Chapter 1 Introduction
... Lying behind much of the work in this thesis are the predictions from a pillar of modern astronomy, the theory of stellar evolution. e changes in the structure of a star over its lifetime are now very well understood, and they are largely determined by a single parameter: its mass. Although the Sun ...
... Lying behind much of the work in this thesis are the predictions from a pillar of modern astronomy, the theory of stellar evolution. e changes in the structure of a star over its lifetime are now very well understood, and they are largely determined by a single parameter: its mass. Although the Sun ...
The Milky Way`s Restless Swarms of Stars
... duce the same dynamics—for stars to arise when globular clusters are born. effect,” says Shara. example, thousands of neutron However, calculations show that it doesn’t “It makes stars milstars within a small volume of take many of them to affect the cluster’s evo- lions or even billions space. Such ...
... duce the same dynamics—for stars to arise when globular clusters are born. effect,” says Shara. example, thousands of neutron However, calculations show that it doesn’t “It makes stars milstars within a small volume of take many of them to affect the cluster’s evo- lions or even billions space. Such ...
Solutions to Homework #4, AST 203, Spring 2012
... aren’t defined, if important steps of explanation are missing, etc. If the answer is written down without *any* context whatsoever, take off 1/3 of the points. One point off per question for inappropriately high precision (which usually means more than 2 significant figures in this homework). No mor ...
... aren’t defined, if important steps of explanation are missing, etc. If the answer is written down without *any* context whatsoever, take off 1/3 of the points. One point off per question for inappropriately high precision (which usually means more than 2 significant figures in this homework). No mor ...
Wide-eyed Telescope Finds its First Transiting
... Embargoed until Tuesday 26th September 00:02 a.m. BST=GMT+1hr The SuperWASP planetary transit telescopes The SuperWASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) project operates two camera systems – one in La Palma in the Canary Islands and one at Sutherland Observatory, South Africa. These telescopes have a ...
... Embargoed until Tuesday 26th September 00:02 a.m. BST=GMT+1hr The SuperWASP planetary transit telescopes The SuperWASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) project operates two camera systems – one in La Palma in the Canary Islands and one at Sutherland Observatory, South Africa. These telescopes have a ...
Wide-eyed Telescope Finds its First Transiting
... Embargoed until Tuesday 26th September 00:02 a.m. BST=GMT+1hr The SuperWASP planetary transit telescopes The SuperWASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) project operates two camera systems – one in La Palma in the Canary Islands and one at Sutherland Observatory, South Africa. These telescopes have a ...
... Embargoed until Tuesday 26th September 00:02 a.m. BST=GMT+1hr The SuperWASP planetary transit telescopes The SuperWASP (Wide Angle Search for Planets) project operates two camera systems – one in La Palma in the Canary Islands and one at Sutherland Observatory, South Africa. These telescopes have a ...
DAY AND NIGHT, SEASONS
... exoplanet, facing away from the star, will be in permanent darkness and hence cold. There will be a twilight zone between these two regions which might be a suitable place for life. Alternatively, life might exist beneath the surface. For planets with an axial tilt life may only be able to survive i ...
... exoplanet, facing away from the star, will be in permanent darkness and hence cold. There will be a twilight zone between these two regions which might be a suitable place for life. Alternatively, life might exist beneath the surface. For planets with an axial tilt life may only be able to survive i ...
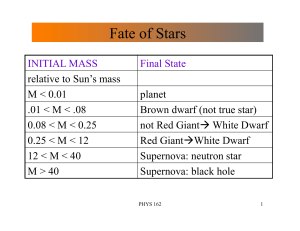
white dwarfs, neutron stars, black hole
... On the other hand, stars with masses 150 times that of the Sun (150Msun) tend to develop such high temperatures that pressure from rapid fusion quickly tears them apart. Thus, main sequence stars can have masses only between about 0.08 and 150 solar masses. Evolutionary Track of our Sun: The Sun is ...
... On the other hand, stars with masses 150 times that of the Sun (150Msun) tend to develop such high temperatures that pressure from rapid fusion quickly tears them apart. Thus, main sequence stars can have masses only between about 0.08 and 150 solar masses. Evolutionary Track of our Sun: The Sun is ...
How do the most massive galaxies constrain theories of
... Fontana et al. 2004 (K20) Glazebrook et al. 2004 (GDDS); Brinchmann & Ellis 2000; Cohen et al. 2000; Rudnick et al. 2004 (FIRES); Drory et al. 2004 (MUNICS); van ...
... Fontana et al. 2004 (K20) Glazebrook et al. 2004 (GDDS); Brinchmann & Ellis 2000; Cohen et al. 2000; Rudnick et al. 2004 (FIRES); Drory et al. 2004 (MUNICS); van ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... whereas super giants may have radii of several 100 solar radii. The masses of stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now ...
... whereas super giants may have radii of several 100 solar radii. The masses of stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now ...
