Lecture 4: Telescopes Web site Stuff from last time Naked eye and magnitudes
... How can you tell if a star is circumpolar from your location? Why do we have time zones? How can you use the stars to get your latitude and longitude? ...
... How can you tell if a star is circumpolar from your location? Why do we have time zones? How can you use the stars to get your latitude and longitude? ...
Homework #2 1. There are two ways to estimate the energy carried
... longer than the gravitational free-fall time of the cloud, tf f ≈ 1/ Ghρi, where hρi is the mean density of the cloud. What happens if tKH < tf f ? b) Estimate the critical radius Rc (in R ) at which tKH ≈ tf f , i.e, at which KH contraction begins, for a given cloud of mass M (in M ). Assume, as ...
... longer than the gravitational free-fall time of the cloud, tf f ≈ 1/ Ghρi, where hρi is the mean density of the cloud. What happens if tKH < tf f ? b) Estimate the critical radius Rc (in R ) at which tKH ≈ tf f , i.e, at which KH contraction begins, for a given cloud of mass M (in M ). Assume, as ...
poster
... The YSOVAR project (Morales-Calderon et al. 2011) monitored about a dozen star forming regions in 3.6 m and 4.5m using the warm mission capabilities of Spitzer. The sampling varies with the region, but most star forming regions were observed 50-100 times, on scales of hours to months. Here, we pre ...
... The YSOVAR project (Morales-Calderon et al. 2011) monitored about a dozen star forming regions in 3.6 m and 4.5m using the warm mission capabilities of Spitzer. The sampling varies with the region, but most star forming regions were observed 50-100 times, on scales of hours to months. Here, we pre ...
Stars and the Milky Way
... line of light that looked like some milk had been spilt. • Stars in our Milky Way can be white, yellow or red. White stars are the hottest and red are the coolest. • It takes light over 100,000 years to travel from one side of the Milky Way to the other. • There is a black hole in the centre of the ...
... line of light that looked like some milk had been spilt. • Stars in our Milky Way can be white, yellow or red. White stars are the hottest and red are the coolest. • It takes light over 100,000 years to travel from one side of the Milky Way to the other. • There is a black hole in the centre of the ...
Curiosities of the Sky
... openings in the sky, for as one continues to gaze it loses its purely metaphysical quality and becomes a kind of entity, like the ocean. The observer is conscious that he can actually see the beginning of its ebon depths, in which the visible universe appears to float like an enchanted island, respl ...
... openings in the sky, for as one continues to gaze it loses its purely metaphysical quality and becomes a kind of entity, like the ocean. The observer is conscious that he can actually see the beginning of its ebon depths, in which the visible universe appears to float like an enchanted island, respl ...
The formation of the galaxy is believed to be similar
... can be divided into 2 phases: a spherical gas cloud (halo) collapsed to form the stars in the Milky Way's spheroid, then rapidly rotating gas collapsed into a disk-shaped configuration of stars. Since disk stars have higher metallicity, which is most likely? Gas ejected from the a) spheroid stars en ...
... can be divided into 2 phases: a spherical gas cloud (halo) collapsed to form the stars in the Milky Way's spheroid, then rapidly rotating gas collapsed into a disk-shaped configuration of stars. Since disk stars have higher metallicity, which is most likely? Gas ejected from the a) spheroid stars en ...
Cepheid
... In Shapley’s day, the LMC and SMC were considered as two isolated offshoots of the Milky Way, different from the spiral nebulae. We now realize that they are ‘dwarf’ galaxies in their own right (but not spirals). ...
... In Shapley’s day, the LMC and SMC were considered as two isolated offshoots of the Milky Way, different from the spiral nebulae. We now realize that they are ‘dwarf’ galaxies in their own right (but not spirals). ...
The University of Sydney Page
... The collapse of the core is stopped by electron degeneracy, which might better be called quantum pressure. Electrons in the core can only have certain energies, and quantum mechanics states that two electrons cannot occupy the same energy level. As the gas becomes very dense, all the available ener ...
... The collapse of the core is stopped by electron degeneracy, which might better be called quantum pressure. Electrons in the core can only have certain energies, and quantum mechanics states that two electrons cannot occupy the same energy level. As the gas becomes very dense, all the available ener ...
129 DYNAMICAL STREAMS IN THE SOLAR NEIGHBOURHOOD B
... stir without heating. In this scenario, the peculiar chemical composition of the Hyades stream (i.e., a metallicity higher than average for field giants) suggests that the group has a common galactocentric origin in the inner Galaxy (where the interstellar medium is more metal-rich than in the solar ...
... stir without heating. In this scenario, the peculiar chemical composition of the Hyades stream (i.e., a metallicity higher than average for field giants) suggests that the group has a common galactocentric origin in the inner Galaxy (where the interstellar medium is more metal-rich than in the solar ...
ppt
... • Every output class needs substantial representation in the training set. • Overlap between classes should be minimized. • Classifier accuracy can be improved with additional information (i.e., flux in different bandpass), but not always! ...
... • Every output class needs substantial representation in the training set. • Overlap between classes should be minimized. • Classifier accuracy can be improved with additional information (i.e., flux in different bandpass), but not always! ...
