Sleep Mar 19 2013x - Lakehead University
... The pontine nucleus, via the thalamus, activate different areas of the cortex, elicit images/emotions, and the cortex attempts to synthesize the disparate images into a coherent whole • This process can account for the often bizarre and nonsensical nature of many dreams; since they are triggered by ...
... The pontine nucleus, via the thalamus, activate different areas of the cortex, elicit images/emotions, and the cortex attempts to synthesize the disparate images into a coherent whole • This process can account for the often bizarre and nonsensical nature of many dreams; since they are triggered by ...
Huffman PowerPoint Slides
... – Natural selection: certain traits are passed on because these traits gave an advantage for survival • Organisms with these traits are able to reproduce and pass on the trait to their offspring ...
... – Natural selection: certain traits are passed on because these traits gave an advantage for survival • Organisms with these traits are able to reproduce and pass on the trait to their offspring ...
Sample
... b) has received, in its dendrites, appropriate inputs from other neurons Correct. A neuron fires after the dendrites receive enough stimulation to trigger the cell body to generate an action potential. c) is unable to transmit information to another neuron d) has become more negative in charge Incor ...
... b) has received, in its dendrites, appropriate inputs from other neurons Correct. A neuron fires after the dendrites receive enough stimulation to trigger the cell body to generate an action potential. c) is unable to transmit information to another neuron d) has become more negative in charge Incor ...
Deep Neural Networks for Anatomical Brain Segmentation
... brain (cortical and sub-cortical areas) into a large number N of anatomical regions, where N is defined by the segmentation protocol (typically around 100). Knowledge of the segmentation protocol is implicitly given through a set of manually labelled 3D brain MRIs. An atlas consists of an MR image a ...
... brain (cortical and sub-cortical areas) into a large number N of anatomical regions, where N is defined by the segmentation protocol (typically around 100). Knowledge of the segmentation protocol is implicitly given through a set of manually labelled 3D brain MRIs. An atlas consists of an MR image a ...
The Cholinergic Hypothesis of Age and Alzheimer`s Disease
... cholinergic marker could be used as an early indicator of AD; 2) it is unlikely that a cholinergic deficit could be identified prior to the patient becoming symptomatic; and 3) only the patients with more severe disease should be a target for cholinergic treatment. In addition, DeKosky and colleague ...
... cholinergic marker could be used as an early indicator of AD; 2) it is unlikely that a cholinergic deficit could be identified prior to the patient becoming symptomatic; and 3) only the patients with more severe disease should be a target for cholinergic treatment. In addition, DeKosky and colleague ...
The caudal part of the frontal cortex is strongly involved - LIRA-Lab
... which maps observed actions on the observer’s internal motor representations (mirror neurons). As briefly described above, area F5 is located in the rostral part of the ventral premotor cortex and consists of two main sectors: F5c, located on the cortical convexity and F5ab, forming the posterior ba ...
... which maps observed actions on the observer’s internal motor representations (mirror neurons). As briefly described above, area F5 is located in the rostral part of the ventral premotor cortex and consists of two main sectors: F5c, located on the cortical convexity and F5ab, forming the posterior ba ...
Chapter 14:The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • The human brain is complex • Brain function is associated with life • This chapter is a study of brain and cranial nerves directly connected to it • Will provide insight into brain circuitry and function ...
... • The human brain is complex • Brain function is associated with life • This chapter is a study of brain and cranial nerves directly connected to it • Will provide insight into brain circuitry and function ...
Background Paper 3 - Yale School of Medicine
... NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Rev Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 April 01. ...
... NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Nat Rev Neurosci. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2013 April 01. ...
FROM MOTIVATION TO ACTION - The University of Texas at Dallas
... articles: Eccles (1973), Ito (I 974), Asanuma (1973), Sessle and Hannan (1976), Wetzel and Stuart (1976), Dubner et al. (1978), Evarts (1979)0 Nauta (1979) and Henneman (1974). The function of the motor system is to organize and coordinate the activities of individual muscles to generate sequences o ...
