moving groups reported in Zuckerman & Song (2004). This means the gyrochronological age is not reliable. ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 18 Notes: Neutron Stars
... (which is not the same as the radio beam we see), and this radiation reduces the kinetic energy of the pulsar, causing it to slow. The slowdown is very slow: a typical pulsar requires of order ten million years to slow down significantly. The magnetic dipole radiation is deposited in the material a ...
... (which is not the same as the radio beam we see), and this radiation reduces the kinetic energy of the pulsar, causing it to slow. The slowdown is very slow: a typical pulsar requires of order ten million years to slow down significantly. The magnetic dipole radiation is deposited in the material a ...
Lab PDF - NMSU Astronomy
... All objects of the same apparent magnitude appear equally bright when viewed from Earth. The 25 brightest stars in the sky are said to be first magnitude or brighter. The unaided eye can find about two thousand stars from first down to sixth magnitude in a dark sky, and large telescopes can reveal t ...
... All objects of the same apparent magnitude appear equally bright when viewed from Earth. The 25 brightest stars in the sky are said to be first magnitude or brighter. The unaided eye can find about two thousand stars from first down to sixth magnitude in a dark sky, and large telescopes can reveal t ...
How common are habitable planets?
... focused on the 42,000 stars that are like the sun or transit, their stars, which causes a slight diminution slightly cooler and smaller, and found 603 – about one hundredth of one percent – in the star's candidate planets orbiting them. Only 10 of these brightness. From among the 150,000 stars were ...
... focused on the 42,000 stars that are like the sun or transit, their stars, which causes a slight diminution slightly cooler and smaller, and found 603 – about one hundredth of one percent – in the star's candidate planets orbiting them. Only 10 of these brightness. From among the 150,000 stars were ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.