Tyler Gray - Angelfire
... M31 is the famous Andromeda galaxy, our nearest large neighbor galaxy, forming the Local Group of galaxies together with its companions (including M32 and M110, two bright dwarf elliptical galaxies), our Milky Way and its companions, M33, and others. Visible to the naked eye even under moderate cond ...
... M31 is the famous Andromeda galaxy, our nearest large neighbor galaxy, forming the Local Group of galaxies together with its companions (including M32 and M110, two bright dwarf elliptical galaxies), our Milky Way and its companions, M33, and others. Visible to the naked eye even under moderate cond ...
Answer to question 1 - Northwestern University
... • What do we need? Precise, small images, the better to find the centers of, and a well defined non-moving background for reference. • Stars are good for making small images, and distant stars or small galaxies are good for reference. ...
... • What do we need? Precise, small images, the better to find the centers of, and a well defined non-moving background for reference. • Stars are good for making small images, and distant stars or small galaxies are good for reference. ...
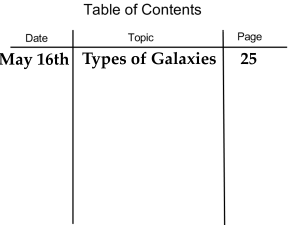
Page 25 - Types of Galaxies
... • These galaxies are neither spiral nor elliptical. • They tend to be smaller objects that are without definite shape and tend to have very hot newer stars mixed in with lots of gas and dust. • These galaxies often have active regions of star formation. Sometimes the irregular shape of these galaxie ...
... • These galaxies are neither spiral nor elliptical. • They tend to be smaller objects that are without definite shape and tend to have very hot newer stars mixed in with lots of gas and dust. • These galaxies often have active regions of star formation. Sometimes the irregular shape of these galaxie ...
The double-degenerate, super-Chandrasekhar nucleus of the
... (M⊙ ). The origin of their complex morphologies is poorly understood1 , although several mechanisms involving binary interaction have been proposed2,3 . In close binary systems, the orbital separation is short enough for the primary star to overfill its Roche lobe as it expands during the Asymptotic ...
... (M⊙ ). The origin of their complex morphologies is poorly understood1 , although several mechanisms involving binary interaction have been proposed2,3 . In close binary systems, the orbital separation is short enough for the primary star to overfill its Roche lobe as it expands during the Asymptotic ...
Night Sky
... earth is rotating counter-clockwise. For an observer on the earth, objects move from east to west (this is true for both northern and southern hemispheres). More accurately put, when looking north, objects in the sky move counter-clockwise. ...
... earth is rotating counter-clockwise. For an observer on the earth, objects move from east to west (this is true for both northern and southern hemispheres). More accurately put, when looking north, objects in the sky move counter-clockwise. ...
We Are Made of Stardust
... hydrogen into helium, releasing nuclear energy. The closest star of the night sky, Alpha Centauri A (within the constellation Centaurus), is very similar in mass, size, color, and brightness to our own sun. It is just 4.3 light years away. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, located just 8. ...
... hydrogen into helium, releasing nuclear energy. The closest star of the night sky, Alpha Centauri A (within the constellation Centaurus), is very similar in mass, size, color, and brightness to our own sun. It is just 4.3 light years away. Sirius, the brightest star in the night sky, located just 8. ...
12_Doppler (Mar 12)
... following statements best describes how the sources of light that produced the two spectra were moving? BLUE ...
... following statements best describes how the sources of light that produced the two spectra were moving? BLUE ...
Astronomy 328 Midterm Exam - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... During the helium-core-burning phase, some hydrogen burning is also occurring in a shell. Thus the star’s luminosity is not due to helium burning alone. Keeping this in mind, assume that the typical luminosity from helium burning is 102 L . Estimate the lifetime of the helium-core-burning phase. (5 ...
... During the helium-core-burning phase, some hydrogen burning is also occurring in a shell. Thus the star’s luminosity is not due to helium burning alone. Keeping this in mind, assume that the typical luminosity from helium burning is 102 L . Estimate the lifetime of the helium-core-burning phase. (5 ...
Core-collapse supernovae and their massive progenitors
... established between certain core-collapse supernovae (SNe) and gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), supporting the collapsar model in which the GRB results from the death throes of a rapidly rotating carbon–oxygen (Wolf–Rayet) star. The Initial Mass Function favours the formation of low- and intermediate-mass s ...
