Age Distributions of Low Mass Stars in the Rho Ophiucus Molecular
... clouds in the constellation Ophiuchus. The coordinates are right ascension of 16h 28m 06s and declination of –24d 32.5s [1]. This makes it accessible from both hemispheres. It consists of two main regions of dense gas and dust. The largest and densest, L1688, is the focus of this work. The Rho Oph c ...
... clouds in the constellation Ophiuchus. The coordinates are right ascension of 16h 28m 06s and declination of –24d 32.5s [1]. This makes it accessible from both hemispheres. It consists of two main regions of dense gas and dust. The largest and densest, L1688, is the focus of this work. The Rho Oph c ...
MS 1512–CB58 - Columbia University Department of Astronomy
... Thanks to its gravitationally lensed nature, the z = 2.7276 galaxy MS 1512−cB58 (or cB58 for short) provides an unusually clear window on the population of starforming galaxies identified at these redshifts through the Lyman break technique (Steidel et al., 1996). Discovered by Yee et al. (1996), cB ...
... Thanks to its gravitationally lensed nature, the z = 2.7276 galaxy MS 1512−cB58 (or cB58 for short) provides an unusually clear window on the population of starforming galaxies identified at these redshifts through the Lyman break technique (Steidel et al., 1996). Discovered by Yee et al. (1996), cB ...
Diapositiva 1
... and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1") resembles, on the best plates, a slightly diffuse star with a very short curved, nebulous "tail" extending for 5" in p.a. 52º. Its visual ma ...
... and 1947 and centered on the diffuse nebula NGC 1999, there appear several peculiar nebulous objects. The brightest of these (referred to hereafter as "No. 1") resembles, on the best plates, a slightly diffuse star with a very short curved, nebulous "tail" extending for 5" in p.a. 52º. Its visual ma ...
The Missing Mass
... • The orbits in spiral galaxies are not quite circles – they are ellipses. These ellipses are slightly tilted with respect to each other. ...
... • The orbits in spiral galaxies are not quite circles – they are ellipses. These ellipses are slightly tilted with respect to each other. ...
White dwarfs that crossed the Chandrasekhar limit
... Einstein’s theory of gravity establishes that space–time is curved around a massive object and it is scale-independent. Broadly speaking, irrespective of where we stand from the gravitating object, the force with which we are pulled is always equal to the inverse of the distance squared. But, the mo ...
... Einstein’s theory of gravity establishes that space–time is curved around a massive object and it is scale-independent. Broadly speaking, irrespective of where we stand from the gravitating object, the force with which we are pulled is always equal to the inverse of the distance squared. But, the mo ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B PMS star
... the emerging flux, and the direct detection of the photospheric spectrum turns out to be very difficult at this early stage of evolution (e.g., Testi et al. 2010). Infrared surveys have revealed several hundred candidate massive YSOs, based on luminosity arguments (e.g., Urquhart et al. 2011). A (K ...
... the emerging flux, and the direct detection of the photospheric spectrum turns out to be very difficult at this early stage of evolution (e.g., Testi et al. 2010). Infrared surveys have revealed several hundred candidate massive YSOs, based on luminosity arguments (e.g., Urquhart et al. 2011). A (K ...
Document
... < .08 Msun (failed stars). Brown Dwarfs do not get hot enough to fuse H, but they do fuse Deuterium for a very short time. Deuterium is an isotope of H, with a neutron. About 1,000 Brown Dwarfs have been found. They radiate in the infrared ...
... < .08 Msun (failed stars). Brown Dwarfs do not get hot enough to fuse H, but they do fuse Deuterium for a very short time. Deuterium is an isotope of H, with a neutron. About 1,000 Brown Dwarfs have been found. They radiate in the infrared ...
Standing in Awe - Auckland Astronomical Society
... 1971, shining faintly at magnitude 15.5. A few fainter galaxies lie around 5861, needing larger telescopes to see. North-east of beta and 1° north of delta lies our next target, NGC 5812, a bright, small, round elliptical galaxy with a brighter central region. Moving 3.8° south and slightly east of ...
... 1971, shining faintly at magnitude 15.5. A few fainter galaxies lie around 5861, needing larger telescopes to see. North-east of beta and 1° north of delta lies our next target, NGC 5812, a bright, small, round elliptical galaxy with a brighter central region. Moving 3.8° south and slightly east of ...
NAM_f2
... sweeps over almost the entire sky in a single orbit. The imaging system has a cadence of four seconds but for a given star we combine the images from a single orbit to produce a system with an effective exposure time of 16 to 20 seconds and a cadence of 100 minutes. ...
... sweeps over almost the entire sky in a single orbit. The imaging system has a cadence of four seconds but for a given star we combine the images from a single orbit to produce a system with an effective exposure time of 16 to 20 seconds and a cadence of 100 minutes. ...
Calculate the Mass of the Milky Way Galaxy
... "cosmic scatter" and is probably due to the fact that the gas clouds that formed the galaxies all had some small additional motion of their own. The recessional velocity of a galaxy at a particular distance inferred from Hubble's law is called the "Hubble velocity". ...
