CP2: KUPKA et al.: Observational signatures of atmospheric velocity
... One of us (FK) has been developing new models of convection based on equations describing local mean values of moments of the distributions of velocity, temperature, density, pressure, etc. These model are reaching the point where it is useful to compare them with velocity fields observed through th ...
... One of us (FK) has been developing new models of convection based on equations describing local mean values of moments of the distributions of velocity, temperature, density, pressure, etc. These model are reaching the point where it is useful to compare them with velocity fields observed through th ...
Astronomy Part 1 Regents Questions
... space slightly larger than the solar system. D) They may contain billions of stars in a space much larger than our solar system. ...
... space slightly larger than the solar system. D) They may contain billions of stars in a space much larger than our solar system. ...
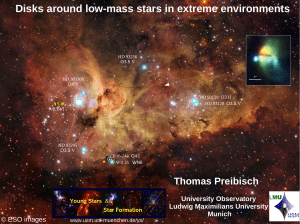
Disks around low-mass stars in extreme environments
... all stars formed at ~ the same time. When the first supernova happens (after > 4 Myr), most low-mass stars have already largely dispersed their disks (i.e. planetesimal formation is already finished). ...
... all stars formed at ~ the same time. When the first supernova happens (after > 4 Myr), most low-mass stars have already largely dispersed their disks (i.e. planetesimal formation is already finished). ...
Astronomy - Dalriada at dalriada.org.uk
... the use of a telescope – which was not invented until the 17th century. 3.2 Constellations Only about 6000 stars are visible by eye unaided, and half of them are below the horizon at any one time. The ancient astronomers only named constellations of bright stars that were familiar to them, so many s ...
... the use of a telescope – which was not invented until the 17th century. 3.2 Constellations Only about 6000 stars are visible by eye unaided, and half of them are below the horizon at any one time. The ancient astronomers only named constellations of bright stars that were familiar to them, so many s ...
Astro 3 Spring, 2004 (Prof
... is called the turnoff point, and is where the main sequence stars are leaving for the red giant branch. If you see what spectral type of stars are leaving, and you know how long they are typically on the main sequence, you can thereby estimate the age o the cluster. Open Clusters are young, loosely ...
... is called the turnoff point, and is where the main sequence stars are leaving for the red giant branch. If you see what spectral type of stars are leaving, and you know how long they are typically on the main sequence, you can thereby estimate the age o the cluster. Open Clusters are young, loosely ...
Measuring Stars
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us The darkened curve is called the main sequence, as this is where most stars are. Also indicated is the white dwarf region; these stars are hot but not very luminous, as they are quite small. ...
ILÍDIO LOPES ()
... The study of magnetic activity in solartype stars is of fundamental importance for stellar structure and evolution. It is ...
... The study of magnetic activity in solartype stars is of fundamental importance for stellar structure and evolution. It is ...
Betelgeuse
... Red supergiant star Right shoulder of Orion constellation derived from the Arabic word bat aldshauzâ, which means “the giant’s shoulder.” or “armpit” 8.5 million yrs old (Sun is 4.6 billion yrs old) 600 light years away 1000 times bigger than the Sun ...
... Red supergiant star Right shoulder of Orion constellation derived from the Arabic word bat aldshauzâ, which means “the giant’s shoulder.” or “armpit” 8.5 million yrs old (Sun is 4.6 billion yrs old) 600 light years away 1000 times bigger than the Sun ...
The Next 2-3 Weeks
... • What is a metric? • The Schwarzschild metric (= non-rotating black hole) • “The orbit of a satellite” (somewhat flakey example) I will present additional material assuming that you have read at least 17.2. ...
... • What is a metric? • The Schwarzschild metric (= non-rotating black hole) • “The orbit of a satellite” (somewhat flakey example) I will present additional material assuming that you have read at least 17.2. ...
April 2011 - Skyscrapers, Inc.
... himself. The light-colored bands and zones in Saturn’s cloud tops are much less prominent than those of Jupiter. (Very little cloud detail can be seen in small telescopes.) However, bright “spots” do develop from time to time. As I write this column at the end of February, a very large bright featur ...
... himself. The light-colored bands and zones in Saturn’s cloud tops are much less prominent than those of Jupiter. (Very little cloud detail can be seen in small telescopes.) However, bright “spots” do develop from time to time. As I write this column at the end of February, a very large bright featur ...
Sample Exam 3
... D) the periods of Cepheid stars are too long to observe in distant galaxies. 24) The Hubble Space Telescope has been used to observe supernova type Ia in distant galaxies, to measure the distance using the brightness law—independent of the velocity redshift distance. The last supernova Ia in the Mil ...
