The Planetarium Fleischmann Planetarium
... mere infant compared to our own 4.5-billionyear-old Sun. It resides 25 light-years away from the Sun. Located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus (the Southern Fish), the Fomalhaut ring is ten times as old as debris disks seen previously around the stars AU Microscopii and Beta Pictoris, where pla ...
... mere infant compared to our own 4.5-billionyear-old Sun. It resides 25 light-years away from the Sun. Located in the constellation Piscis Austrinus (the Southern Fish), the Fomalhaut ring is ten times as old as debris disks seen previously around the stars AU Microscopii and Beta Pictoris, where pla ...
NAM_f2
... sweeps over almost the entire sky in a single orbit. The imaging system has a cadence of four seconds but for a given star we combine the images from a single orbit to produce a system with an effective exposure time of 16 to 20 seconds and a cadence of 100 minutes. ...
... sweeps over almost the entire sky in a single orbit. The imaging system has a cadence of four seconds but for a given star we combine the images from a single orbit to produce a system with an effective exposure time of 16 to 20 seconds and a cadence of 100 minutes. ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 1 Notes: Observing Stars
... extended mnemonic Oh Be A Fine Girl/guy, Kiss Me Like That, which proves one thing – astronomers have way too much time on their hands. There has been a theoretical proposal that a new type of spectral class should appear for objects even dimmer than T dwarfs, although no examples of such an object ...
... extended mnemonic Oh Be A Fine Girl/guy, Kiss Me Like That, which proves one thing – astronomers have way too much time on their hands. There has been a theoretical proposal that a new type of spectral class should appear for objects even dimmer than T dwarfs, although no examples of such an object ...
Are We Alone in the Universe?
... ✤ Now we know of nearly 2,000! Some estimates put the number of Earth-like planets in habitable zones at 20% of all stars! ✤ 400 billion stars in the Milky Way x 20% = 80 billion potentially habitable planets! Statistically, the answer is: There have to be other life forms out there ...
... ✤ Now we know of nearly 2,000! Some estimates put the number of Earth-like planets in habitable zones at 20% of all stars! ✤ 400 billion stars in the Milky Way x 20% = 80 billion potentially habitable planets! Statistically, the answer is: There have to be other life forms out there ...
L2 Star formation Part I
... -what we observe is the PMF (present MF): high mass stars disappear very quickly. ...
... -what we observe is the PMF (present MF): high mass stars disappear very quickly. ...
Constellation Classification Cards*
... numbers, e.g., Thuban = 3.65, are the dimmest stars. For Set B, there are six cards with three numbers. Stars with three numbers and a slash, e.g., Mintaka = 2.23 (3.2/3.3), are binary stars. Use the first number given for the combined brightness of the two stars when forming the graph. Stars with t ...
... numbers, e.g., Thuban = 3.65, are the dimmest stars. For Set B, there are six cards with three numbers. Stars with three numbers and a slash, e.g., Mintaka = 2.23 (3.2/3.3), are binary stars. Use the first number given for the combined brightness of the two stars when forming the graph. Stars with t ...
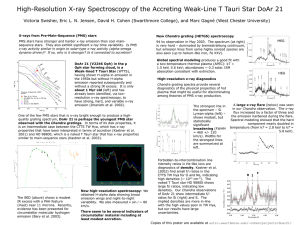
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... PMS stars have stronger and harder x-ray emission than cool mainsequence stars. They also exhibit significant x-ray time variability. Is PMS x-ray activity similar in origin to solar-type x-ray activity (alpha-omega dynamo driven)? If so, why is it stronger? Is it connected to accretion? ...
... PMS stars have stronger and harder x-ray emission than cool mainsequence stars. They also exhibit significant x-ray time variability. Is PMS x-ray activity similar in origin to solar-type x-ray activity (alpha-omega dynamo driven)? If so, why is it stronger? Is it connected to accretion? ...
Lecture 11
... • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? – Hot gas in accretion disks can emit X-rays – The accretion disk can dump material which may become hot and dense enough to under nuclear fusion. • What is a white dwarf supernova – White dwarf accretes gas from companion until it ex ...
... • What can happen to a white dwarf in a close binary system? – Hot gas in accretion disks can emit X-rays – The accretion disk can dump material which may become hot and dense enough to under nuclear fusion. • What is a white dwarf supernova – White dwarf accretes gas from companion until it ex ...
