Lecture 6-1: Schematic Evolution of Stars as seen from the core
... L = 4π R 2 σ Teff4 L ∝ Teffς ...
... L = 4π R 2 σ Teff4 L ∝ Teffς ...
plagiarism - Homeschool
... How to use the info without plagiarizing: surface would reach all the way out to Everything has a temperature, and Jupiter. Betelgeuse's color is bright red. everything radiates light, and the two are On the other hand, another supergiant not unconnected. In fact, the hotter a body star, Rigel, with ...
... How to use the info without plagiarizing: surface would reach all the way out to Everything has a temperature, and Jupiter. Betelgeuse's color is bright red. everything radiates light, and the two are On the other hand, another supergiant not unconnected. In fact, the hotter a body star, Rigel, with ...
2014-2015 SCIENCE Instructional Curriculum Plan Grade: K
... SC.5.E.5.In.1: Identify that a galaxy is made of a very large number of stars and the planets that SC.5.E.5.1 Recognize that a galaxy consists of gas, dust, and many stars, including any objects orbiting the stars. Identify orbit them. our home galaxy as the Milky Way. SC.5.E.5.Su.1: Recognize that ...
... SC.5.E.5.In.1: Identify that a galaxy is made of a very large number of stars and the planets that SC.5.E.5.1 Recognize that a galaxy consists of gas, dust, and many stars, including any objects orbiting the stars. Identify orbit them. our home galaxy as the Milky Way. SC.5.E.5.Su.1: Recognize that ...
What makes stars tick?
... and cool. This time, it’s on the asymptotic giant branch. A star less than 4 M can’t get hot enough to begin carbon fusion. So the star’s layers — including the hydrogen and helium shells — continue to expand. ...
... and cool. This time, it’s on the asymptotic giant branch. A star less than 4 M can’t get hot enough to begin carbon fusion. So the star’s layers — including the hydrogen and helium shells — continue to expand. ...
The Milky Way
... that has been ionized by young, massive, hot stars. Their light is highly red-shifted because especially the star-forming regions are moving away from us at high speed. This is the red color of interstellar dust that is present in the molecular clouds out of which stars are formed. Star forming regi ...
... that has been ionized by young, massive, hot stars. Their light is highly red-shifted because especially the star-forming regions are moving away from us at high speed. This is the red color of interstellar dust that is present in the molecular clouds out of which stars are formed. Star forming regi ...
17_LectureOutline
... These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc ...
... These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc ...
- MNASSA Page
... more than 30 arc minutes. It is a very nice object to study through binoculars. The Magellanic Cloud is home to NGC 2070, also known as Bennett 35, the great looped nebula situated in the south-eastern part of the Cloud and probably one of the most amazing objects in the southern night sky. Known as ...
... more than 30 arc minutes. It is a very nice object to study through binoculars. The Magellanic Cloud is home to NGC 2070, also known as Bennett 35, the great looped nebula situated in the south-eastern part of the Cloud and probably one of the most amazing objects in the southern night sky. Known as ...
Here
... the x-axis of the plot, and some measure of the intrinsic luminosity is plotted on the y-axis. ...
... the x-axis of the plot, and some measure of the intrinsic luminosity is plotted on the y-axis. ...
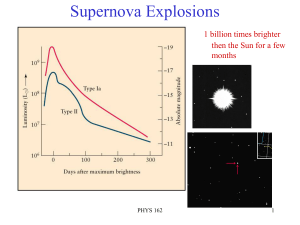
Supernovas 10/19
... Supernova 2014j – Jan 2014 In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. Discovered at undergrad session Univ Coll London (SN1972 e was 11 MLY but pre “modern”) ...
... Supernova 2014j – Jan 2014 In M82 (Ursa Major). Type Ia. Closest of this type observed in modern times. 11.5 million LY away. Discovered at undergrad session Univ Coll London (SN1972 e was 11 MLY but pre “modern”) ...
PDF
... They do not undermine conventional astrology, but to add a lost dimension to it. The Earliest Astrologers and The Sacred, Living Sphere We have grown so used to seeing the planets and the zodiac, alone, as powerful that it can come as a surprise to find that for the early practitioners of astrology, ...
... They do not undermine conventional astrology, but to add a lost dimension to it. The Earliest Astrologers and The Sacred, Living Sphere We have grown so used to seeing the planets and the zodiac, alone, as powerful that it can come as a surprise to find that for the early practitioners of astrology, ...
Unit 13―The “Fixed” Stars
... Easy Calculation: Now that we have a magnitude scale that allows us to classify stars deeper into space, suppose we determine that a new star has a magnitude of 10. Using the above equation, show that this new star has a luminosity of 1/100th of a star with magnitude of 5 as it should. Note that in ...
... Easy Calculation: Now that we have a magnitude scale that allows us to classify stars deeper into space, suppose we determine that a new star has a magnitude of 10. Using the above equation, show that this new star has a luminosity of 1/100th of a star with magnitude of 5 as it should. Note that in ...
Astronomy in 1936 The History of the Universe
... Good news, Professor Hubble! Even though it is 1936, you have been awarded access to the internet (at only $39.95/month, directly chargeable to your VISA card). So you don’t have to waste any more time freezing at telescopes in order to classify galaxies. You can just look at them over the web! Here ...
... Good news, Professor Hubble! Even though it is 1936, you have been awarded access to the internet (at only $39.95/month, directly chargeable to your VISA card). So you don’t have to waste any more time freezing at telescopes in order to classify galaxies. You can just look at them over the web! Here ...