... articles: Eccles (1973), Ito (I 974), Asanuma (1973), Sessle and Hannan (1976), Wetzel and Stuart (1976), Dubner et al. (1978), Evarts (1979)0 Nauta (1979) and Henneman (1974). The function of the motor system is to organize and coordinate the activities of individual muscles to generate sequences o ...
- Reppert Lab
... et al., 2003; Reppert et al., 2004). Electrophysiological recordings have revealed that neurons in the central brain respond to skylight cues with changes in firing frequency and that the central complex, a midline-spanning group of neuropils in the center of the brain, is the most likely candidate ...
... et al., 2003; Reppert et al., 2004). Electrophysiological recordings have revealed that neurons in the central brain respond to skylight cues with changes in firing frequency and that the central complex, a midline-spanning group of neuropils in the center of the brain, is the most likely candidate ...
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE
... Most of our basic functions (sensory & motor) are equally controlled by both left & right hemispheres (remember communication exists through corpus callosum). ...
... Most of our basic functions (sensory & motor) are equally controlled by both left & right hemispheres (remember communication exists through corpus callosum). ...
- Princeton University
... mice: head-mounted microscopes and head restraint. A head-mounted microscope requires innovative engineering to miniaturize the excitation, laser scanning, and fluorescence collection. One such device demonstrated stable TPM of capillaries in awake and resting adult rats (Helmchen et al., 2001); how ...
... mice: head-mounted microscopes and head restraint. A head-mounted microscope requires innovative engineering to miniaturize the excitation, laser scanning, and fluorescence collection. One such device demonstrated stable TPM of capillaries in awake and resting adult rats (Helmchen et al., 2001); how ...
Disproportion of cerebral surface areas and volumes in
... National Hospital or the Chalfont Centre for Epilepsy. Patient details are given in Table 1. There was no significant difference between the ages of the controls and the ages of the patients (Mann–Whitney, two-tailed, P . 0.2). ...
... National Hospital or the Chalfont Centre for Epilepsy. Patient details are given in Table 1. There was no significant difference between the ages of the controls and the ages of the patients (Mann–Whitney, two-tailed, P . 0.2). ...
Nouns, verbs, objects, actions, and abstractions
... The debate concerning lexical vs. semantic differences as the primary factor for neural differentiation might be addressed with the exploration of well-matched word categories orthogonalised for semantic and lexical factors, such that the contribution of these factors to brain activation in specific ...
... The debate concerning lexical vs. semantic differences as the primary factor for neural differentiation might be addressed with the exploration of well-matched word categories orthogonalised for semantic and lexical factors, such that the contribution of these factors to brain activation in specific ...
Brain and effort: brain activation and effort-related working
... Baddeley and Hitch, 1974; Miyake and Shah, 1999). Hence, working memory capacity is a key determinant to reading, language comprehension, intelligence, and many other activities involving reasoning or planning for the future (Kyllonen and Christal, 1990; Engle et al., 1999; Conway et al., 2002; Acke ...
... Baddeley and Hitch, 1974; Miyake and Shah, 1999). Hence, working memory capacity is a key determinant to reading, language comprehension, intelligence, and many other activities involving reasoning or planning for the future (Kyllonen and Christal, 1990; Engle et al., 1999; Conway et al., 2002; Acke ...
A proposed common neural mechanism for categorization and
... perspective be mediated by an eye movement–related area such as LIP, but the same type of decision reported by an arm movement might be mediated by an arm movement–related area, such as the parietal reach region. From an evolutionary perspective, the intentional framework could have developed by ...
... perspective be mediated by an eye movement–related area such as LIP, but the same type of decision reported by an arm movement might be mediated by an arm movement–related area, such as the parietal reach region. From an evolutionary perspective, the intentional framework could have developed by ...
`What` and `where` in the human brain
... visually guided grasping movements, despite her profound inability to describe or recognize these same features of the object. What is the evidence, however, that parietal cortex is mediating these visually guided movements? According to Goodale and Milner 145,46,48*1, patient D.F. suffered an anoxi ...
... visually guided grasping movements, despite her profound inability to describe or recognize these same features of the object. What is the evidence, however, that parietal cortex is mediating these visually guided movements? According to Goodale and Milner 145,46,48*1, patient D.F. suffered an anoxi ...
