Psychology Chapter 19: Group Interaction
... i. Person with a split brain can hold a ball in their right hand and say it was a ball, but not holding it in their left hand. 3. Shows how unique and the specialize functions and skills of each hemisphere 4. Remained practically unchanged in intelligence, emotion and personality ...
... i. Person with a split brain can hold a ball in their right hand and say it was a ball, but not holding it in their left hand. 3. Shows how unique and the specialize functions and skills of each hemisphere 4. Remained practically unchanged in intelligence, emotion and personality ...
Module 4 revised
... different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain ...
... different types of soft tissue; allows us to see structures within the brain ...
Flyer - Energy Kinesiology Association
... Nervous System! Instructor: Jacque Mooney There are only two cell types in the Nervous System – Glial Cells & Neurons. While Glial Cells out-number Neurons by 40 to 100 times, it was believed they only provided a matrix and passive support for Neuron function, and Neurons did all the Neurotransmissi ...
... Nervous System! Instructor: Jacque Mooney There are only two cell types in the Nervous System – Glial Cells & Neurons. While Glial Cells out-number Neurons by 40 to 100 times, it was believed they only provided a matrix and passive support for Neuron function, and Neurons did all the Neurotransmissi ...
Neurotransmitters
... Cerebral Cortex, which is involved in a variety of higher cognitive, emotional, sensory, and motor functions, is more developed in humans than any other animal. It is what we see when we picture a human brain, the gray matter with a multitude of folds covering the cerebrum. The brain is divided into ...
... Cerebral Cortex, which is involved in a variety of higher cognitive, emotional, sensory, and motor functions, is more developed in humans than any other animal. It is what we see when we picture a human brain, the gray matter with a multitude of folds covering the cerebrum. The brain is divided into ...
File
... • b. Includes the auditory areas, each of which receives auditory information primarily from the opposite ear. (hearing and memory) • c. One of the key areas of speech known as Wernicke’s Area is located in this lobe (written and spoken language) ...
... • b. Includes the auditory areas, each of which receives auditory information primarily from the opposite ear. (hearing and memory) • c. One of the key areas of speech known as Wernicke’s Area is located in this lobe (written and spoken language) ...
Print › Nervous System | Quizlet
... Transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles making them move. ...
... Transmit information from the central nervous system to the muscles making them move. ...
Chapter 14 - FacultyWeb
... Wernike’s area in the parietal lobe General interpretive area of the temporal lobe Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe Broca’s area in the frontal lobe ...
... Wernike’s area in the parietal lobe General interpretive area of the temporal lobe Primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe Broca’s area in the frontal lobe ...
What a Frog s Eye tells the Frog s brain
... There a re 4 such sheets in the brain corresponding to the 4 operations These maps are spatially registered In effect what the above 4 operations do performs as a “bug detector” They respond best when a dark object, smaller than the receptive field, enters that field, stops, and moves around i ...
... There a re 4 such sheets in the brain corresponding to the 4 operations These maps are spatially registered In effect what the above 4 operations do performs as a “bug detector” They respond best when a dark object, smaller than the receptive field, enters that field, stops, and moves around i ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
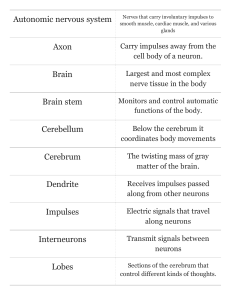
... Neuron - specialized cell that lies within the nervous system; conducts electrochemical signals along their length body - major portion of neuron axon - transmits signals to other structures (groups are nerves) dendrite - receive signals from other neurons 3 Classifications of Neurons Sensory Neuron ...
... Neuron - specialized cell that lies within the nervous system; conducts electrochemical signals along their length body - major portion of neuron axon - transmits signals to other structures (groups are nerves) dendrite - receive signals from other neurons 3 Classifications of Neurons Sensory Neuron ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 7
... 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or gla ...
... 1. What are the three major overlapping functions of the nervous system? a) Sensory input—information gathered from stimuli inside and outside the body b) Integration—processes and interprets sensory input and decides what should be done c) Motor output—response performed by activating muscle or gla ...
Self as a function of the brain
... • There are no good arguments against convergence of the neural modeling process in embodied systems and brain-like structure to conscious artifacts. • Artificial minds of brain-like systems will have to claim qualia; they will be as real in artificial systems as they are in our brains. • Measures o ...
