AST1100 Lecture Notes
... HR-diagrams are often made from stellar clusters, a collection of stars which have been born from the same cloud of gas and which are still gravitationally bound to each other. The advantage with this is that all stars have very similar age. This makes it easier to predict the distribution of the st ...
... HR-diagrams are often made from stellar clusters, a collection of stars which have been born from the same cloud of gas and which are still gravitationally bound to each other. The advantage with this is that all stars have very similar age. This makes it easier to predict the distribution of the st ...
Astrophysics * Glossary - Uplift Summit International
... than needed to produce Olbers's Paradox. Universe is not infinitely old, so light from distant stars would not yet have reached us. The fact that the Universe has a finite age together with reduced light energy from the red shift in the expansion of the universe provides a solution to Olbers’ parado ...
... than needed to produce Olbers's Paradox. Universe is not infinitely old, so light from distant stars would not yet have reached us. The fact that the Universe has a finite age together with reduced light energy from the red shift in the expansion of the universe provides a solution to Olbers’ parado ...
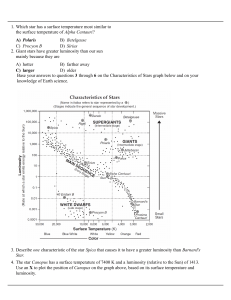
A) Polaris B) Betelgeuse C) Procyon B D) Sirius 1. Which star has a
... 32. Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovian planets in stage 5 have A) larger diameters B) higher densities C) shorter periods of revolution D) longer periods of rotation 33. Approximately how long ago did stage 4 end and stage 5 begin? A) 1 billion years B) 5 billion years C) 20 billion yea ...
... 32. Compared to the terrestrial planets, the Jovian planets in stage 5 have A) larger diameters B) higher densities C) shorter periods of revolution D) longer periods of rotation 33. Approximately how long ago did stage 4 end and stage 5 begin? A) 1 billion years B) 5 billion years C) 20 billion yea ...
Chapter 34: Cosmology FYI 1. Radar Ranging 2. Triangulation idea
... PS 110A-Hatch-Ch. 34 50 Video: spectrum as function of (fast) time ...
... PS 110A-Hatch-Ch. 34 50 Video: spectrum as function of (fast) time ...
The Milky Way Galaxy is Heading for a Major Cosmic Collision
... showing flattened shape – (camera angle zoom-out) Andromeda and M33 heading towards Milky Way – (4 billion years) Direct Milky Way – Andromeda collision ...
... showing flattened shape – (camera angle zoom-out) Andromeda and M33 heading towards Milky Way – (4 billion years) Direct Milky Way – Andromeda collision ...
The Dynamics of the Galaxies in the Local Group
... Similar to Milky Way (shape, size, mass) One of few galaxies that can be seen with naked eye First described by astronomers >1000 years ago ...
... Similar to Milky Way (shape, size, mass) One of few galaxies that can be seen with naked eye First described by astronomers >1000 years ago ...
CPW Science Passage
... Two students discuss the evolution of the Algol system – Algol A, a 3.6-solar-mass MS star; Algol B, a 0.8-solar-mass post-MS star; and Algol C, a 1.7-solar-mass MS star. (One solar mass = the Sun’s mass.) The 3 stars orbit a mutual center of mass, with Algol A and Algol B much closer to each other ...
... Two students discuss the evolution of the Algol system – Algol A, a 3.6-solar-mass MS star; Algol B, a 0.8-solar-mass post-MS star; and Algol C, a 1.7-solar-mass MS star. (One solar mass = the Sun’s mass.) The 3 stars orbit a mutual center of mass, with Algol A and Algol B much closer to each other ...
Summary: Star Formation Near and Far
... shall try to summarize with a few brief and personal comments where I think we have come in the past fifty years in understanding star formation, as illustrated by the many interesting contributions that we have heard at this meeting. The meeting included a remarkable range of topics and scales, fro ...
... shall try to summarize with a few brief and personal comments where I think we have come in the past fifty years in understanding star formation, as illustrated by the many interesting contributions that we have heard at this meeting. The meeting included a remarkable range of topics and scales, fro ...
CURRICULUM COMMITTEE COURSE PROPOSAL FORM
... The discovery of exoplanets is one of the greatest revolutions in modern astronomy. Over eighteen hundred exoplanets have been discovered to date. The universe is teeming with planets - hot Jupiter-like planets skimming the surfaces of their stars, free-floating planets far from any star, super-Eart ...
