objects in telescope are farther than they appear
... be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.10 This detection limit means that the apparent star diameters Galileo sees will be smaller than twice the Airy Disk radius (Figure 2). What's more, dimmer stars will appear to have smaller diameters than brighter stars (Figure 3) ...
... be detected, such sky conditions and the sensitivity of the human eye.10 This detection limit means that the apparent star diameters Galileo sees will be smaller than twice the Airy Disk radius (Figure 2). What's more, dimmer stars will appear to have smaller diameters than brighter stars (Figure 3) ...
Lecture 13, PPT version
... Galaxy). All of the stars formed at roughly the same time. Globular clusters have lots of RED stars, but no BLUE stars (because they died long ago and were not “replenished”). ...
... Galaxy). All of the stars formed at roughly the same time. Globular clusters have lots of RED stars, but no BLUE stars (because they died long ago and were not “replenished”). ...
TRANSIT
... you see M44 with the naked eye? It is obvious from a dark site in the moors but I was surprised to be able to just pick it out from my own garden too. If you view M35 with a telescope, see if you can find the little, close-by, open cluster NGC 2158. This cluster is actually similar in physical size ...
... you see M44 with the naked eye? It is obvious from a dark site in the moors but I was surprised to be able to just pick it out from my own garden too. If you view M35 with a telescope, see if you can find the little, close-by, open cluster NGC 2158. This cluster is actually similar in physical size ...
Astronomy 401 Lecture 1 Overview of the Universe 1 Class overview
... point in its interior. Solid angles can also be measured in square degrees: 1 sr = (180/π)2 square degrees. Note: Most astronomers use CGS (centimeter-gram-second) units, instead of the MKS (meter-kilogramsecond) units you are used to from physics classes. We will mostly use MKS units in this class, ...
... point in its interior. Solid angles can also be measured in square degrees: 1 sr = (180/π)2 square degrees. Note: Most astronomers use CGS (centimeter-gram-second) units, instead of the MKS (meter-kilogramsecond) units you are used to from physics classes. We will mostly use MKS units in this class, ...
Powerpoint
... Rotation of the Disk Sun moves at 225 km/sec around center. An orbit takes 240 million years. Stars closer to center take less time to orbit. Stars further from center take longer. => rotation not rigid like a phonograph record or a merry-go-round. Rather, ...
... Rotation of the Disk Sun moves at 225 km/sec around center. An orbit takes 240 million years. Stars closer to center take less time to orbit. Stars further from center take longer. => rotation not rigid like a phonograph record or a merry-go-round. Rather, ...
Chapter 3 Cosmology 3.1 The Doppler effect
... The Andromeda galaxy is the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. Andromeda can just about be seen by the unaided eye on a clear night. By taking photographs of Andromeda using a large telescope, Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness w ...
... The Andromeda galaxy is the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. Andromeda can just about be seen by the unaided eye on a clear night. By taking photographs of Andromeda using a large telescope, Edwin Hubble was able to identify Cepheid variable stars in Andromeda. These stars vary in brightness w ...
chapter 7 review questions
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What is an atom? 4. The process of removing an electron from a stable nucleus is known as ____________. ** ionization GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? 5. In the diagram below, draw the transition that would emit a photon with the smallest wavelength. ...
... GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: What is an atom? 4. The process of removing an electron from a stable nucleus is known as ____________. ** ionization GUIDEPOST CATEGORY: How do atoms interact with light? 5. In the diagram below, draw the transition that would emit a photon with the smallest wavelength. ...
Star Birth
... if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change B. Its mass would increase C. Its internal pressure would increase ...
... if it were not able to radiate away its thermal energy? A. It would continue contracting, but its temperature would not change B. Its mass would increase C. Its internal pressure would increase ...
but restricted to nearby large stars
... If the stress on the tubes reaches a certain limit, they curl up like a rubber band and puncture the sun's surface. Convection is inhibited at the puncture points; the energy flux from the sun's interior decreases; and with it surface temperature. ...
... If the stress on the tubes reaches a certain limit, they curl up like a rubber band and puncture the sun's surface. Convection is inhibited at the puncture points; the energy flux from the sun's interior decreases; and with it surface temperature. ...
Slide 1
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
... •Ellipticals have lots of globular clusters (about twice that of disk galaxies) •these fall into two groups based on color •color determined by metallicity, with more metal-rich GCs (redder) possibly the result of galaxy mergers •Ellipticals have much less cool, atomic gas than spiral galaxies •< 1 ...
L10 - QUB Astrophysics Research Centre
... paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. Hence a process prevents them completing their movement up the AGB, while losing mass at the Reimer’s rate. This is a superwind which removes the envelope ma ...
... paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. Hence a process prevents them completing their movement up the AGB, while losing mass at the Reimer’s rate. This is a superwind which removes the envelope ma ...
4. Massive Stars and HII Regions
... Due to the lower densities H II Regions around established massive stars have sizes in the range 1 – 30 pc (the number of UV photons covers a wide range: B2: 4 · 1044 , T=20000 K; O8.5 2 · 1048 , T=35500 K; O4: 9 · 1049 , T=50000 K). There are however much more compact H II regions observed (We cann ...
... Due to the lower densities H II Regions around established massive stars have sizes in the range 1 – 30 pc (the number of UV photons covers a wide range: B2: 4 · 1044 , T=20000 K; O8.5 2 · 1048 , T=35500 K; O4: 9 · 1049 , T=50000 K). There are however much more compact H II regions observed (We cann ...
