10. The Lives of the Stars
... larger, redder, and much more luminous — at least for a while. . . ...
... larger, redder, and much more luminous — at least for a while. . . ...
What is a white dwarf?
... usually made mostly of carbon (some are made mostly of helium; others of oxygen or other elements heavier than carbon, up to and including iron). Their name comes from the fact they are 'born' glowing white-hot with high temperatures (remember that the core of a normal star has a higher temperature ...
... usually made mostly of carbon (some are made mostly of helium; others of oxygen or other elements heavier than carbon, up to and including iron). Their name comes from the fact they are 'born' glowing white-hot with high temperatures (remember that the core of a normal star has a higher temperature ...
Astronomical Filters on Skynet Telescopes
... Measuring physical properties of stars Astronomers use filters to measure properties of astronomical objects, a good example being the temperature of a star. Cooler stars look redder, and hotter stars look bluer. By quantifying how red or blue a star looks, we can relate this measurement to its temp ...
... Measuring physical properties of stars Astronomers use filters to measure properties of astronomical objects, a good example being the temperature of a star. Cooler stars look redder, and hotter stars look bluer. By quantifying how red or blue a star looks, we can relate this measurement to its temp ...
lab 11 only - Penn State University
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
... spherical cloud of stars that surrounds the entire galaxy). The halo is much larger than the bulge. Our Milky Way Galaxy is made up of mostly stars, gas, and dust. The dust blocks out light from distant stars, and makes it hard to see a lot of the galaxy, especially the bulge and parts of the disk. ...
PHYS3380_110415_bw - The University of Texas at Dallas
... ・After the hydrogen is used up in the core, the helium core contracts, and heats the hydrogen rich layer just outside of the core. The hydrogen ignites in the shell around the core and the Sun moves to the right in the HR diagram. ・When the outer layers of the Sun become convective, the luminosity o ...
... ・After the hydrogen is used up in the core, the helium core contracts, and heats the hydrogen rich layer just outside of the core. The hydrogen ignites in the shell around the core and the Sun moves to the right in the HR diagram. ・When the outer layers of the Sun become convective, the luminosity o ...
First Stars II
... Star formation in large objects (Tvir>104K) Evolution of T in the prestellar collapse Fragmentaion scale vs 5UV intensity radiation: Jn=W Bn(10 K) from massive PopIII stars ...
... Star formation in large objects (Tvir>104K) Evolution of T in the prestellar collapse Fragmentaion scale vs 5UV intensity radiation: Jn=W Bn(10 K) from massive PopIII stars ...
- saspcsus
... different stars can be seen in different seasons. B. Students know the way in which the Moon’s appearance changes during the four-week lunar cycle. C. Students know telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the Moon and the planets. The number of stars that can ...
... different stars can be seen in different seasons. B. Students know the way in which the Moon’s appearance changes during the four-week lunar cycle. C. Students know telescopes magnify the appearance of some distant objects in the sky, including the Moon and the planets. The number of stars that can ...
Chapter 25 - Haiku Learning
... mass. The hottest blue stars are about 50 times more massive than the sun, while the coolest red stars are only 1/10 as massive. Therefore, on the H-R diagram, the main-sequence stars appear in decreasing order, from hotter, more massive blue stars to cooler, less massive red stars. Above and to the ...
... mass. The hottest blue stars are about 50 times more massive than the sun, while the coolest red stars are only 1/10 as massive. Therefore, on the H-R diagram, the main-sequence stars appear in decreasing order, from hotter, more massive blue stars to cooler, less massive red stars. Above and to the ...
Supernovae and supernova remnants
... emission and, in the outer layers, by convection. The photons emitted from the center (excluding the neutrinos) are scattered, absorbed and re-emitted by the surrounding material. Therefore, photons that are created in the center of the star cannot be directly detected. The photons that we detect ...
... emission and, in the outer layers, by convection. The photons emitted from the center (excluding the neutrinos) are scattered, absorbed and re-emitted by the surrounding material. Therefore, photons that are created in the center of the star cannot be directly detected. The photons that we detect ...
chapter16StarBirth
... • Photons exert a slight amount of pressure when they strike matter • Very massive stars are so luminous that the collective pressure of photons drives their matter into space ...
... • Photons exert a slight amount of pressure when they strike matter • Very massive stars are so luminous that the collective pressure of photons drives their matter into space ...
Our Galaxy -- The Milky Way PowerPoint
... – Neutral hydrogen strongly concentrated in the disk • Doppler shift of various nebulae reveals arm structure – Four major spiral arms – The Solar System is in the small Orion arm ...
... – Neutral hydrogen strongly concentrated in the disk • Doppler shift of various nebulae reveals arm structure – Four major spiral arms – The Solar System is in the small Orion arm ...
Summary: Star Formation Near and Far
... other outflows are in fact much more conspicuous properties of newly formed stars than is any evidence for continuing gas infall, and for some years they seemed to contradict the theoretical models in this respect. Now it is clear that infall, outflow, and rotation are all present simultaneously in ...
... other outflows are in fact much more conspicuous properties of newly formed stars than is any evidence for continuing gas infall, and for some years they seemed to contradict the theoretical models in this respect. Now it is clear that infall, outflow, and rotation are all present simultaneously in ...
How far away are the Stars?
... Parallax Angle is Small! • The closer the object the larger the parallax. • Parallaxes are usually very small. Parallax of Venus at closest approach (45 million km) is 1 arc minute! • Parallax of nearby (25 light years) stars not observed/measured until 1839! ...
... Parallax Angle is Small! • The closer the object the larger the parallax. • Parallaxes are usually very small. Parallax of Venus at closest approach (45 million km) is 1 arc minute! • Parallax of nearby (25 light years) stars not observed/measured until 1839! ...