No Slide Title
... What is the rare astronomical event involving the explosion of the majority of the material in a star, which results in an extremely bright, short-lived object that gives off vast quantities of energy? ...
... What is the rare astronomical event involving the explosion of the majority of the material in a star, which results in an extremely bright, short-lived object that gives off vast quantities of energy? ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 11 Notes: Stellar
... contrast, instability occurs when any small deviation from an equilibrium solution tends to drive the system further and further away from it. The classic example of an unstable system is a pencil standing on its point. If one could get the pencil to balance completely perfectly, it would be in equi ...
... contrast, instability occurs when any small deviation from an equilibrium solution tends to drive the system further and further away from it. The classic example of an unstable system is a pencil standing on its point. If one could get the pencil to balance completely perfectly, it would be in equi ...
UCAC4 is a compiled, all-sky star catalog covering mainly the 8 to
... • 3 = secondary peak found on each side of primary • 4 = case 1 after successful double fit (small separ. blended image) • 5 = case 2 after successful double fit (most likely real double) • 6 = case 3 after successful double fit (brighter secondary picked) Caution: often a dsf= 1 or 2 image is paire ...
... • 3 = secondary peak found on each side of primary • 4 = case 1 after successful double fit (small separ. blended image) • 5 = case 2 after successful double fit (most likely real double) • 6 = case 3 after successful double fit (brighter secondary picked) Caution: often a dsf= 1 or 2 image is paire ...
Black-Body SNR Formulation of Astronomical Camera
... where m is the brightness magnitude assigned to a star observed from Earth, f (·) is the mean spectral flux density at top of Earth’s atmosphere averaged over a defined band and Q(·) is the normalizing constant for that band [8]. We will not go into more details about astronomical magnitude systems ...
... where m is the brightness magnitude assigned to a star observed from Earth, f (·) is the mean spectral flux density at top of Earth’s atmosphere averaged over a defined band and Q(·) is the normalizing constant for that band [8]. We will not go into more details about astronomical magnitude systems ...
Stellar Evolution : The Life and Death of Our Luminous Neighbors
... event horizon - The location around a black hole where the escape velocity equals the speed of light; the surface of a black hole fusion - combination of lower mass nuclides into higher mass nuclides helium flash - The nearly explosive beginning of helium burning in the dense core of a red giant sta ...
... event horizon - The location around a black hole where the escape velocity equals the speed of light; the surface of a black hole fusion - combination of lower mass nuclides into higher mass nuclides helium flash - The nearly explosive beginning of helium burning in the dense core of a red giant sta ...
Conference Summary Richard Ellis (Caltech) ITALIA
... • Masses and colors of z~2-3 red galaxies (Henriques, Conselice) • Evidence of star formation thresholds (Faber) • Timescale of truncation and AGN feedback (Somerville, Faber) • Morphology versus color (red disks) ...
... • Masses and colors of z~2-3 red galaxies (Henriques, Conselice) • Evidence of star formation thresholds (Faber) • Timescale of truncation and AGN feedback (Somerville, Faber) • Morphology versus color (red disks) ...
MHD_of_Accretion_Disks
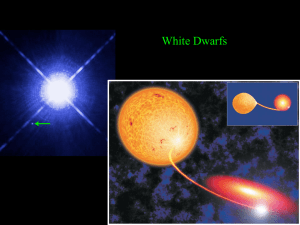
... binary systems. In a binary system, the higher mass star will evolve faster and will eventually become a compact object - either a white dwarf star, a neutron star, or black hole. When the lower mass star later evolves into an expansion phase, it may be so close to the compact star that its outer at ...
... binary systems. In a binary system, the higher mass star will evolve faster and will eventually become a compact object - either a white dwarf star, a neutron star, or black hole. When the lower mass star later evolves into an expansion phase, it may be so close to the compact star that its outer at ...
The Properties of Stars Early in its history, the universe organized
... Some important properties of a star are its mass, size, surface temperature, color, and luminosity. The mass of our sun (one solar mass) is about 2.0 x 1030 kilograms. This constitutes about 99.9% of the mass of the entire solar system. The masses of other stars range from about 60 solar masses to a ...
... Some important properties of a star are its mass, size, surface temperature, color, and luminosity. The mass of our sun (one solar mass) is about 2.0 x 1030 kilograms. This constitutes about 99.9% of the mass of the entire solar system. The masses of other stars range from about 60 solar masses to a ...
PowerPoint
... Most of the stars in a cluster form about the same time. Stars in the Omega Centauri globular cluster are estimated to be about 14 billion years old. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... Most of the stars in a cluster form about the same time. Stars in the Omega Centauri globular cluster are estimated to be about 14 billion years old. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Chapter 25 - Haiku Learning
... he star Proxima Centauri is about 100 million times farther away from Earth than the moon. Yet, besides the sun, it is the closest star to Earth. The universe is incomprehensibly large. What is the nature of this vast universe? Do stars move, or do they remain in one place? Does the universe extend ...
... he star Proxima Centauri is about 100 million times farther away from Earth than the moon. Yet, besides the sun, it is the closest star to Earth. The universe is incomprehensibly large. What is the nature of this vast universe? Do stars move, or do they remain in one place? Does the universe extend ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.