The Celestial Sphere
... The ancients thought the stars were stuck in a sphere half of which could be seen as a dome overhead at any given time This they called the celestial sphere. The celestial sphere does not actually exist But it is still a useful way to think about the sky. ...
... The ancients thought the stars were stuck in a sphere half of which could be seen as a dome overhead at any given time This they called the celestial sphere. The celestial sphere does not actually exist But it is still a useful way to think about the sky. ...
Extra-Solar Planets
... If one observed the Sun from a distance of 10 pc, it’s the size of its wobble on the sky (due mostly to Jupiter and Saturn) would be less than 0.002. In comparison, because of blurring by the atmosphere, stars have sizes of about 1 on the sky. It is very difficult to measure such small wobbles fro ...
... If one observed the Sun from a distance of 10 pc, it’s the size of its wobble on the sky (due mostly to Jupiter and Saturn) would be less than 0.002. In comparison, because of blurring by the atmosphere, stars have sizes of about 1 on the sky. It is very difficult to measure such small wobbles fro ...
Abundance of Elements
... I. Derive the stellar parameters of M dwarfs using the synthetic spectra in the long wavelength region of the optical spectra (over 8000 Å), which is relatively less contaminated by molecular lines as well as telluric lines. Test the synthetic spectrum for K2 III type star : HD 110014 ...
... I. Derive the stellar parameters of M dwarfs using the synthetic spectra in the long wavelength region of the optical spectra (over 8000 Å), which is relatively less contaminated by molecular lines as well as telluric lines. Test the synthetic spectrum for K2 III type star : HD 110014 ...
Astronomy Lecture 3b
... D.subduction of hydrogen into the Sun's surface E.rising plumes of dark, hot material ___ 16. The atmosphere of ? is mostly molecular nitrogen; it may have a liquid nitrogen, ethane and methane ocean up to a depth of one kilometer, beneath which may be a layer of acetylene. A.Iapetus B.Triton C.Mir ...
... D.subduction of hydrogen into the Sun's surface E.rising plumes of dark, hot material ___ 16. The atmosphere of ? is mostly molecular nitrogen; it may have a liquid nitrogen, ethane and methane ocean up to a depth of one kilometer, beneath which may be a layer of acetylene. A.Iapetus B.Triton C.Mir ...
Astronomy - SparkNotes
... 2. Pick an interval of time (e.g., a month). In that amount of time, the line connecting a planet to the Sun will sweep over the same area, regardless of where it is on its elliptical orbit. • Implication: Planets move faster when they are closer to the sun (see Figure 2). ...
... 2. Pick an interval of time (e.g., a month). In that amount of time, the line connecting a planet to the Sun will sweep over the same area, regardless of where it is on its elliptical orbit. • Implication: Planets move faster when they are closer to the sun (see Figure 2). ...
Chapter 17 Star Stuff
... • Changes in brightness or temperature show up on the H-R Diagram • Dying stars form their own branch away from the main sequence line ...
... • Changes in brightness or temperature show up on the H-R Diagram • Dying stars form their own branch away from the main sequence line ...
Neil F. Comins - Kuwait Life Sciences Company
... PREFACE away. View 2,500,000 stars along with more than 170 deep-space objects such as galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. Travel 15,000 years in time, check out the view from the International Space Station, and see planets up close from any one of their moons. Included are stunning OpenGL graph ...
... PREFACE away. View 2,500,000 stars along with more than 170 deep-space objects such as galaxies, star clusters, and nebulae. Travel 15,000 years in time, check out the view from the International Space Station, and see planets up close from any one of their moons. Included are stunning OpenGL graph ...
SGHS Faulkes ASISTM Star Cluster Photometry
... magnitude for the image or fainter. In the magnitude scale the closer to 0 the number is the brighter the star is. So most or all of the stars should be a fainter than the reference star so their magnitudes should be larger positive numbers (the magnitude scale is shown on the scale below). ...
... magnitude for the image or fainter. In the magnitude scale the closer to 0 the number is the brighter the star is. So most or all of the stars should be a fainter than the reference star so their magnitudes should be larger positive numbers (the magnitude scale is shown on the scale below). ...
a MS Word version.
... star points usually seen on an HR Diagram. How do we know that sequences listed as "giant..." are plotting actual giant stars? Same question for "dwarf..."? ...
... star points usually seen on an HR Diagram. How do we know that sequences listed as "giant..." are plotting actual giant stars? Same question for "dwarf..."? ...
Ursa Minor

Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.