The Sky This Month Mar Apr 2015
... Ref. http://www.amsmeteors.org/meteor-showers/meteor-shower-calendar/ Lyrids (April 16 to 25) The Lyrids are a medium strength, narrow maximum meteor shower, peaking before dawn on April 22nd. Derived from debris from comet C/1861 G1 Thatcher, the meteors are medium speed that generally lack persist ...
... Ref. http://www.amsmeteors.org/meteor-showers/meteor-shower-calendar/ Lyrids (April 16 to 25) The Lyrids are a medium strength, narrow maximum meteor shower, peaking before dawn on April 22nd. Derived from debris from comet C/1861 G1 Thatcher, the meteors are medium speed that generally lack persist ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Analysis
... At what line strength do lines become sensitive to microturbulence? Why is it hard to determine abundances from lines on the “flat part” of the curve of growth? ...
... At what line strength do lines become sensitive to microturbulence? Why is it hard to determine abundances from lines on the “flat part” of the curve of growth? ...
Galaxy Evolution
... Fig. 2.—Top: Determination of cluster and group baryon fractions within r500 as a function of M500 (bottom axis) and velocity dispersion (top axis). X-ray gas mass fractions from Vikhlinin et al. (2006; circles) and Gastaldello et al. (2006; triangles) and the stellar mass fractions ( BCG +ICL+galax ...
... Fig. 2.—Top: Determination of cluster and group baryon fractions within r500 as a function of M500 (bottom axis) and velocity dispersion (top axis). X-ray gas mass fractions from Vikhlinin et al. (2006; circles) and Gastaldello et al. (2006; triangles) and the stellar mass fractions ( BCG +ICL+galax ...
ASTR-264-Lecture
... Review: over a period of 10 weeks, Mars appears to stop, back up, then go forward Most advanced geocentric model was that of Ptolemy (100-170), the Ptolemaic Model: Accurate enough to be used for 1500 years Arabic translation of Ptolemy’s work named Almagest (greatest compilation) He does have plane ...
... Review: over a period of 10 weeks, Mars appears to stop, back up, then go forward Most advanced geocentric model was that of Ptolemy (100-170), the Ptolemaic Model: Accurate enough to be used for 1500 years Arabic translation of Ptolemy’s work named Almagest (greatest compilation) He does have plane ...
Writer`s Workshop Series The Art of Science Fiction - Sci Fi
... of the planet with lines of latitude and longitude. When someone specifies a point’s longitude, what they are doing is measuring the angle east or west along the equator between location being specified and a reference. By international agreement, the place that acts as the reference is the Royal Ob ...
... of the planet with lines of latitude and longitude. When someone specifies a point’s longitude, what they are doing is measuring the angle east or west along the equator between location being specified and a reference. By international agreement, the place that acts as the reference is the Royal Ob ...
13.1 Introduction 13.2 The Red Giant Branch
... Table 13.1 gives some representative values for the sizes and luminosities of red giant stars; a main sequence G V star may end up as a high-K or low-M luminosity class III giant. Note that the values in Table 13.1 depend largely on the spectral type, and not on the mass: stars of a wide range of ma ...
... Table 13.1 gives some representative values for the sizes and luminosities of red giant stars; a main sequence G V star may end up as a high-K or low-M luminosity class III giant. Note that the values in Table 13.1 depend largely on the spectral type, and not on the mass: stars of a wide range of ma ...
Document
... H-R diagrams are useful because they help astronomers categorize stars into groups: Main sequence stars, like the Sun, are in a very stable part of their life cycle. White dwarfs are hot and dim and cannot be seen without a telescope. Red giants are cool and bright and some can be seen witho ...
... H-R diagrams are useful because they help astronomers categorize stars into groups: Main sequence stars, like the Sun, are in a very stable part of their life cycle. White dwarfs are hot and dim and cannot be seen without a telescope. Red giants are cool and bright and some can be seen witho ...
ph507lecnote06
... This energy can provide the fuel which allows the endothermic fusion reactions to create very high mass elements such as Uranium. The ...
... This energy can provide the fuel which allows the endothermic fusion reactions to create very high mass elements such as Uranium. The ...
