Link again
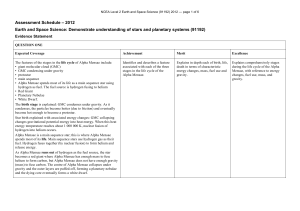
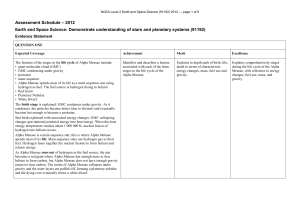
... The second law is that a line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. The third law is that the squares of the sidereal periods of the planets are proportional to the cubes of their semimajor axes. An ellipse is an imperfect circle with a longest diameter call ...
... The second law is that a line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in equal intervals of time. The third law is that the squares of the sidereal periods of the planets are proportional to the cubes of their semimajor axes. An ellipse is an imperfect circle with a longest diameter call ...
Order of Magnitude Icebreaker
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
... ★ Use your physical intuition, not google! ★ Remember: Multiple approaches possible! ...
Life Cycle of a Star Vocabulary
... • The core collapses and results in a giant explosion. © KeslerScience.com ...
... • The core collapses and results in a giant explosion. © KeslerScience.com ...
Planisphere - Geneva 304
... The given sky map is from www.skymaps.com. You can download and print out a single copy of this sky map each month for free. The instructions for use are given on the outside of the circle. To use it, you simply hold the map above your head with the printed NORTH on the circle closest to you and fac ...
... The given sky map is from www.skymaps.com. You can download and print out a single copy of this sky map each month for free. The instructions for use are given on the outside of the circle. To use it, you simply hold the map above your head with the printed NORTH on the circle closest to you and fac ...
Note - Overflow Education
... stars a wealth of information, including its colour or effective temperature can be determined. ...
... stars a wealth of information, including its colour or effective temperature can be determined. ...
Supercomputer simulation provides missing link between turbulence, hypernovae and gamma-ray bursts
... “The breakthrough here is that Philipp’s team starts from a relatively weak magnetic field and shows it building up to be a very strong and large-scale coherent magnetic field of the kind that is usually assumed to be there when people make models of gamma-ray bursts,” Quataert said. Brightest even ...
... “The breakthrough here is that Philipp’s team starts from a relatively weak magnetic field and shows it building up to be a very strong and large-scale coherent magnetic field of the kind that is usually assumed to be there when people make models of gamma-ray bursts,” Quataert said. Brightest even ...
138KB - NZQA
... characteristics, ie star type, size, mass, luminosity and fuel usage and links this to their positions on the HR diagram. ...
... characteristics, ie star type, size, mass, luminosity and fuel usage and links this to their positions on the HR diagram. ...
58KB - NZQA
... characteristics, ie star type, size, mass, luminosity and fuel usage and links this to their positions on the HR diagram. ...
... characteristics, ie star type, size, mass, luminosity and fuel usage and links this to their positions on the HR diagram. ...
Blowin` in the wind: both `negative` and `positive` feedback in an
... radiatively-driven winds are available. We present SINFONI near infrared integral field spectroscopy of XID2028, an obscured, radio-quiet z = 1.59 QSO, in which we clearly resolve a fast (1500 km/s) and extended (up to 13 kpc from the black hole) outflow in the [OIII] lines emitting gas, whose large v ...
... radiatively-driven winds are available. We present SINFONI near infrared integral field spectroscopy of XID2028, an obscured, radio-quiet z = 1.59 QSO, in which we clearly resolve a fast (1500 km/s) and extended (up to 13 kpc from the black hole) outflow in the [OIII] lines emitting gas, whose large v ...
visual photometry - El Camino College
... professional astronomers.) The standard stars that are closest in brightness to the unknown star will determine an upper and lower limits for the unknown’s visual magnitude. In other words, if the unknown is fainter than standard 1, but is brighter than standard 2, the visual magnitude should lie be ...
... professional astronomers.) The standard stars that are closest in brightness to the unknown star will determine an upper and lower limits for the unknown’s visual magnitude. In other words, if the unknown is fainter than standard 1, but is brighter than standard 2, the visual magnitude should lie be ...
Topic 3: The Spectroscope - Danielle`s science9 weebly
... Astronomers refract the light from distant stars to determine what the star is made of. Stars have dark bands in distinct sequences and thicknesses on their spectra. Each element that is present in the star creates its own black-line ‘fingerprint’. The spectra of the star are then compared to known ...
... Astronomers refract the light from distant stars to determine what the star is made of. Stars have dark bands in distinct sequences and thicknesses on their spectra. Each element that is present in the star creates its own black-line ‘fingerprint’. The spectra of the star are then compared to known ...
Activity 1 - Mathematical and Scientific Methods
... Activity 22: Post-Activity Quiz (Got this far on Wednesday.) ...
... Activity 22: Post-Activity Quiz (Got this far on Wednesday.) ...
Visual Photometry - El Camino College
... professional astronomers.) The standard stars that are closest in brightness to the unknown star will determine an upper and lower limits for the unknown’s visual magnitude. In other words, if the unknown is fainter than standard 1, but is brighter than standard 2, the visual magnitude should lie be ...
