Chapter 13: Interstellar Matter and Star Formation
... (b) Interstellar gas causes absorption lines in stellar spectra. These lines can be distinguished from absorption lines of a stellar atmosphere in three ways. (i) Absorption lines due to interstellar gas tend to be narrower than those produced by a star’s atmosphere. (ii) Lines caused by a stellar a ...
... (b) Interstellar gas causes absorption lines in stellar spectra. These lines can be distinguished from absorption lines of a stellar atmosphere in three ways. (i) Absorption lines due to interstellar gas tend to be narrower than those produced by a star’s atmosphere. (ii) Lines caused by a stellar a ...
Finding North without a Compass
... If a needle and a silk cloth are available, you can stroke the needle repeatedly towards the same direction to make it magnetized. If a magnet is available, then that is even better. The magnetized needle can then be suspended on a line to freely align itself to the NorthSouth line. It can also be p ...
... If a needle and a silk cloth are available, you can stroke the needle repeatedly towards the same direction to make it magnetized. If a magnet is available, then that is even better. The magnetized needle can then be suspended on a line to freely align itself to the NorthSouth line. It can also be p ...
astro 001 - courses.psu.edu
... 23. In 5000 years (in the year 7002, to be precise), the star Polaris will be just as close to the north celestial pole as it is today. a) True b) False ...
... 23. In 5000 years (in the year 7002, to be precise), the star Polaris will be just as close to the north celestial pole as it is today. a) True b) False ...
Accretion Disk
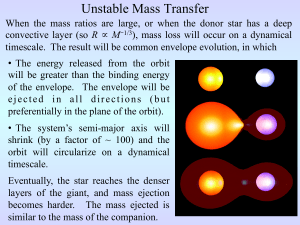
... still be two stars: a low mass star still burning hydrogen, and a helium proto-white dwarf. The separation will be very small, and the hot core will ionize the ejected envelope, producing a planetary nebula. ...
... still be two stars: a low mass star still burning hydrogen, and a helium proto-white dwarf. The separation will be very small, and the hot core will ionize the ejected envelope, producing a planetary nebula. ...
Educator`s Guide for Dark Star Adventure
... Distances in space are so vast that ‘miles’ are too small. To measure such vast distances we have to use bigger ‘rulers.’ One way astronomers have found to measure the enormous distances in space is to use “light speed” to describe them. Here’s an example: our own Sun is 93,000,000 miles away. Since ...
... Distances in space are so vast that ‘miles’ are too small. To measure such vast distances we have to use bigger ‘rulers.’ One way astronomers have found to measure the enormous distances in space is to use “light speed” to describe them. Here’s an example: our own Sun is 93,000,000 miles away. Since ...
Powerpoint
... the increased density triggers star formation. This may contribute to propagation of the arms. The origin of the spiral arms is not yet understood. ...
... the increased density triggers star formation. This may contribute to propagation of the arms. The origin of the spiral arms is not yet understood. ...
1.2.43The stellar populations of the Milky Way
... stars, which is consistent with star formation in the spheroid ceasing long ago. Because this population is so old, only low-mass stars (which have long lifetimes) still shine as main sequence stars burning hydrogen in their cores. The more massive stars that formed at the same time as the surviving ...
... stars, which is consistent with star formation in the spheroid ceasing long ago. Because this population is so old, only low-mass stars (which have long lifetimes) still shine as main sequence stars burning hydrogen in their cores. The more massive stars that formed at the same time as the surviving ...
OCR Physics A Refer to the Physics A datasheet for data, formulae
... b The table below gives the velocity and distance of five galaxies observed in different constellations. Galaxy in constellation of ...
... b The table below gives the velocity and distance of five galaxies observed in different constellations. Galaxy in constellation of ...
Targets and their Environments - Pathways Towards Habitable Planets
... High-[Fe/H] stars more likely to host Jupiter-like planets ...
... High-[Fe/H] stars more likely to host Jupiter-like planets ...
10 Stellar Evolution - Journigan-wiki
... Nothing made of matter can survive the trip across the black hole’s event horizon and through. In general relativity, it is a general term for a boundary in space-time, defined with respect to an observer, beyond which events cannot affect the observer. Light emitted beyond the horizon can never rea ...
... Nothing made of matter can survive the trip across the black hole’s event horizon and through. In general relativity, it is a general term for a boundary in space-time, defined with respect to an observer, beyond which events cannot affect the observer. Light emitted beyond the horizon can never rea ...
chapter16StarBirth
... Fusion and Contraction • Fusion will not begin in a contracting cloud if some sort of force stops contraction before the core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its ...
... Fusion and Contraction • Fusion will not begin in a contracting cloud if some sort of force stops contraction before the core temperature rises above 107 K. • Thermal pressure cannot stop contraction because the star is constantly losing thermal energy from its ...
Rotation
... the star. E.g., CN processing, s-process, He, etc. 2) Structurally, the helium and heavy element core – once its mass has been determined is insensitive to the presence of the envelope. If the entire envelope is lost however, the star enters a phase of rapid Wolf-Rayet mass loss that does greatly af ...
... the star. E.g., CN processing, s-process, He, etc. 2) Structurally, the helium and heavy element core – once its mass has been determined is insensitive to the presence of the envelope. If the entire envelope is lost however, the star enters a phase of rapid Wolf-Rayet mass loss that does greatly af ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.