Stages 7 to 9 - Sun
... Off the Main Sequence - The Evolution of a Sun-like Star Stages 7 - 9 While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
... Off the Main Sequence - The Evolution of a Sun-like Star Stages 7 - 9 While on the main sequence, the star is burning hydrogen. It’s luminosity is determined by the stars mass. The most intense fusion is occurring at the center regions of the core (highest pressure and temperature). ...
THE MONTHLY SKY GUIDE, SIXTH EDITION
... magnitude, and so on. The faintest objects that can be detected by telescopes on Earth are about magnitude 25. ...
... magnitude, and so on. The faintest objects that can be detected by telescopes on Earth are about magnitude 25. ...
star pattern identification : application to the precise attitude
... The Auroral Spacecraft is one of the four satellites launched for the Interball project by the Russian Space Agency in cooperation with the international scientific community which are dedicated to magnetospheric research. This spacecraft is subject to the effects of energy exchange between the flex ...
... The Auroral Spacecraft is one of the four satellites launched for the Interball project by the Russian Space Agency in cooperation with the international scientific community which are dedicated to magnetospheric research. This spacecraft is subject to the effects of energy exchange between the flex ...
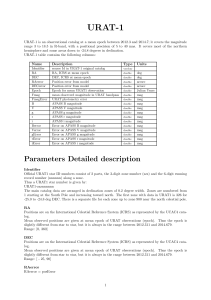
URAT-1 - Gaia Portal
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
... Official URAT1 star ID numbers consist of 2 parts, the 3-digit zone number (zzz) and the 6-digit running record number (nnnnnn) along a zone. Thus a URAT1 star number is given by: URAT1-zzznnnnnn The main catalog data are arranged in declination zones of 0.2 degree width. Zones are numbered from 1 s ...
Planning Observations
... The basic characteristics for the target objects need to be cataloged to correctly calculate signal-to-noise ratios and exposure times. Astronomers no longer need to worry about keeping volumes of data tables around to get this information from as there are many resources online from which to obtain ...
... The basic characteristics for the target objects need to be cataloged to correctly calculate signal-to-noise ratios and exposure times. Astronomers no longer need to worry about keeping volumes of data tables around to get this information from as there are many resources online from which to obtain ...
Feedback - Cambridge University Press
... Inventories of both stars and gas suggest that the most massive clusters contain most if not all of their cosmic abundance of baryons, i.e., fb ≈ fb,cos (Leauthaud et al. 2012, Dai et al. 2010). Lower mass halos appear to have fb < fb,cos , with fb dropping to 0.1 or smaller for halos with Mh < 1011 ...
... Inventories of both stars and gas suggest that the most massive clusters contain most if not all of their cosmic abundance of baryons, i.e., fb ≈ fb,cos (Leauthaud et al. 2012, Dai et al. 2010). Lower mass halos appear to have fb < fb,cos , with fb dropping to 0.1 or smaller for halos with Mh < 1011 ...
Cartwheel Galaxy - Chandra X
... diameter (in light years) of the blue ring of star formation in Arp 147 and compare this to the size of the ring in the Cartwheel Galaxy. Figure 8. HST image of the Arp 147 with the locations of 12 detected X-ray sources marked with circles. ...
... diameter (in light years) of the blue ring of star formation in Arp 147 and compare this to the size of the ring in the Cartwheel Galaxy. Figure 8. HST image of the Arp 147 with the locations of 12 detected X-ray sources marked with circles. ...
VARIOUS MEASUREMENTS OF TIME
... Since the earth rotates on its axis from west to east, all heavenly bodies (i.e. the sun and the fixed stars) appear to revolve from east to west (i.e. in clock-wise direction) around the earth. Such motion of the heavenly bodies is known as apparent motion. We may consider the earth to turn on it a ...
... Since the earth rotates on its axis from west to east, all heavenly bodies (i.e. the sun and the fixed stars) appear to revolve from east to west (i.e. in clock-wise direction) around the earth. Such motion of the heavenly bodies is known as apparent motion. We may consider the earth to turn on it a ...
A Planetary System Around Our Nearest Star is Emerging
... planet is as massive as Earth, only 13% more massive, although too hot for life. This new result opens the possibilit might be other Earth-size planets in the Alpha Centauri system, including some potentially habitable. The Alpha Centauri stellar system consists of three stars about 4.4 light years ...
... planet is as massive as Earth, only 13% more massive, although too hot for life. This new result opens the possibilit might be other Earth-size planets in the Alpha Centauri system, including some potentially habitable. The Alpha Centauri stellar system consists of three stars about 4.4 light years ...
A Global Citizen of the Skies
... Q6: If you were a Viking living in Britain 1000 years ago, how would the stellar constellations you know be compared to today’s constellations? Here we develop an understanding that the UK has never been an isolated community. It demonstrates how even staying in your own country and cultural region, ...
... Q6: If you were a Viking living in Britain 1000 years ago, how would the stellar constellations you know be compared to today’s constellations? Here we develop an understanding that the UK has never been an isolated community. It demonstrates how even staying in your own country and cultural region, ...
Starbursts – from 30 Doradus to Lyman
... range of amplitudes – and redshifts – suggesting a galaxy classification sequence similar to the Hubble tuning fork, but now from M82-like starbursts via ultraluminous infrared galaxies to the recently discovered SCUBA galaxies, as well as from Lyman-break galaxies through luminous compact blue gala ...
... range of amplitudes – and redshifts – suggesting a galaxy classification sequence similar to the Hubble tuning fork, but now from M82-like starbursts via ultraluminous infrared galaxies to the recently discovered SCUBA galaxies, as well as from Lyman-break galaxies through luminous compact blue gala ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.