... professional astronomers.) The standard stars that are closest in brightness to the unknown star will determine an upper and lower limits for the unknown’s visual magnitude. In other words, if the unknown is fainter than standard 1, but is brighter than standard 2, the visual magnitude should lie be ...
Angular Measurement
... • If the Moon were twice as far away, it would appear half as big—15´ across—even though its actual size would be the same. • Thus, angular size by itself is not enough to determine the actual diameter of an object—the distance must also be known. ...
... • If the Moon were twice as far away, it would appear half as big—15´ across—even though its actual size would be the same. • Thus, angular size by itself is not enough to determine the actual diameter of an object—the distance must also be known. ...
Lecture 1
... 1. How many light-years are in 10 parsecs? 2. How many light-years could a human travel in a space craft? 3. Which is larger, a parsec or an AU? 4. Why do you think we have two units, the parsec and the light year, when they are so close to each other? (1 parsec = 3.26 light-years) ...
... 1. How many light-years are in 10 parsecs? 2. How many light-years could a human travel in a space craft? 3. Which is larger, a parsec or an AU? 4. Why do you think we have two units, the parsec and the light year, when they are so close to each other? (1 parsec = 3.26 light-years) ...
Birth of Stars
... Evidence that Planets Form around Other Stars It is very hard to see a planet orbiting another star Planets around other stars may be detected indirectly One way is to look for disks of material from which planets might be condensing A big disk is more visible than a small planet Look for the evolu ...
... Evidence that Planets Form around Other Stars It is very hard to see a planet orbiting another star Planets around other stars may be detected indirectly One way is to look for disks of material from which planets might be condensing A big disk is more visible than a small planet Look for the evolu ...
powerpoints - Georgia Southern University Astrophysics
... • The elements and their relative abundances are different for Type Ia and Type II remnants because the progenitors are different. Type Ia remnants from white dwarfs - usually show relatively strong Si, S, Ar, Ca, and Fe, and weak O, Ne, and Mg lines; Type II remnants - from massive stars generally ...
... • The elements and their relative abundances are different for Type Ia and Type II remnants because the progenitors are different. Type Ia remnants from white dwarfs - usually show relatively strong Si, S, Ar, Ca, and Fe, and weak O, Ne, and Mg lines; Type II remnants - from massive stars generally ...
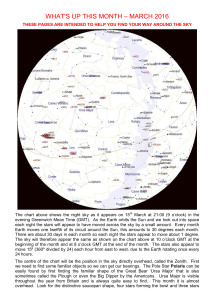
what`s up this month – march 2016
... VENUS is just 25º west of the Sun and will be very close to the eastern horizon as the Sun rises. It will be very difficult to see even though it is very bright at magnitude -3.8. MARS rises over the eastern horizon at about midnight and will be observable until the sky begins to brighten at dawn. I ...
... VENUS is just 25º west of the Sun and will be very close to the eastern horizon as the Sun rises. It will be very difficult to see even though it is very bright at magnitude -3.8. MARS rises over the eastern horizon at about midnight and will be observable until the sky begins to brighten at dawn. I ...
Name - CLC Charter School
... large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can leave behind something more. For this to happen though, the ...
... large transfer of matter and energy, there is a very different kind of star left. This star is called a spinning neutron star. Neutron stars produce radio waves in a steady stream or in random bursts. But if a star is massive enough, it can leave behind something more. For this to happen though, the ...
Exploring the Moon and Stars
... • The Moon is illuminated by sunlight. • The portions of the Moon facing the Earth but not visible during many of the phases are hidden in the Moon’s own shadow. ...
... • The Moon is illuminated by sunlight. • The portions of the Moon facing the Earth but not visible during many of the phases are hidden in the Moon’s own shadow. ...
Andromeda Galaxy www.AssignmentPoint.com The Andromeda
... The Andromeda Galaxy (/ænˈdrɒmɨdə/), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million lightyears) from Earth. It is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and was often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. It received i ...
... The Andromeda Galaxy (/ænˈdrɒmɨdə/), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224, is a spiral galaxy approximately 780 kiloparsecs (2.5 million lightyears) from Earth. It is the nearest major galaxy to the Milky Way and was often referred to as the Great Andromeda Nebula in older texts. It received i ...
Astronomy Report Southern Cross Authors Maria Constanza Pavez
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
... This circumpolar constellation (always situated above the horizon) of the South Hemisphere, is located between the Centauri and the Fly constellations, just above the Polar Antarctic Circle and it is crossed by the Milky Way. The Crux is visible the whole year between 25 N and 90 S degrees of latitu ...
Spectroscopy Lecture 10
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
... – Found Sirius B at Northwestern’s Dearborn Observatory Procyon B found in 1895 at Lick – Was it a star that had cooled and dimmed? Spectrum of 40 Eri B observed – an A star! – It must be hot – Must have small radius to be so faint – The first “w hite dwarf” Adams found Sirius B is also an A star ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.