AST1100 Lecture Notes
... do not have the correct energy will pass the atom without being absorbed. For this reason, only radiation at frequency ν with photon energy E = hν corresponding to the difference in the energy level of the atoms in the stellar atmosphere will be absorbed. We will thus have dark lines in the spectra ...
... do not have the correct energy will pass the atom without being absorbed. For this reason, only radiation at frequency ν with photon energy E = hν corresponding to the difference in the energy level of the atoms in the stellar atmosphere will be absorbed. We will thus have dark lines in the spectra ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 40-
... It’s the size of the distances between the stars. And this cloud has stars forming in it. And in the upper right drawing — or picture; it’s actually a photograph — you see an arrow pointing at a couple of very bright stars that have just recently formed in this cloud. Now, here are a couple of color ...
... It’s the size of the distances between the stars. And this cloud has stars forming in it. And in the upper right drawing — or picture; it’s actually a photograph — you see an arrow pointing at a couple of very bright stars that have just recently formed in this cloud. Now, here are a couple of color ...
Booklet 5 – Stellar Processes and Evolution
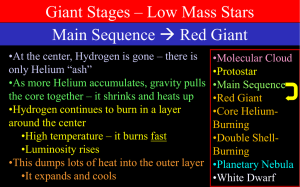
... Initially, they evolve in the same way as low mass stars, turning into red giants and undergoing a core helium burning phase. In medium mass stars, however, the burning of helium into carbon is no longer the end phase of stellar evolution. When the core helium supply is exhausted, the additional mas ...
... Initially, they evolve in the same way as low mass stars, turning into red giants and undergoing a core helium burning phase. In medium mass stars, however, the burning of helium into carbon is no longer the end phase of stellar evolution. When the core helium supply is exhausted, the additional mas ...
Slide 1
... 3C 273 has z=0.15, which corresponds to a distance of about 2 billion light years. We are seeing the object as it looked 2 ...
... 3C 273 has z=0.15, which corresponds to a distance of about 2 billion light years. We are seeing the object as it looked 2 ...
Dec - National Capital Astronomers
... As it turns out, Super Moon is more of an astrological term than astronomical. It was first created and used in 1979 by astrologer Richard Nolle for his article in Dell Publishing’s Horoscope magazine. He used the term to describe a full Moon that “is at or near 90%” of its closest orbital pass of E ...
... As it turns out, Super Moon is more of an astrological term than astronomical. It was first created and used in 1979 by astrologer Richard Nolle for his article in Dell Publishing’s Horoscope magazine. He used the term to describe a full Moon that “is at or near 90%” of its closest orbital pass of E ...
TAP702-0: Red shift - Teaching Advanced Physics
... central disc, showing both red shifts and blue shifts. These show that one side of this gas disc is approaching us whilst the other side is receding. The disc seems to be rotating at a speed of about 550 km s–1. There is no evidence that the whole galaxy is rotating. ...
... central disc, showing both red shifts and blue shifts. These show that one side of this gas disc is approaching us whilst the other side is receding. The disc seems to be rotating at a speed of about 550 km s–1. There is no evidence that the whole galaxy is rotating. ...
HR Diagram Explorer Worksheet
... this equation to explain the results you found in the table of the previous question. Refer to the background material you have previously reviewed. ...
... this equation to explain the results you found in the table of the previous question. Refer to the background material you have previously reviewed. ...
TAP702-0: Red shift - Teaching Advanced Physics
... central disc, showing both red shifts and blue shifts. These show that one side of this gas disc is approaching us whilst the other side is receding. The disc seems to be rotating at a speed of about 550 km s–1. There is no evidence that the whole galaxy is rotating. ...
... central disc, showing both red shifts and blue shifts. These show that one side of this gas disc is approaching us whilst the other side is receding. The disc seems to be rotating at a speed of about 550 km s–1. There is no evidence that the whole galaxy is rotating. ...
Document
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
... • Bright (V ~ 21 at 110 kpc) • Variable stars (P ~ 0.6 day) with distinct light curves ( ~1 mag amplitude) → easily identifiable ...
Giant Stars
... •At 100 million K, three Heliums can join to make carbon plus a little energy 3He C + Energy •With a little higher temperature, they can add one more to make oxygen C + He O + Energy •These processes produce far less energy than hydrogen burning ...
... •At 100 million K, three Heliums can join to make carbon plus a little energy 3He C + Energy •With a little higher temperature, they can add one more to make oxygen C + He O + Energy •These processes produce far less energy than hydrogen burning ...