... The discovery of exoplanets is one of the greatest revolutions in modern astronomy. Over eighteen hundred exoplanets have been discovered to date. The universe is teeming with planets - hot Jupiter-like planets skimming the surfaces of their stars, free-floating planets far from any star, super-Eart ...
Powerpoint Review
... A nebula condensed into a protostar The protostar formed a main sequence star The sun is currently a main sequence star. More specifically the sun is in the middle of its main sequence stage. At some point in the future, the sun will end its main sequence stage and it will begin to swell to form a r ...
... A nebula condensed into a protostar The protostar formed a main sequence star The sun is currently a main sequence star. More specifically the sun is in the middle of its main sequence stage. At some point in the future, the sun will end its main sequence stage and it will begin to swell to form a r ...
Brown et al. 2008 Studying Resolved Stellar
... 2004, 2007). This is the white dwarf cooling age method, whereby the age is derived from modeling the distribution of white dwarfs in the cluster color-magnitude diagram. Figure 7 illustrates the sensitivity of the appearance of the white dwarf cooling sequence to age. The method is less sensitive t ...
... 2004, 2007). This is the white dwarf cooling age method, whereby the age is derived from modeling the distribution of white dwarfs in the cluster color-magnitude diagram. Figure 7 illustrates the sensitivity of the appearance of the white dwarf cooling sequence to age. The method is less sensitive t ...
Unit 1
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
... A star’s location on the HR diagram is given by its temperature (x-axis) and luminosity (y-axis) We see that many stars are located on a diagonal line running from cool, dim stars to hot bright stars ...
b. false - UW Canvas
... good representation of how stars “work,” we would conclude that a. the hotter the star is, the more luminous it is, and the brighter the colors will be overall. b. the cooler the star, the less luminous it is; the brighter part of the spectrum will be toward longer wavelengths. c. the luminosity of ...
... good representation of how stars “work,” we would conclude that a. the hotter the star is, the more luminous it is, and the brighter the colors will be overall. b. the cooler the star, the less luminous it is; the brighter part of the spectrum will be toward longer wavelengths. c. the luminosity of ...
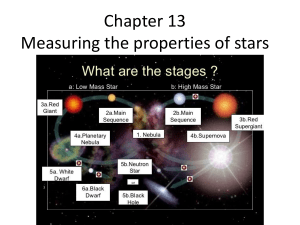
Chapter 13 Measuring the properties of stars
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
... The amount of energy emitted by a star each second is the ____ and is measured in ____. A. Apparent brightness; degrees K B. Temperature; degrees K C. Apparent brightness; Watts D. Luminosity; Watts ...
Tutor Marked Assignment
... (b) What is the Chandrasekhar limit? Discuss the fate of stars whose masses are beyond the Chandrasekhar limit. (c) What causes emission of pulses from a rotating neutron star? ...
... (b) What is the Chandrasekhar limit? Discuss the fate of stars whose masses are beyond the Chandrasekhar limit. (c) What causes emission of pulses from a rotating neutron star? ...
The View From Earth
... 1. Earth: (1) rotates on an axis once every 24 hours; (2) revolves about the Sun with period 365.25 days; (3) accompanies the Sun (and other planets) as it moves relative to other stars in its immediate neighborhood; (4) orbits about the center of the Milky Way galaxy, with period 230 million years; ...
... 1. Earth: (1) rotates on an axis once every 24 hours; (2) revolves about the Sun with period 365.25 days; (3) accompanies the Sun (and other planets) as it moves relative to other stars in its immediate neighborhood; (4) orbits about the center of the Milky Way galaxy, with period 230 million years; ...
Chapter 15 Surveying the Stars
... What are giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs? Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: Those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and ...
... What are giants, supergiants, and white dwarfs? Off the Main Sequence • Stellar properties depend on both mass and age: Those that have finished fusing H to He in their cores are no longer on the main sequence. • All stars become larger and redder after exhausting their core hydrogen: giants and ...
WSN 42 (2016) 132-142
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
... There are seven main spectral type each letter of the alphabet has become known. Each subspectra, which are numbered from 0 to 90. Stars according to their spectral characteristics to be classified. Star from radiation spectrum analysis of the elements that show radiation of different wavelengths, c ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.