We Are Stardust: Synthesis of the Elements Essential for Life Aparna
... • Thus, a general pattern emerges: when the star exhausts one fuel, it can no longer support itself against gravity, so it contracts until it reaches a core temperature that can ignite the product of the previous fuel. Since this product is a heavier element than the initial fuel, this process requi ...
... • Thus, a general pattern emerges: when the star exhausts one fuel, it can no longer support itself against gravity, so it contracts until it reaches a core temperature that can ignite the product of the previous fuel. Since this product is a heavier element than the initial fuel, this process requi ...
Boy Scout Astronomy Merit Badge Workbook
... b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North St ...
... b. Identify at least eight conspicuous stars, five of which are of magnitude 1 or brighter. c. Make two sketches of the Big Dipper. In one sketch, show the Big Dipper’s orientation in the early evening sky. In another sketch, show its position several hours later. In both sketches, show the North St ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... Text Problems: Answer the following Review Questions from Nick Strobel’s AstronomyNotes: Chapter 3: Astronomy Without a Telescope ...
... Text Problems: Answer the following Review Questions from Nick Strobel’s AstronomyNotes: Chapter 3: Astronomy Without a Telescope ...
Lecture 12: Galaxies View of the Galaxy from within Comparison to
... Spiral Galaxies: Sa, Sb, and Sc Spiral galaxies have a bulge, a disk, spiral arms, and a halo. • Sa galaxies have a bright bulge with tightly wound spiral arms. • Sb galaxies have fainter bulges and more loosely wound spiral arms. • Sc galaxies have faint bulges, and blue, loosely wound spiral ar ...
... Spiral Galaxies: Sa, Sb, and Sc Spiral galaxies have a bulge, a disk, spiral arms, and a halo. • Sa galaxies have a bright bulge with tightly wound spiral arms. • Sb galaxies have fainter bulges and more loosely wound spiral arms. • Sc galaxies have faint bulges, and blue, loosely wound spiral ar ...
SPECTRAL ANALYSIS OF A NEWLY DISCOVERED HgMn STAR
... We detected extreme overabundance of Mn (2.26 dex), Zr (3.30 dex), Y (3.27 dex), and Hg (5.00 dex). We derived also overabundances of Ti (1.20 dex), Cr (0.76 dex), and Ni (0.63 dex). We failed to identify more Hg II lines in the range from 5590 to 5840 Å due to the telluric lines. Telluric lines sho ...
... We detected extreme overabundance of Mn (2.26 dex), Zr (3.30 dex), Y (3.27 dex), and Hg (5.00 dex). We derived also overabundances of Ti (1.20 dex), Cr (0.76 dex), and Ni (0.63 dex). We failed to identify more Hg II lines in the range from 5590 to 5840 Å due to the telluric lines. Telluric lines sho ...
pkt 14 Astrophysics
... O - 30,000 - 60,000 K, ionized H, weak H lines, spectral lines are spread out. O types are rare and gigantic. B -10,000 - 30,000K, H lines are stronger, lines are less spread out (Rigel, Spica are type B stars) A - 7,500 - 10,000K, strong H lines, Mg, Ca lines appear (H and K) (Sirius, Deneb and Veg ...
... O - 30,000 - 60,000 K, ionized H, weak H lines, spectral lines are spread out. O types are rare and gigantic. B -10,000 - 30,000K, H lines are stronger, lines are less spread out (Rigel, Spica are type B stars) A - 7,500 - 10,000K, strong H lines, Mg, Ca lines appear (H and K) (Sirius, Deneb and Veg ...
Canis Majoris
... earth were the size of a golf ball, Canis Majoris would be the height of Mt. Everest. It is estimated that the diameter of Canis Majoris is 1.7 billion miles. As you can see in the picture on the right, the sun is only one pixel when compared to Canis Majoris. The chart on the left compares the size ...
... earth were the size of a golf ball, Canis Majoris would be the height of Mt. Everest. It is estimated that the diameter of Canis Majoris is 1.7 billion miles. As you can see in the picture on the right, the sun is only one pixel when compared to Canis Majoris. The chart on the left compares the size ...
Stellar Evolution
... What happens when a star, fusing hydrogen into helium on the main sequence, exhausts the hydrogen in the core? • hydrogen burning stops, star loses energy • core contracts, and gets hotter • higher temperature allows new nuclear reactions to start that are very slow at the ~15 million K temperature ...
... What happens when a star, fusing hydrogen into helium on the main sequence, exhausts the hydrogen in the core? • hydrogen burning stops, star loses energy • core contracts, and gets hotter • higher temperature allows new nuclear reactions to start that are very slow at the ~15 million K temperature ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... In the core of a main sequence stars core h-burning is happening…that is the fusion of hydrogen into helium through the p-p chain in the core. The main sequence stars are so stable, only very slowly changing their luminosity, radius and temperature while on the main sequence, because of the natural ...
... In the core of a main sequence stars core h-burning is happening…that is the fusion of hydrogen into helium through the p-p chain in the core. The main sequence stars are so stable, only very slowly changing their luminosity, radius and temperature while on the main sequence, because of the natural ...