Lecture 10 Spectra of Stars and Binaries
... Spectroscopic Binaries • Most binaries are too far away to see both stars separately. • But, you can detect their orbital moZons by the periodic Doppler shiCs of their spectral lines. – Determine the orbit period & size from velociZes. ...
... Spectroscopic Binaries • Most binaries are too far away to see both stars separately. • But, you can detect their orbital moZons by the periodic Doppler shiCs of their spectral lines. – Determine the orbit period & size from velociZes. ...
Powerpoint
... - at least 30 kpc across - contains globular clusters, old stars, little gas and dust, much "dark matter" ...
... - at least 30 kpc across - contains globular clusters, old stars, little gas and dust, much "dark matter" ...
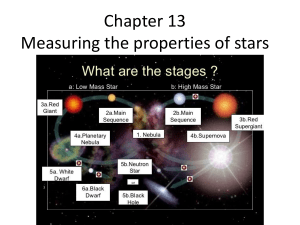
Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... Star A star is located at the top left of the H-R diagram and has the same luminosity as Star B which is located at the top right of the H-R diagram. How must these stars differ? A. Star A is hotter and bigger than Star B. B. Star A is cooler and bigger than Star B. C. Star A is hotter and smaller ...
... Star A star is located at the top left of the H-R diagram and has the same luminosity as Star B which is located at the top right of the H-R diagram. How must these stars differ? A. Star A is hotter and bigger than Star B. B. Star A is cooler and bigger than Star B. C. Star A is hotter and smaller ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... whereas super giants may have radii of several 100 solar radii. The masses of stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now s ...
... whereas super giants may have radii of several 100 solar radii. The masses of stars range from 0.08M⊙ for the least massive stars up to about 100M⊙ for the most massive stars. We will later discuss theoretical arguments explaining why there is a lower and an upper limit of star masses. We will now s ...
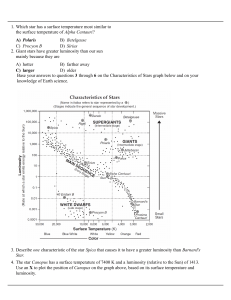
A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 1. Which star has a
... A) in the Sun by fusion B) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere C) from the movement of crustal plates D) during nuclear decay 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud ...
... A) in the Sun by fusion B) when water condenses in Earth's atmosphere C) from the movement of crustal plates D) during nuclear decay 23. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below, which shows an inferred sequence in which our solar system formed from a giant interstellar cloud ...
Advanced STARS - WordPress.com
... Jupiter is made mostly of gases and is therefore known as a ‘gas giant’ It is 2 ½ times larger than all the other planets in the solar system combined It has the shortest day of all the planets: 9 hours and 55 minutes It orbits the sun once every 11.8 earth years It’s atmosphere is divided ...
... Jupiter is made mostly of gases and is therefore known as a ‘gas giant’ It is 2 ½ times larger than all the other planets in the solar system combined It has the shortest day of all the planets: 9 hours and 55 minutes It orbits the sun once every 11.8 earth years It’s atmosphere is divided ...
Capturing Heaven - Communicating Astronomy with the Public Journal
... supernova, and leave a slowly fading splash of light and colour known as a supernova remnant. Stars can also be community dwellers. This means that they exist not only as singular specks in the depths of space, but in clusters and galaxies as well. It is also possible that they will not always be sh ...
... supernova, and leave a slowly fading splash of light and colour known as a supernova remnant. Stars can also be community dwellers. This means that they exist not only as singular specks in the depths of space, but in clusters and galaxies as well. It is also possible that they will not always be sh ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram Outline
... 16631 single stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue with relative distance precision better than 10% and sigma_(B-V) less than or equal to 0.025 mag. Colors indicate number of stars in a cell of 0.01 mag in (B-V) and 0.05 mag in V magnitude ...
... 16631 single stars from the Hipparcos Catalogue with relative distance precision better than 10% and sigma_(B-V) less than or equal to 0.025 mag. Colors indicate number of stars in a cell of 0.01 mag in (B-V) and 0.05 mag in V magnitude ...
Animated Planets PowerPoint Presentation
... The next visible comet is Comet Faye. Comet Faye's last perihelion was on November 15, 2006. It reached an apparent magnitude of 9.5 during that orbit. The orbital period of Comet Faye is 7.55 years Its next perihelion will occur on May 29, 2014. During this next appearance, its apparent magnitude i ...
... The next visible comet is Comet Faye. Comet Faye's last perihelion was on November 15, 2006. It reached an apparent magnitude of 9.5 during that orbit. The orbital period of Comet Faye is 7.55 years Its next perihelion will occur on May 29, 2014. During this next appearance, its apparent magnitude i ...
Cygnus (constellation)

Cygnus /ˈsɪɡnəs/ is a northern constellation lying on the plane of the Milky Way, deriving its name from the Latinized Greek word for swan. The swan is one of the most recognizable constellations of the northern summer and autumn, it features a prominent asterism known as the Northern Cross (in contrast to the Southern Cross). Cygnus was among the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and it remains one of the 88 modern constellations.Cygnus contains Deneb, one of the brightest stars in the night sky and one corner of the Summer Triangle, as well as some notable X-ray sources and the giant stellar association of Cygnus OB2. One of the stars of this association, NML Cygni, is one of the largest stars currently known. The constellation is also home to Cygnus X-1, a distant X-ray binary containing a supergiant and unseen massive companion that was the first object widely held to be a black hole. Many star systems in Cygnus have known planets as a result of the Kepler Mission observing one patch of the sky, the patch is the area around Cygnus. In addition, most of the eastern part of Cygnus is dominated by the Hercules–Corona Borealis Great Wall, a giant galaxy filament that is the largest known structure in the observable universe; covering most of the northern sky.