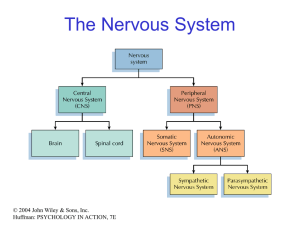
The Nervous System
... Maintains daily necessary body functions Remember as the “D” division - digestion, defecation, and diuresis ...
... Maintains daily necessary body functions Remember as the “D” division - digestion, defecation, and diuresis ...
Nervous System Ch 9
... • Outer layer of gray matter is the cerebral cortex; made up of lobes; composed mainly of dendrites and cell bodies of neurons • Interior of the cerebrum composed mainly of white matter (that is nerve fibers arranged in bundles called tracts) • Functions of the cerebrum—mental processes of all types ...
... • Outer layer of gray matter is the cerebral cortex; made up of lobes; composed mainly of dendrites and cell bodies of neurons • Interior of the cerebrum composed mainly of white matter (that is nerve fibers arranged in bundles called tracts) • Functions of the cerebrum—mental processes of all types ...
Structural changes that occur during normal aging of primate
... seem to acquire more lipofuscin than the excitatory pyramidal neurons. Also, large neurons have more lipofuscin than smaller ones, but this is not a rule, so that among the larger cortical neurons, the Meynert cells of visual cortex [27] come to contain little age pigment, while the Betz cells of mo ...
... seem to acquire more lipofuscin than the excitatory pyramidal neurons. Also, large neurons have more lipofuscin than smaller ones, but this is not a rule, so that among the larger cortical neurons, the Meynert cells of visual cortex [27] come to contain little age pigment, while the Betz cells of mo ...
Neuronal fiber tracts connecting the brain and ventral nerve cord of
... Many aspects of insect behavior entail stereotyped sequences of movement that are controlled by neuronal circuits, called central pattern generators (CPGs; Marder et al., 2005). CPGs are located in the ventral nerve cord (CPGs controlling behaviors involving movement of the wings, legs, and abdomen) ...
... Many aspects of insect behavior entail stereotyped sequences of movement that are controlled by neuronal circuits, called central pattern generators (CPGs; Marder et al., 2005). CPGs are located in the ventral nerve cord (CPGs controlling behaviors involving movement of the wings, legs, and abdomen) ...
Whole-brain functional imaging at cellular resolution using light
... on the number of neurons that can be imaged at the same time and the total brain size of the animal under study. Thus, interactions between neurons in different brain areas are easily missed, and functionally related ensembles of neurons are undetectable if their activity is not tightly locked to a ...
... on the number of neurons that can be imaged at the same time and the total brain size of the animal under study. Thus, interactions between neurons in different brain areas are easily missed, and functionally related ensembles of neurons are undetectable if their activity is not tightly locked to a ...
Chapter 3 - University of South Alabama
... the synapse instead of norepinephrine. There is too much dopamine in the brain. Some of the excess dopamine is converted extracellulary into 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). 6-OH-DA is a neurotoxin that selectively ...
... the synapse instead of norepinephrine. There is too much dopamine in the brain. Some of the excess dopamine is converted extracellulary into 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA). 6-OH-DA is a neurotoxin that selectively ...
The influence of James and Darwin on Cajal and his
... It should be noted that the experimental approach for the study of the psychology of learning attracted considerable interest from psychologists at the time. It was then that experiments with ...
... It should be noted that the experimental approach for the study of the psychology of learning attracted considerable interest from psychologists at the time. It was then that experiments with ...
Loss of autophagy in the central nervous system causes
... (Fig. 1b). We also observed growth retardation as early as P14 in these mice (data not shown). Furthermore, the mice showed motor and behavioural deficits, including abnormal limb-clasping reflexes (Fig. 1c) and tremor, and in some cases, they walked on their tiptoes. In a rotarod test, most Atg7 fl ...
... (Fig. 1b). We also observed growth retardation as early as P14 in these mice (data not shown). Furthermore, the mice showed motor and behavioural deficits, including abnormal limb-clasping reflexes (Fig. 1c) and tremor, and in some cases, they walked on their tiptoes. In a rotarod test, most Atg7 fl ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.