Dec 2016 - Astronomical Society of Northern New England
... star, becoming very stable once again and lasting for another 10 billion years on top of the 10 billion years that this star was living and fusing hydrogen and helium to produce prodigious amounts of energy. The shells of expelled gas of planetary nebulae can be seen all over our galaxy. We give the ...
... star, becoming very stable once again and lasting for another 10 billion years on top of the 10 billion years that this star was living and fusing hydrogen and helium to produce prodigious amounts of energy. The shells of expelled gas of planetary nebulae can be seen all over our galaxy. We give the ...
GRAVITATIONAL RADIATION FROM ACCRETING NEUTRON STARS
... obviously in X-ray binary systems, and some of these are potential strong gravitational wave sources [4]. But accretion occurs in other situations, most notably in Thorne-Zytkow objects, which are the stage of evolution of massive X-ray binaries that occurs after the X-ray phase, when the giant comp ...
... obviously in X-ray binary systems, and some of these are potential strong gravitational wave sources [4]. But accretion occurs in other situations, most notably in Thorne-Zytkow objects, which are the stage of evolution of massive X-ray binaries that occurs after the X-ray phase, when the giant comp ...
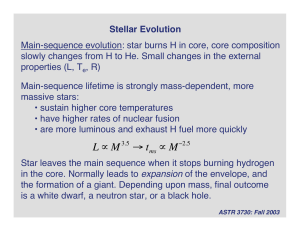
Lecture 30
... For stars with masses between 0.5 Msun and 8 Msun, core burning ends with the core a mixture of carbon and oxygen. Envelope is now very large, and weakly bound to the core. Final stages of burning generate a lot of luminosity, which acts to blow away the envelope: ...
... For stars with masses between 0.5 Msun and 8 Msun, core burning ends with the core a mixture of carbon and oxygen. Envelope is now very large, and weakly bound to the core. Final stages of burning generate a lot of luminosity, which acts to blow away the envelope: ...
Fixed Stars - Mark Dodich
... arrest because he said the earth orbited around the Sun. Edward VIII abdicated the right to the throne of England rather than deny his love for a divorced woman. ...
... arrest because he said the earth orbited around the Sun. Edward VIII abdicated the right to the throne of England rather than deny his love for a divorced woman. ...
Theory of Massive Star Formation
... The Observed IMF IMF properties: • Peak at ~0.1 – 1 M" • Powerlaw tail (slope ~ −2.3) at high mass, up to 120 – 300 M • (Nearly) universal − very limited evidence for weak variation ...
... The Observed IMF IMF properties: • Peak at ~0.1 – 1 M" • Powerlaw tail (slope ~ −2.3) at high mass, up to 120 – 300 M • (Nearly) universal − very limited evidence for weak variation ...
Lecture Eleven (Powerpoint format)
... the reasoning processes of eminent scientists engaged in a great controversy for which the evidence on both sides is fragmentary and partly faulty. This debate illustrates forcefully how tricky it is to pick one's way through the treacherous ground that characterizes research at the frontiers of sci ...
... the reasoning processes of eminent scientists engaged in a great controversy for which the evidence on both sides is fragmentary and partly faulty. This debate illustrates forcefully how tricky it is to pick one's way through the treacherous ground that characterizes research at the frontiers of sci ...
19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... 3. Trace the orbital velocities of objects in different directions relative to our position. ...
... 3. Trace the orbital velocities of objects in different directions relative to our position. ...
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
Night Sky
... Because the earth is rotating the sky appears to rotate. Viewed from above the north pole, the earth is rotating counter-clockwise. For an observer on the earth, objects move from east to west (this is true for both northern and southern hemispheres). More accurately put, when looking north, objects ...
... Because the earth is rotating the sky appears to rotate. Viewed from above the north pole, the earth is rotating counter-clockwise. For an observer on the earth, objects move from east to west (this is true for both northern and southern hemispheres). More accurately put, when looking north, objects ...
01 - University of Warwick
... the most comprehensive search for gas around 15 different ”This indicates that gas giant planets like Jupiter and Saturn sun-like stars, most with ages ranging from 3 million to 30 have already formed in these young solar system analogs, or they never will,” Meyer said. million years. Astronomers su ...
... the most comprehensive search for gas around 15 different ”This indicates that gas giant planets like Jupiter and Saturn sun-like stars, most with ages ranging from 3 million to 30 have already formed in these young solar system analogs, or they never will,” Meyer said. million years. Astronomers su ...
featured in the Arizona Daily Star
... piece of a star and study it in the laboratory. That’s what I do — I study pieces of ancient stardust. But instead of using a telescope, I use a microscope to look for stardust inside meteorites. Over their lifetimes, stars shed matter that can condense into solid mineral grains — stardust — if cond ...
... piece of a star and study it in the laboratory. That’s what I do — I study pieces of ancient stardust. But instead of using a telescope, I use a microscope to look for stardust inside meteorites. Over their lifetimes, stars shed matter that can condense into solid mineral grains — stardust — if cond ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.