... "cosmic scatter" and is probably due to the fact that the gas clouds that formed the galaxies all had some small additional motion of their own. The recessional velocity of a galaxy at a particular distance inferred from Hubble's law is called the "Hubble velocity". ...
Document
... Stars (cont.) E. Death of a Star - 4 Solar Masses or more (cont). -After Supernova explosion, stellar remnant is dependant upon how much of core is left. -1. Neutron “Star”-- Core remnant is between 1.4 and 3.0 solar masses - Compression will be so great that protons and electrons of matter in core ...
... Stars (cont.) E. Death of a Star - 4 Solar Masses or more (cont). -After Supernova explosion, stellar remnant is dependant upon how much of core is left. -1. Neutron “Star”-- Core remnant is between 1.4 and 3.0 solar masses - Compression will be so great that protons and electrons of matter in core ...
27B Star Life Cycle and the HR Diagram
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
... all of the known stars were put on their graph, several obvious groups became apparent. By examining the differences in these groups, later astronomers were able to realize that the groups were best described as stars in different periods in their life cycle, rather than completely different types o ...
13.5 The HR Diagram By the early 1900s, astronomers had learned
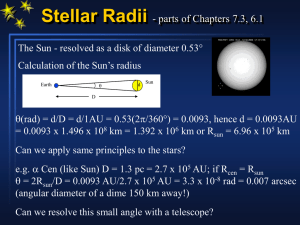
... We find from such measurements that all stars have nearly the same composition of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, with a trace of the heavier elements. Most have surface temperatures between about 3000 and 30,000 K and masses between about 0.1 and 30 M⊙. The HR diagram offers a simple, pictorial ...
... We find from such measurements that all stars have nearly the same composition of about 71% hydrogen and 27% helium, with a trace of the heavier elements. Most have surface temperatures between about 3000 and 30,000 K and masses between about 0.1 and 30 M⊙. The HR diagram offers a simple, pictorial ...
Astronomy 21 – Test 2 – Answers
... Active galaxies emit non-thermal radiation from their centers. This is synchrotron emission where electrons get accelerated in a magnetic field. AGN’s often have jets that propagate through the ISM/IGM. X-ray emission is often observed from the accretion disk surrounding the black hole. 15. What is ...
... Active galaxies emit non-thermal radiation from their centers. This is synchrotron emission where electrons get accelerated in a magnetic field. AGN’s often have jets that propagate through the ISM/IGM. X-ray emission is often observed from the accretion disk surrounding the black hole. 15. What is ...
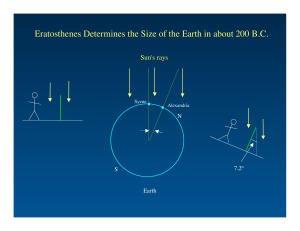
Eratosthenes Determines the Size of the Earth in about 200 B.C.
... • The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. • Rotation axis inclined 23.5° away from the perpendicular to the orbital plane. => This causes solar illumination and number of daylight hours to vary at any location throughout the year. ...
... • The Earth’s axis of rotation is tilted with respect to the plane of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun. • Rotation axis inclined 23.5° away from the perpendicular to the orbital plane. => This causes solar illumination and number of daylight hours to vary at any location throughout the year. ...
Open clusters in the Third Galactic Quadrant III. Alleged binary
... of the interval instead of the fitting uncertainty. Regardless of the metal content adopted, the fitting error of the apparent distance modulus for each cluster was estimated by eye as discussed below. Cluster ages were derived by the same technique of fitting the isochrone (Girardi et al. 2000) set ...
... of the interval instead of the fitting uncertainty. Regardless of the metal content adopted, the fitting error of the apparent distance modulus for each cluster was estimated by eye as discussed below. Cluster ages were derived by the same technique of fitting the isochrone (Girardi et al. 2000) set ...
Oct - Seattle Astronomical Society
... Repeat that phrase 4000 times and you start to get an idea what life is like in distant galaxy J100054+023436. Astronomers using NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope and ground-based observatories have found that the galaxy gives birth to as many as 4000 stars a year. For comparison, in the same period of ...
... Repeat that phrase 4000 times and you start to get an idea what life is like in distant galaxy J100054+023436. Astronomers using NASA’s Spitzer Space Telescope and ground-based observatories have found that the galaxy gives birth to as many as 4000 stars a year. For comparison, in the same period of ...
Lecture18
... • Stars come in many luminosities • If astronomers could tell what the luminosity of a star ...
... • Stars come in many luminosities • If astronomers could tell what the luminosity of a star ...
Chapter 16
... 1. The density wave theory was first proposed by Lindblad in 1960. It is a model for spiral galaxies that proposes that the arms are the result of density waves sweeping around the galaxy. 2. A density wave is a wave in which areas of high and low pressure move through the medium. 3. The density wav ...
... 1. The density wave theory was first proposed by Lindblad in 1960. It is a model for spiral galaxies that proposes that the arms are the result of density waves sweeping around the galaxy. 2. A density wave is a wave in which areas of high and low pressure move through the medium. 3. The density wav ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.