Apr 2016 - Bays Mountain Park
... and has also been the chairperson of the club as well. She also writes an ongoing science column in this very newsletter every month. Her presentation will be on Margaret Geller, a woman in astronomy who has met both success and frustration in her quest to discover the structure of the Universe. Thi ...
... and has also been the chairperson of the club as well. She also writes an ongoing science column in this very newsletter every month. Her presentation will be on Margaret Geller, a woman in astronomy who has met both success and frustration in her quest to discover the structure of the Universe. Thi ...
Properties of Stars - Montana State University Extended University
... In order to better understand how stars are constructed, astronomers look for correlations between stellar properties. The easiest way to do this is make a plot of one intrinsic property vs. another intrinsic property. An intrinsic property is one that does not depend on the distance the star is fro ...
... In order to better understand how stars are constructed, astronomers look for correlations between stellar properties. The easiest way to do this is make a plot of one intrinsic property vs. another intrinsic property. An intrinsic property is one that does not depend on the distance the star is fro ...
stars - Moore Public Schools
... underworld and watched over this realm, as well as, the Osiris, the God of the Underworld. Every year, the Egyptians watched a celestial or sky drama unfold as the their God Horus, the son of Osiris, embarked on his journey to visit his father, crossing the great cosmic river, the Milky Way, and reu ...
... underworld and watched over this realm, as well as, the Osiris, the God of the Underworld. Every year, the Egyptians watched a celestial or sky drama unfold as the their God Horus, the son of Osiris, embarked on his journey to visit his father, crossing the great cosmic river, the Milky Way, and reu ...
plagiarism - things to know - Science Department
... How to use the info without plagiarizing: surface would reach all the way out to Everything has a temperature, and Jupiter. Betelgeuse's color is bright red. everything radiates light, and the two are On the other hand, another supergiant not unconnected. In fact, the hotter a body star, Rigel, with ...
... How to use the info without plagiarizing: surface would reach all the way out to Everything has a temperature, and Jupiter. Betelgeuse's color is bright red. everything radiates light, and the two are On the other hand, another supergiant not unconnected. In fact, the hotter a body star, Rigel, with ...
Beyond the Solar System By Patti Hutchison ANSWER THE
... the galaxies in the universe are spiral galaxies. A spiral galaxy looks like a twirling octopus. In the "arms" of the galaxy, new stars are formed. Some of them are very large. They cause the surrounding clouds of dust to glow brightly, also. Spiral galaxies are beautiful to see. New stars are not f ...
... the galaxies in the universe are spiral galaxies. A spiral galaxy looks like a twirling octopus. In the "arms" of the galaxy, new stars are formed. Some of them are very large. They cause the surrounding clouds of dust to glow brightly, also. Spiral galaxies are beautiful to see. New stars are not f ...
Why Aren`t All Galaxies Barred?
... the mass of the bulge to be much greater than one would guess from its luminosity. As we increase the mass of the bulge component in the computer models, we reduce the growth rate of the bar. Eventually, when the bulge is roughly twice as massive as the entire disk, we find that the bar instability ...
... the mass of the bulge to be much greater than one would guess from its luminosity. As we increase the mass of the bulge component in the computer models, we reduce the growth rate of the bar. Eventually, when the bulge is roughly twice as massive as the entire disk, we find that the bar instability ...
Review: How does a star`s mass determine its life story?
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas ...
... — Use orbital properties of companion — Measure velocity and distance of orbiting gas ...
FROM MOLECULAR CLOUDS TO STARS 1 Star formation and the
... density enhancements in relatively small, cold regions called ”Dense Cores”. Stars form inside these cores and the mass of the dense cores settles the upper limit of the star masses. The masses of the Dense Cores have a lower limit given by the Jeans Mass (see § 3), that depends on the temperature o ...
... density enhancements in relatively small, cold regions called ”Dense Cores”. Stars form inside these cores and the mass of the dense cores settles the upper limit of the star masses. The masses of the Dense Cores have a lower limit given by the Jeans Mass (see § 3), that depends on the temperature o ...