Lect15-3-23-11-stars..
... There were some stars in the cluster on the main sequence, and some more massive stars had already begun to move off to the right of the main sequence. However, the least luminous stars in the cluster, the lowest mass stars were mostly located a bit above the main sequence. stars, sequence Now you c ...
... There were some stars in the cluster on the main sequence, and some more massive stars had already begun to move off to the right of the main sequence. However, the least luminous stars in the cluster, the lowest mass stars were mostly located a bit above the main sequence. stars, sequence Now you c ...
MSci Astrophysics 210PHY412 - Queen's University Belfast
... paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. Hence a process prevents them completing their movement up the AGB, while losing mass at the Reimer’s rate. This is a superwind which removes the envelope ma ...
... paucity of very bright stars on the AGB. The latter (Prialnik P. 161) comes from the number of AGB stars expected compared to observed is >10. Hence a process prevents them completing their movement up the AGB, while losing mass at the Reimer’s rate. This is a superwind which removes the envelope ma ...
Modified True/False - Indicate whether the statement is true or false
... ____ 21. HS-ESS1-1 Which of the following stages is the earliest in the development of a star? a. Nebula c. Neutron star b. Protostar d. Giant ____ 22. HS-ESS1-1 All stars, including the Sun, have the following identical composition: a. 73 percent hydrogen; 25 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen b. ...
... ____ 21. HS-ESS1-1 Which of the following stages is the earliest in the development of a star? a. Nebula c. Neutron star b. Protostar d. Giant ____ 22. HS-ESS1-1 All stars, including the Sun, have the following identical composition: a. 73 percent hydrogen; 25 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen b. ...
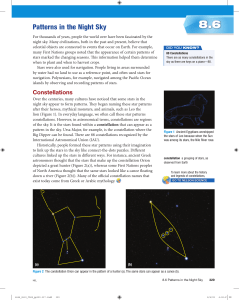
Patterns in the Night Sky
... events that held significant spiritual meaning. On the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, the ancient Mayans built a giant pyramid, El Castillo, that is aligned to the Sun’s movement in the sky. At sunset on the spring and fall equinoxes, a corner of the structure casts a shadow that resembles a plumed sn ...
... events that held significant spiritual meaning. On the Yucatán Peninsula of Mexico, the ancient Mayans built a giant pyramid, El Castillo, that is aligned to the Sun’s movement in the sky. At sunset on the spring and fall equinoxes, a corner of the structure casts a shadow that resembles a plumed sn ...
Surveying the Stars
... Direct mass measurements are possible only for stars in binary star systems. ...
... Direct mass measurements are possible only for stars in binary star systems. ...
Lecture 1 Coordinate Systems - Department of Physics & Astronomy
... Measured through filter centered at 365nm and effective bandwidth of 68nm. – B,the star’s blue magnitude. Measured through filter centered at 440nm and ...
... Measured through filter centered at 365nm and effective bandwidth of 68nm. – B,the star’s blue magnitude. Measured through filter centered at 440nm and ...
The Birth, Life, and Death of Stars
... Born in Ulm, Germany in 1879 and died in Princeton in 1955 Questions the basic tenets of Quantum Mechanics: God does not play dice with the Universe ... Yet, is awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics: ... for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect 1905 Einstein’s Miracle Year while wo ...
... Born in Ulm, Germany in 1879 and died in Princeton in 1955 Questions the basic tenets of Quantum Mechanics: God does not play dice with the Universe ... Yet, is awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics: ... for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect 1905 Einstein’s Miracle Year while wo ...
powerpoint file
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
... The surface gravity is so high that a 150 pound person would weigh a million tons. You would be squeezed flatter than a piece of paper. The fastest pulsar known has a period of 0.0014 s. The star spins 642 times per second. Dozens of such “millisecond pulsars” are known. More are being discovered. I ...
Nebular theory
... The Nebular Theory – How did our Solar System form? Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at lea ...
... The Nebular Theory – How did our Solar System form? Our theory about how the solar system formed is called the nebular theory. This activity will help you understand how we think the solar system formed. 1. Write your observations from the video that shows how the planets orbit the sun. Write at lea ...
Perseus (constellation)

Perseus, named after the Greek mythological hero Perseus, is a constellation in the northern sky. It was one of 48 listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy and among the 88 modern constellations defined by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). It is located in the northern celestial hemisphere near several other constellations named after legends surrounding Perseus, including Andromeda to the west and Cassiopeia to the north. Perseus is also bordered by Aries and Taurus to the south, Auriga to the east, Camelopardalis to the north, and Triangulum to the west.The galactic plane of the Milky Way passes through Perseus but is mostly obscured by molecular clouds. The constellation's brightest star is the yellow-white supergiant Alpha Persei (also called Mirfak), which shines at magnitude 1.79. It and many of the surrounding stars are members of an open cluster known as the Alpha Persei Cluster. The best-known star, however, is Algol (Beta Persei), linked with ominous legends because of its variability, which is noticeable to the naked eye. Rather than being an intrinsically variable star, it is an eclipsing binary. Other notable star systems in Perseus include X Persei, a binary system containing a neutron star, and GK Persei, a nova that peaked at magnitude 0.2 in 1901. The Double Cluster, comprising two open clusters quite near each other in the sky, was known to the ancient Chinese. The constellation gives its name to the Perseus Cluster (Abell 426), a massive galaxy cluster located 250 million light-years from Earth. It hosts the radiant of the annual Perseids meteor shower—one of the most prominent meteor showers in the sky.