... D) the periods of Cepheid stars are too long to observe in distant galaxies. 24) The Hubble Space Telescope has been used to observe supernova type Ia in distant galaxies, to measure the distance using the brightness law—independent of the velocity redshift distance. The last supernova Ia in the Mil ...
color magnitude diagrams - AST 114, Astronomy Lab II for Spring
... the application of the inverse-square law for nearby stars. If a star is close enough to us we see it move relative to distant stars as we orbit the Sun through Parallax. By measuring how much it appears to move we can estimate the distance to the star. If we know the distance to the star, and we ca ...
... the application of the inverse-square law for nearby stars. If a star is close enough to us we see it move relative to distant stars as we orbit the Sun through Parallax. By measuring how much it appears to move we can estimate the distance to the star. If we know the distance to the star, and we ca ...
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... • In the first year of the period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
... • In the first year of the period Chih-ho, …, a guest star appeared several degrees SE of Thien-kuan. After more than a year it gradually became invisible.−p564. ...
Galactic Star Formation Science with Integral Field
... resolved observations of collimated outflows toward protostars with higher mass than the sun-like T Tauris. • Keck Observatory LGS AO + OSIRIS IFU Observations of the very young Herbig Ae star LkHa 233 • Investigate whether the similarity on large spatial scales between outflows from T Tauri and Her ...
... resolved observations of collimated outflows toward protostars with higher mass than the sun-like T Tauris. • Keck Observatory LGS AO + OSIRIS IFU Observations of the very young Herbig Ae star LkHa 233 • Investigate whether the similarity on large spatial scales between outflows from T Tauri and Her ...
Orbital Instabilities in Triaxial Mass Distributions and
... Simulations of Embedded Clusters • Modified NBODY2(and 6) Codes (S. Aarseth) ...
... Simulations of Embedded Clusters • Modified NBODY2(and 6) Codes (S. Aarseth) ...
Compact stars
... are made up mainly of degenerate matter—typically, carbon and oxygen nuclei in a sea of degenerate electrons. White dwarfs arise from the cores of main-sequence stars and are therefore very hot when they are formed. As they cool they will redden and dim until they eventually become dark black dwarfs ...
... are made up mainly of degenerate matter—typically, carbon and oxygen nuclei in a sea of degenerate electrons. White dwarfs arise from the cores of main-sequence stars and are therefore very hot when they are formed. As they cool they will redden and dim until they eventually become dark black dwarfs ...
ASTRONOMY WEBQUEST…… EXPLORE THE UNIVERSE
... Date February 23, 2012 Answer all of the questions by typing them on this document. Save your work and then attach this document to an e-mail to me. I am Mr. Aguilar, your 8th grade science teacher. 1. If your home is your universe, how would you like your home to be? Would you like your home to be ...
... Date February 23, 2012 Answer all of the questions by typing them on this document. Save your work and then attach this document to an e-mail to me. I am Mr. Aguilar, your 8th grade science teacher. 1. If your home is your universe, how would you like your home to be? Would you like your home to be ...
June - Magic Valley Astronomical Society
... 6/3 Saturn (angular size 18.4", magnitude 0.0) is at opposition at 7:00; Mercury is 0.73° north of the Moon, the Moon is at perigee, subtending 33' 5" from a distance of 361,140 kilometers (224,402 miles), at 10:56 6/4 The Moon is 8.8° south of the bright open cluster M45 (the Pleiades) at 3:00; Jup ...
... 6/3 Saturn (angular size 18.4", magnitude 0.0) is at opposition at 7:00; Mercury is 0.73° north of the Moon, the Moon is at perigee, subtending 33' 5" from a distance of 361,140 kilometers (224,402 miles), at 10:56 6/4 The Moon is 8.8° south of the bright open cluster M45 (the Pleiades) at 3:00; Jup ...
Measuring Stars` Properties - Test 1 Study Guide
... (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation ! same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detail. Other techniques for dist ...
... (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation ! same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detail. Other techniques for dist ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Section 1
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
... from Earth, is caused by the movement of Earth. • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun cause ...
Starry Night Lab
... 10. Set for 9 pm, 10 days in the future. Where is the constellation you found before (higher or lower)? Go to 9 pm, 20 days from now and see where the constellation is now. 11. Summarize what you've just found: (circle the right answer) A given star rises 4 minutes [earlier/later] each night. We cal ...
... 10. Set for 9 pm, 10 days in the future. Where is the constellation you found before (higher or lower)? Go to 9 pm, 20 days from now and see where the constellation is now. 11. Summarize what you've just found: (circle the right answer) A given star rises 4 minutes [earlier/later] each night. We cal ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.