Galaxies Galaxies M81
... The “Discovery” of Galaxies • Beginning of the 20th century, what we now call galaxies were referred to as “spiral nebulae” • Believed to be clouds of gas and stars associated with Milky Way. • In 1924 Edwin Hubble measured distance to the “Great Nebula in Andromeda” (M 31) and found its distance t ...
... The “Discovery” of Galaxies • Beginning of the 20th century, what we now call galaxies were referred to as “spiral nebulae” • Believed to be clouds of gas and stars associated with Milky Way. • In 1924 Edwin Hubble measured distance to the “Great Nebula in Andromeda” (M 31) and found its distance t ...
MySci Unit 23
... A. The Earth, Sun, and Moon are part of a larger system that includes other planets and smaller celestial bodies a. Observe and identify the Earth is one of several planets within a solar system that orbits the Sun b. Observe and identify the Moon orbits the Earth in about a month Identify that plan ...
... A. The Earth, Sun, and Moon are part of a larger system that includes other planets and smaller celestial bodies a. Observe and identify the Earth is one of several planets within a solar system that orbits the Sun b. Observe and identify the Moon orbits the Earth in about a month Identify that plan ...
PH607lec08
... and Ho is essentially an inverse Hubble time. Can define a Hubble length: c / H0 ~ 4000 Mpc at which this expression for the recession velocity extrapolates to the speed of light - more detailed relativistic treatment is needed for distances of this order. Can also define a Hubble time: 1 / H0 ~ 101 ...
... and Ho is essentially an inverse Hubble time. Can define a Hubble length: c / H0 ~ 4000 Mpc at which this expression for the recession velocity extrapolates to the speed of light - more detailed relativistic treatment is needed for distances of this order. Can also define a Hubble time: 1 / H0 ~ 101 ...
Constellation Classification Cards*
... and appears that way in both sets. Use the first number for Albireo when forming the graph. Albireo is a beautiful double star (the stars are close to each other in the sky, but may not be orbiting each other, i.e., not a binary). 7. Students with stars less than 0 on the brightness scale should tak ...
... and appears that way in both sets. Use the first number for Albireo when forming the graph. Albireo is a beautiful double star (the stars are close to each other in the sky, but may not be orbiting each other, i.e., not a binary). 7. Students with stars less than 0 on the brightness scale should tak ...
printer-friendly version of benchmark
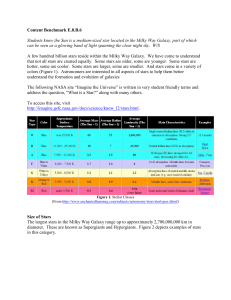
... http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_luminosity.html. Absolute magnitude correlates with the luminosity of a star. Luminosity can be thought of as the quantity of energy released by the star per unit of time, and is proportional both to the temperature of a star and ...
... http://outreach.atnf.csiro.au/education/senior/astrophysics/photometry_luminosity.html. Absolute magnitude correlates with the luminosity of a star. Luminosity can be thought of as the quantity of energy released by the star per unit of time, and is proportional both to the temperature of a star and ...
Magnetic Accretion onto Neutron Stars A crucial difference between
... is flung out by this interaction, as if the field was like a propeller (hence this is called the “propeller effect” or, more generally, a centrifugal barrier). If so, one expects that the mass accretion rate would drop drastically if the propeller phase were entered. Ask class: in what circumstance ...
... is flung out by this interaction, as if the field was like a propeller (hence this is called the “propeller effect” or, more generally, a centrifugal barrier). If so, one expects that the mass accretion rate would drop drastically if the propeller phase were entered. Ask class: in what circumstance ...
Sky Maps Teacher`s Guide - Northern Stars Planetarium
... Galaxies are large group of stars that are gravitationally bound together in space. We are in a galaxy known as the Milky Way. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy containing approximately 200 billion stars with an expanse of 100,000 light years from side to side. Latitude and Longitude locates position ...
... Galaxies are large group of stars that are gravitationally bound together in space. We are in a galaxy known as the Milky Way. The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy containing approximately 200 billion stars with an expanse of 100,000 light years from side to side. Latitude and Longitude locates position ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.