Visual Measurements of the Multiple Star
... tronomic eyepiece is being used without a Barlow lens 8.1 with a position angle of 210 degrees and a separaand cannot effectively measure dim stars or ones with tion of 0.3 arc seconds (Mason 2009). This separation small separations. The choice of neglected double was just within the Dawes limit for ...
... tronomic eyepiece is being used without a Barlow lens 8.1 with a position angle of 210 degrees and a separaand cannot effectively measure dim stars or ones with tion of 0.3 arc seconds (Mason 2009). This separation small separations. The choice of neglected double was just within the Dawes limit for ...
The Galaxies
... Somehow it drives a repulsive force that acts on all matter. It gets stronger the more space there is between two globs of matter. It is extremely weak on “local” scales (millions of light years), but gets overwhelmingly strong on “cosmological” scales (tens of billions of light ...
... Somehow it drives a repulsive force that acts on all matter. It gets stronger the more space there is between two globs of matter. It is extremely weak on “local” scales (millions of light years), but gets overwhelmingly strong on “cosmological” scales (tens of billions of light ...
z - STScI
... • Star-formation rates • Metallicities/reddening • Kinematics of bound groups/proto Milky Way galaxies ...
... • Star-formation rates • Metallicities/reddening • Kinematics of bound groups/proto Milky Way galaxies ...
Stellar Spectroscopy (GA 3.0) - National Optical Astronomy
... surface of the star, but most of what is known about stars is determined from the many spectral lines seen in their spectrum. A close inspection of a star’s spectrum will reveal many absorption lines, and for some stars, emission lines as well. These spectral lines can be used to determine an incred ...
... surface of the star, but most of what is known about stars is determined from the many spectral lines seen in their spectrum. A close inspection of a star’s spectrum will reveal many absorption lines, and for some stars, emission lines as well. These spectral lines can be used to determine an incred ...
ALMA_BoJun605_Gruppioni
... ALMA factor 10-100 better in resolution ALMA @1.3 mm vs. PdBI sensitivity Continuum factor 100 better (6 µ Jy/beam in 1 hr) Spectral line factor 30 better (1.1 mJy/beam in 10 hr) ...
... ALMA factor 10-100 better in resolution ALMA @1.3 mm vs. PdBI sensitivity Continuum factor 100 better (6 µ Jy/beam in 1 hr) Spectral line factor 30 better (1.1 mJy/beam in 10 hr) ...
Talk - The Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics
... • Difference in magnitudes is “color” – Astronomical definition ...
... • Difference in magnitudes is “color” – Astronomical definition ...
Advanced STARS - WordPress.com
... It is 2 ½ times larger than all the other planets in the solar system combined It has the shortest day of all the planets: 9 hours and 55 minutes It orbits the sun once every 11.8 earth years It’s atmosphere is divided into cloud belts and zones. The Great Red Spot is a huge storm on Jupit ...
... It is 2 ½ times larger than all the other planets in the solar system combined It has the shortest day of all the planets: 9 hours and 55 minutes It orbits the sun once every 11.8 earth years It’s atmosphere is divided into cloud belts and zones. The Great Red Spot is a huge storm on Jupit ...
Stellar population models in the Near-Infrared Meneses
... is needed to fully reproduce the behaviour of the galaxies. The analysis of the DCO index also suggests that a more detailed treatment of the AGB phase, including thermally pulsating AGB stars, is required to fully understand these galaxies. Finally, it is clear that environment plays a role in the ...
... is needed to fully reproduce the behaviour of the galaxies. The analysis of the DCO index also suggests that a more detailed treatment of the AGB phase, including thermally pulsating AGB stars, is required to fully understand these galaxies. Finally, it is clear that environment plays a role in the ...
Dear Leif - LEIF.org
... gained the experience from doing that, they appear to have used interchange arguments to guide subsequent analysis of new systems that are 'close' to those that they had analysed previously and understood. In this regard I acknowledge that Wolff and Patrone on p231 appear to claim that their perturb ...
... gained the experience from doing that, they appear to have used interchange arguments to guide subsequent analysis of new systems that are 'close' to those that they had analysed previously and understood. In this regard I acknowledge that Wolff and Patrone on p231 appear to claim that their perturb ...
Dear Leif - LEIF.org
... gained the experience from doing that, they appear to have used interchange arguments to guide subsequent analysis of new systems that are 'close' to those that they had analysed previously and understood. In this regard I acknowledge that Wolff and Patrone on p231 appear to claim that their perturb ...
... gained the experience from doing that, they appear to have used interchange arguments to guide subsequent analysis of new systems that are 'close' to those that they had analysed previously and understood. In this regard I acknowledge that Wolff and Patrone on p231 appear to claim that their perturb ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.