Lab 7
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
... Introduction: By looking at an apparently flat background of stars at night or at a star chart printed on a page, we often forget about the three-dimensional nature of the universe. In this exercise, you will construct (with welding rods and Styrofoam balls) a model of nearby space including many of ...
Chapter 20
... arms—because a wave of compression passes by. Still another possibility is that a nearby star explodes (a “supernova”; see Chapter 13), sending out a shock wave that compresses the gas and dust. ...
... arms—because a wave of compression passes by. Still another possibility is that a nearby star explodes (a “supernova”; see Chapter 13), sending out a shock wave that compresses the gas and dust. ...
Word doc - UC-HiPACC - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Observatory Global Telescope Network and adjunct assistant professor at UC Santa Barbara. In 2006 and 2007, two objects caught by the detectors of the Supernova Legacy Survey looked like supernovae—stars exploding in cataclysmic stellar suicide—but did not act like familiar supernovae. Instead of br ...
... Observatory Global Telescope Network and adjunct assistant professor at UC Santa Barbara. In 2006 and 2007, two objects caught by the detectors of the Supernova Legacy Survey looked like supernovae—stars exploding in cataclysmic stellar suicide—but did not act like familiar supernovae. Instead of br ...
Integrative Studies 410 Our Place in the Universe
... • there are ~ 100 billion galaxies in the observable Universe • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
... • there are ~ 100 billion galaxies in the observable Universe • measure distances to other galaxies using the periodluminosity relationship for Cepheid variables • Type I supernovae also used to measure distances – Predictable luminosity – a standard candle ...
Second Semester Study Guide
... 25. What conclusion can be drawn from the fact that some planets with solid surfaces and satellites have impact craters? A. Collisions between Solar System bodies and planetesimals were common at one time. B. The young planets had softer surfaces. C. Volcanoes were very active in the early stages of ...
... 25. What conclusion can be drawn from the fact that some planets with solid surfaces and satellites have impact craters? A. Collisions between Solar System bodies and planetesimals were common at one time. B. The young planets had softer surfaces. C. Volcanoes were very active in the early stages of ...
Starfarer
... steer towards whichever star rises or sets in the direction of the island destination. The bearing of the destination is the azimuth or bearing of its guiding star, at rise if the course is an easterly one and at set if it is westerly. Although stars rise 4 minutes earlier each night, so that after ...
... steer towards whichever star rises or sets in the direction of the island destination. The bearing of the destination is the azimuth or bearing of its guiding star, at rise if the course is an easterly one and at set if it is westerly. Although stars rise 4 minutes earlier each night, so that after ...
1. The catalogue structure
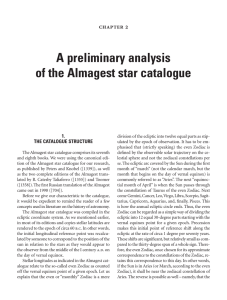
... We have partially processed this enormous body of material. First of all, it is very useful to indicate the location of the constellations mentioned in Ptolemy’s star catalogue geometrically. Let us use a modern map that specifies constellation boundaries for this end. In fig. 2.1. these boundaries ...
... We have partially processed this enormous body of material. First of all, it is very useful to indicate the location of the constellations mentioned in Ptolemy’s star catalogue geometrically. Let us use a modern map that specifies constellation boundaries for this end. In fig. 2.1. these boundaries ...
Skinner Chapter 3
... 42. The Sun's three outermost layers are called the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The photosphere is an intensely turbulent zone, which emits the light that reaches the Earth. The chromosphere and corona are both low-density, transparent layers of very hot gas; they are observable o ...
... 42. The Sun's three outermost layers are called the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. The photosphere is an intensely turbulent zone, which emits the light that reaches the Earth. The chromosphere and corona are both low-density, transparent layers of very hot gas; they are observable o ...
Presentation
... have such alignment, and the fraction decreases for planets with larger orbits. For a planet orbiting a sun-sized star at 1AU, the probability of a random alignment producing a transit is ...
... have such alignment, and the fraction decreases for planets with larger orbits. For a planet orbiting a sun-sized star at 1AU, the probability of a random alignment producing a transit is ...
stellar spectra instructor notes
... A major accomplishment in subsequent years was the classification of all stars brighter than ~10th magnitude photographic by Annie Jump Cannon from objective prism plates taken at observatories operated by the Harvard College Observatory. The resulting Henry Draper Catalogue and Extension (HD and HD ...
... A major accomplishment in subsequent years was the classification of all stars brighter than ~10th magnitude photographic by Annie Jump Cannon from objective prism plates taken at observatories operated by the Harvard College Observatory. The resulting Henry Draper Catalogue and Extension (HD and HD ...
galaxy.
... • The zone of avoidance must be an artifact of something in our galaxyperhaps dust extinction- blocking our view of galaxies in the Milky Way. • S Andromeda was not a normal nova. It was something else, something much brighter. • Slipher’s observations of several spiral nebulae showed that they had ...
... • The zone of avoidance must be an artifact of something in our galaxyperhaps dust extinction- blocking our view of galaxies in the Milky Way. • S Andromeda was not a normal nova. It was something else, something much brighter. • Slipher’s observations of several spiral nebulae showed that they had ...
Ursa Minor

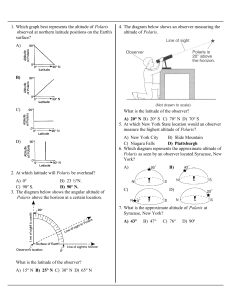
Ursa Minor (Latin: ""Smaller She-Bear"", contrasting with Ursa Major), also known as the Little Bear, is a constellation in the northern sky. Like the Great Bear, the tail of the Little Bear may also be seen as the handle of a ladle, hence the name Little Dipper. It was one of the 48 constellations listed by the 2nd-century astronomer Ptolemy, and remains one of the 88 modern constellations. Ursa Minor has traditionally been important for navigation, particularly by mariners, due to Polaris being the North Star.Polaris, the brightest star in the constellation, is a yellow-white supergiant and the brightest Cepheid variable star in the night sky, ranging from apparent magnitude 1.97 to 2.00. Beta Ursae Minoris, also known as Kochab, is an aging star that has swollen and cooled to become an orange giant with an apparent magnitude of 2.08, only slightly fainter than Polaris. Kochab and magnitude 3 Gamma Ursae Minoris have been called the ""guardians of the pole star"". Planets have been detected orbiting four of the stars, including Kochab. The constellation also contains an isolated neutron star—Calvera—and H1504+65, the hottest white dwarf yet discovered with a surface temperature of 200,000 K.