... established between certain core-collapse supernovae (SNe) and gamma-ray bursts (GRBs), supporting the collapsar model in which the GRB results from the death throes of a rapidly rotating carbon–oxygen (Wolf–Rayet) star. The Initial Mass Function favours the formation of low- and intermediate-mass s ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... stellar winds or by interactions with the close binary companion. e loss of the hydrogen envelope from the primary means that these stripped core-collapse supernovae tend to show little or no hydrogen, and are therefore classed as Type Ib (containing helium lines) or Type Ic (containing no helium li ...
... stellar winds or by interactions with the close binary companion. e loss of the hydrogen envelope from the primary means that these stripped core-collapse supernovae tend to show little or no hydrogen, and are therefore classed as Type Ib (containing helium lines) or Type Ic (containing no helium li ...
Alpha Centauri 3
... or its orbit will be unstable. If that distance exceeds about one fifth of the closest approach of the other star, then the gravitational pull of that second star can disrupt the orbit of the planet. Recent numerical integrations, however, suggest that stable planetary orbits exist: within three AUs ...
... or its orbit will be unstable. If that distance exceeds about one fifth of the closest approach of the other star, then the gravitational pull of that second star can disrupt the orbit of the planet. Recent numerical integrations, however, suggest that stable planetary orbits exist: within three AUs ...
12 The Milky Way - Journigan-wiki
... range from a few hundred thousand stars to several million per cluster. Their radii usually range form 40 to 160 light-years. Because they are more massive, they pull their stars into a tighter ball. Astronomers estimate that between 150 to 200 globular clusters exist within the Milky Way. ...
... range from a few hundred thousand stars to several million per cluster. Their radii usually range form 40 to 160 light-years. Because they are more massive, they pull their stars into a tighter ball. Astronomers estimate that between 150 to 200 globular clusters exist within the Milky Way. ...
Getting to Know: Structure of the Universe
... Galaxies are huge. Our own Milky Way galaxy is just 100,000 light years across and contains ...
... Galaxies are huge. Our own Milky Way galaxy is just 100,000 light years across and contains ...
The Galaxy–Dark Matter Connection
... Satellites more concentrated than centrals @ fixed stellar mass. However: Fraction of galaxies with C>3 ~ is the same! Ellipticals are not produced by environmental processes acting on satellites ...
... Satellites more concentrated than centrals @ fixed stellar mass. However: Fraction of galaxies with C>3 ~ is the same! Ellipticals are not produced by environmental processes acting on satellites ...
Constituents of the Milky Way
... cloud of gas and dust enriched by those metals can then form a new generation of stars. As a result, a star born more recently has a higher fraction of metals, or a higher metallicity, than a star born long ago. So we can estimate the ages of stars by measuring ...
... cloud of gas and dust enriched by those metals can then form a new generation of stars. As a result, a star born more recently has a higher fraction of metals, or a higher metallicity, than a star born long ago. So we can estimate the ages of stars by measuring ...
Star-Forming Nuclear Rings in Spiral Galaxies
... the vicinity of hot O- or B-type stars. Given that the ionisation energy for the He i line is higher than that of Brg, it requires the presence of hotter and more massive stars, and hence its brightness falls off more rapidly after an instantaneous burst than that of the Brg line. The time range cov ...
... the vicinity of hot O- or B-type stars. Given that the ionisation energy for the He i line is higher than that of Brg, it requires the presence of hotter and more massive stars, and hence its brightness falls off more rapidly after an instantaneous burst than that of the Brg line. The time range cov ...
The Sky
... Mesopotamia over 5,000 years ago. – Other constellations were added by Babylonian, Egyptian, and Greek astronomers during the classical age. – Of these ancient constellations, 48 are still in use. ...
... Mesopotamia over 5,000 years ago. – Other constellations were added by Babylonian, Egyptian, and Greek astronomers during the classical age. – Of these ancient constellations, 48 are still in use. ...
Geoscience Final Review material
... d. All above, except “a”, but including “b” and “c” 130. The shortest wavelengths are a. Red c. Gamma b. Blue d. Radio 131. A light-year is a. The distance light travels in a year c. The time it takes for light to travel b. As far as it is from Earth to Vega d. The distance across our Solar System 1 ...
... d. All above, except “a”, but including “b” and “c” 130. The shortest wavelengths are a. Red c. Gamma b. Blue d. Radio 131. A light-year is a. The distance light travels in a year c. The time it takes for light to travel b. As far as it is from Earth to Vega d. The distance across our Solar System 1 ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.