Introduction to Neural Networks
... What are connectionist neural networks? • Connectionism refers to a computer modeling approach to computation that is loosely based upon the architecture of the brain. • Many different models: – Multiple, individual “nodes” or “units” that operate at the same time (in parallel) – A network that con ...
... What are connectionist neural networks? • Connectionism refers to a computer modeling approach to computation that is loosely based upon the architecture of the brain. • Many different models: – Multiple, individual “nodes” or “units” that operate at the same time (in parallel) – A network that con ...
1. Receptor cells
... digestion, at the same time decreasing heart rate and blood flow to skeletal muscles ...
... digestion, at the same time decreasing heart rate and blood flow to skeletal muscles ...
Introduction to the brain and behaviour
... A. They allow more blood to flow to the neurons as the brain requires more oxygen and nutrients than other organs of the body. B. They provide some protection against injury by acting as a shock absorber if the brain is jolted. C. They allow the brain more room to grow because they progressively unf ...
... A. They allow more blood to flow to the neurons as the brain requires more oxygen and nutrients than other organs of the body. B. They provide some protection against injury by acting as a shock absorber if the brain is jolted. C. They allow the brain more room to grow because they progressively unf ...
File chapter 2 vocab pp
... above the kidneys. They secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (nonadrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress. ...
... above the kidneys. They secrete the hormones epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (nonadrenaline), which help to arouse the body in times of stress. ...
Desirable Teacher Behaviors Figure 1.1
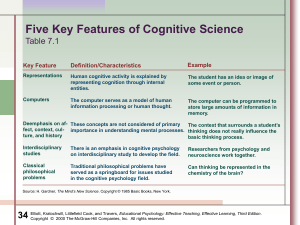
... The context that surrounds a student’s fect, context, cul- importance in understanding mental processes. thinking does not really influence the ture, and history basic thinking process. Interdisciplinary studies ...
... The context that surrounds a student’s fect, context, cul- importance in understanding mental processes. thinking does not really influence the ture, and history basic thinking process. Interdisciplinary studies ...
Intro-biological
... in sensory information, organizes and synthesizes data, then provides direction for motor output to the rest of the body. The CNS is made up of the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord. The brain is the main data centre of the body and consists of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning ...
... in sensory information, organizes and synthesizes data, then provides direction for motor output to the rest of the body. The CNS is made up of the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord. The brain is the main data centre of the body and consists of the cerebrum which regulates higher level functioning ...
Adolescents Brain Development
... in response to threat—all body response—fight or flight • Neurochemical systems cause a cascade of changes in attention, impulse control, sleep patterns, and fine motor control • Chronic activation of the neural pathways involved in fear creates “memories” which shape a person’s perception of and re ...
... in response to threat—all body response—fight or flight • Neurochemical systems cause a cascade of changes in attention, impulse control, sleep patterns, and fine motor control • Chronic activation of the neural pathways involved in fear creates “memories” which shape a person’s perception of and re ...
Physiological Mechanisms of Behavior
... biological, chemical, and physical principles are discussed throughout the course. All of this scientific information is connected to the mind and behavior, demonstrating clearly how humans can be scientifically studied as part of the world of nature. As you will see, the physiological perspective i ...
... biological, chemical, and physical principles are discussed throughout the course. All of this scientific information is connected to the mind and behavior, demonstrating clearly how humans can be scientifically studied as part of the world of nature. As you will see, the physiological perspective i ...
Introductory Assignment to the Nervous System
... What do we call the electrical signals that have reached the end of an axon and have become chemical signals? What special nerve cells allow us to see, hear, feel, taste, and smell the world around ...
... What do we call the electrical signals that have reached the end of an axon and have become chemical signals? What special nerve cells allow us to see, hear, feel, taste, and smell the world around ...
Older Brain Structures
... A.P. Psychology Lecture. . . Click on link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= m17gLs4jnLw Note: She is lecturing from a different book, but the material is the same. . . ...
... A.P. Psychology Lecture. . . Click on link https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= m17gLs4jnLw Note: She is lecturing from a different book, but the material is the same. . . ...
Nervous System
... • Nerves There are two parts to the nervous system: 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain & Spinal Cord – process incoming & outgoing messages 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves – connects all neurons to the central nervous system ...
... • Nerves There are two parts to the nervous system: 1. Central Nervous System (CNS): Brain & Spinal Cord – process incoming & outgoing messages 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): Nerves – connects all neurons to the central nervous system ...
Halle Berry as a Computational Brain Abstraction
... distributed representation. Conceptual abstractions are therefore concluded to be based on cells that receive abstracted input through their connections to lower-‐level neurons, providing a computational framework for ...
... distributed representation. Conceptual abstractions are therefore concluded to be based on cells that receive abstracted input through their connections to lower-‐level neurons, providing a computational framework for ...