Nova
... space by the nova. Another Hubble picture taken 467 days after the explosion [left] provided the first glimpse of the ring and a mysterious bar-like structure. But the image interpretation was severely hampered by the telescope's blurred vision ...
... space by the nova. Another Hubble picture taken 467 days after the explosion [left] provided the first glimpse of the ring and a mysterious bar-like structure. But the image interpretation was severely hampered by the telescope's blurred vision ...
Sun, Moon, Earth,
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
No Slide Title
... binary system with unseen companion • high orbital velocity shows companion too massive for neutron star • now confirmed as a 11 (+/- 2) solar mass black hole • predicted to flare again in 2033 ...
... binary system with unseen companion • high orbital velocity shows companion too massive for neutron star • now confirmed as a 11 (+/- 2) solar mass black hole • predicted to flare again in 2033 ...
WORD - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbits ...
... d. everything in the universe that lies above Earth's atmosphere. 02. Which of the following terms would not be associated with astronomy? a. horoscope b. telescope c. astrolabe d. celestial sphere 03. A planet is an object which a. occurs only in our solar system. b. is too faint to see. c. orbits ...
G485 5.5.1 Structure of the Universe
... Way. This black hole is relatively small in size, having a radius of only 6.25 light-hours, but it is massive because of the extraordinary amount of matter it contains, estimated at about 3.7 million solar masses! ...
... Way. This black hole is relatively small in size, having a radius of only 6.25 light-hours, but it is massive because of the extraordinary amount of matter it contains, estimated at about 3.7 million solar masses! ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... Even though the Sun is much larger than the moon the distances are such that they subtend nearly the same angle. ...
... Even though the Sun is much larger than the moon the distances are such that they subtend nearly the same angle. ...
Finish up Sun and begin Stars of the Sun Test 1 Study
... 4.3 light years = 4 x 1013 km (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detai ...
... 4.3 light years = 4 x 1013 km (1 AU = distance Earth to Sun = 8 light minutes) • Close stars use stellar parallax (heliocentric parallax or triangulation same meaning) • Can “easily” measure distance using parallax to a few 100 LY. Need telescope: first observed in 1838. Study close stars in detai ...
Practice Exam for 3 rd Astronomy Exam
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
... OB Association In the Milky Way Galaxy there are very many Giant Molecular Clouds (GMC). A typical GMC contains most hydrogen and helium gas and microscopic solid particles of ice and rocky material known collectively as “dust”. The typical GMC may be 300 ly in diameter and encompass 300,000 solar m ...
Big Bang Theory
... Introduction: Based at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles, Edwin Hubble was the first to observe Cepheid variable stars in many “spiral nebulae.” Using the period-luminosity relationship discovered by Henrietta Swan Leavitt, Hubble estimated the distances to these “nebulae” and determined ...
... Introduction: Based at the Mount Wilson Observatory near Los Angeles, Edwin Hubble was the first to observe Cepheid variable stars in many “spiral nebulae.” Using the period-luminosity relationship discovered by Henrietta Swan Leavitt, Hubble estimated the distances to these “nebulae” and determined ...
Stars and Galaxies - La Salle Elementary Public Schools No 122
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
... • When a star’s hydrogen supply is nearly gone, the star leaves the main sequence and begins the next stage of its life cycle. • All stars form in the same way, but stars die in different ways, depending on their masses. ...
Chapter 10 The Bizarre Stellar Graveyard
... • What would it be like to visit a black hole? – You can orbit a black hole like any other object of the same mass—black holes don’t suck! – Near the event horizon, time slows down and tidal forces are very strong. ...
... • What would it be like to visit a black hole? – You can orbit a black hole like any other object of the same mass—black holes don’t suck! – Near the event horizon, time slows down and tidal forces are very strong. ...
How many stars are in the Milky Way Galaxy?
... Most of the matter in the Galaxy has not yet been identified • According to Kepler’s Third Law, the farther a star is from the center, the slower it should orbit • Observations show that speed actually increases with distance from the center • This could be due to gravity from extra mass we cannot ...
... Most of the matter in the Galaxy has not yet been identified • According to Kepler’s Third Law, the farther a star is from the center, the slower it should orbit • Observations show that speed actually increases with distance from the center • This could be due to gravity from extra mass we cannot ...
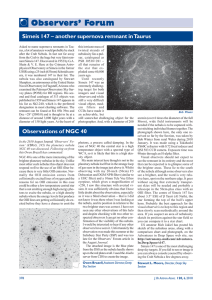
Observers` Forum - British Astronomical Association
... which is impacting on the local medium. At the points of impact the bow shock generates Herbig−Haro (HH) objects as pairs on either side of the star. In the case of PV Cep three major pairs are clearly seen, with other knots of material present. There is circumstantial evidence that PV Cep is moving ...
... which is impacting on the local medium. At the points of impact the bow shock generates Herbig−Haro (HH) objects as pairs on either side of the star. In the case of PV Cep three major pairs are clearly seen, with other knots of material present. There is circumstantial evidence that PV Cep is moving ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.