Nervous System - Northwest ISD Moodle
... •Controls certain respiratory functions (autonomic functions) ...
... •Controls certain respiratory functions (autonomic functions) ...
Exercise and the Bra..
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
... down into a form easily burned by neurons. This substance is released into the space between the cells and the neurons swallow it, maintaining their energy levels. But while scientists knew that the brain had and could access these energy stores, they had been unable to study when the brain’s stored ...
Nervous System - Effingham County Schools
... Nervous System Disorders Multiple Sclerosis- Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. Symptoms include: loss of motor skills, blindness, numbness, and loss of balance. Caused by white blood cells attacking the ne ...
... Nervous System Disorders Multiple Sclerosis- Disorder in which the myelin surrounding neurons deteriorate making it hard for signals to travel from one neuron to the next. Symptoms include: loss of motor skills, blindness, numbness, and loss of balance. Caused by white blood cells attacking the ne ...
Chapter 2
... area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations Association Areas More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex Specialization and Integration hemisphere’s special functions--called hemispheric specialization or laterali ...
... area at the front of the parietal lobes that registers and processes body sensations Association Areas More intelligent animals have increased “uncommitted” or association areas of the cortex Specialization and Integration hemisphere’s special functions--called hemispheric specialization or laterali ...
11.3: The Central Nervous System The nervous system consists of
... The Brain is the major centre that receives, integrates, stores, and retrieves information. The Brain and its network of interneurons provide the basis for our voluntary movements, consciousness, behaviour, emotions, learning, reasoning, language and memory. The brain contains grey and white matter, ...
... The Brain is the major centre that receives, integrates, stores, and retrieves information. The Brain and its network of interneurons provide the basis for our voluntary movements, consciousness, behaviour, emotions, learning, reasoning, language and memory. The brain contains grey and white matter, ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY STUDY GUIDE
... What part of the brain allows us to consciously move our skeletal muscles? Where is this area? What is controlled in the Broca’s area? Which hemisphere is this usually in? What happens when there is damage to the Broca’s area? Where are areas of higher intellectual reasoning located? Where are compl ...
... What part of the brain allows us to consciously move our skeletal muscles? Where is this area? What is controlled in the Broca’s area? Which hemisphere is this usually in? What happens when there is damage to the Broca’s area? Where are areas of higher intellectual reasoning located? Where are compl ...
Describe the parts of the brain activated in the following situation
... Involved in the formation of memories of what to paint, and how to set perspective, as well as memories of mixing colors and painting techniques The cerebral cortex will oversee will oversee all aspects of the artist’s behavior. Sensory projection areas in the occipital, temporal, parietal lobes wil ...
... Involved in the formation of memories of what to paint, and how to set perspective, as well as memories of mixing colors and painting techniques The cerebral cortex will oversee will oversee all aspects of the artist’s behavior. Sensory projection areas in the occipital, temporal, parietal lobes wil ...
Brain PowerPoint
... mistakes is not healthy for a growing, adaptive brain repeated electrical stimulation, along with increased input of nutrients, fosters cell growth through dendritic branching and formation of new synapses new synapses usually appear after learning occurs memory is enhanced through relevant, varied, ...
... mistakes is not healthy for a growing, adaptive brain repeated electrical stimulation, along with increased input of nutrients, fosters cell growth through dendritic branching and formation of new synapses new synapses usually appear after learning occurs memory is enhanced through relevant, varied, ...
The Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology
... interacts with a computer by studying not only input-output techniques, but also human factors involved in the interchange. Research groups in the Human-Computer Intelligent Interaction are: ...
... interacts with a computer by studying not only input-output techniques, but also human factors involved in the interchange. Research groups in the Human-Computer Intelligent Interaction are: ...
the teenage brain webquest
... http://www.nimh.nih.gov/news/science-news/2004/imaging-study-shows-brainmaturing.shtml Focus on paragraphs 4-6 http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/teenbrain.cfm Read the first three paragraphs of Teenage Brain : A Work In Progress. After reading this part of the article, answer the following questions. ...
... http://www.nimh.nih.gov/news/science-news/2004/imaging-study-shows-brainmaturing.shtml Focus on paragraphs 4-6 http://www.nimh.nih.gov/publicat/teenbrain.cfm Read the first three paragraphs of Teenage Brain : A Work In Progress. After reading this part of the article, answer the following questions. ...
European Neuroscience Conference for Doctoral Students
... views of hippocampus, the changes in firing patterns of hippocampal neurons occurring during learning, the existence of “time cells” that fire at specific time points during a task, etc. To do so, Dr. Eichenbaum laboratory has adopted a multidisciplinary point of view, using disparate techniques, su ...
... views of hippocampus, the changes in firing patterns of hippocampal neurons occurring during learning, the existence of “time cells” that fire at specific time points during a task, etc. To do so, Dr. Eichenbaum laboratory has adopted a multidisciplinary point of view, using disparate techniques, su ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.