... • There are no good arguments against convergence of the neural modeling process in embodied systems and brain-like structure to conscious artifacts. • Artificial minds of brain-like systems will have to claim qualia; they will be as real in artificial systems as they are in our brains. • Measures o ...
Overview
... The cells in the right side control the voluntary motor movements of the left side of the body. The left side controls the right side. The frontal lobe also controls speech. ...
... The cells in the right side control the voluntary motor movements of the left side of the body. The left side controls the right side. The frontal lobe also controls speech. ...
History and some Cognitive Neuroscience History
... How can you stay focused on your conversation?! You must filter out extraneous information. ...
... How can you stay focused on your conversation?! You must filter out extraneous information. ...
Slide ()
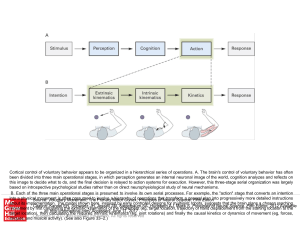
... Cortical control of voluntary behavior appears to be organized in a hierarchical series of operations. A. The brain's control of voluntary behavior has often been divided into three main operational stages, in which perception generates an internal neuronal image of the world, cognition analyzes and ...
... Cortical control of voluntary behavior appears to be organized in a hierarchical series of operations. A. The brain's control of voluntary behavior has often been divided into three main operational stages, in which perception generates an internal neuronal image of the world, cognition analyzes and ...
EXPLORING PSYCHOLOGY (8th edition) David Myers
... Both photos from Daniel Weinberger, M.D., CBDB, NIMH ...
... Both photos from Daniel Weinberger, M.D., CBDB, NIMH ...
Brain Anatomy - Lone Star College System
... Both photos from Daniel Weinberger, M.D., CBDB, NIMH ...
... Both photos from Daniel Weinberger, M.D., CBDB, NIMH ...
Module 3 Brain`s Building Blocks
... a slowing of voluntary movements and feelings of depression. As the disease progresses: Patients develop a peculiar shuffling walk May suddenly freeze in space for minutes or hours at a time. Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1 ...
... a slowing of voluntary movements and feelings of depression. As the disease progresses: Patients develop a peculiar shuffling walk May suddenly freeze in space for minutes or hours at a time. Parkinson’s is caused by a destruction of neurons that produce the neurotransmitter Dopamine 1 ...
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves
... • The two cerebral hemispheres share many functions • Each hemisphere also performs unique functions • Functional specialization of each hemisphere is more pronounced in men • Females generally have larger connections between 2 sides ...
... • The two cerebral hemispheres share many functions • Each hemisphere also performs unique functions • Functional specialization of each hemisphere is more pronounced in men • Females generally have larger connections between 2 sides ...
HW CH 5 PSY 2513 Submit your answers on canvas
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
... the areas of the brain are strongly committed to specific functions, and there is a high capacity for learning. b. if a part of the cortex is damaged, other parts can take over the tasks it would have handled. c. spatial skills develop more rapidly than language skills and are easier to recover afte ...
Nervous System
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory-uses receptors to gather information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts ...
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory-uses receptors to gather information from all over the body 2. Interpretation-the brain then processes the information into possible responses 3. Response-sends messages back through the system of nerve cells to control body parts ...
lecture 02
... CT technique developed – when highly focused x-rays are passed through the body, the beam is affected in predictable ways by the relative density of the tissue – by passing a beam through the body at many different angles it becomes possible to reconstruct an image of the body ...
... CT technique developed – when highly focused x-rays are passed through the body, the beam is affected in predictable ways by the relative density of the tissue – by passing a beam through the body at many different angles it becomes possible to reconstruct an image of the body ...
Overview of the Brain
... – Meaning, no single part of the brain is responsible for vision, language, social behavior, or other complex capabilities. – Or “integrated brain functions” ...
... – Meaning, no single part of the brain is responsible for vision, language, social behavior, or other complex capabilities. – Or “integrated brain functions” ...
Cognitive neuroscience

Cognitive neuroscience is an academic field concerned with the scientific study of biological substrates underlying cognition, with a specific focus on the neural substrates of mental processes. It addresses the questions of how psychological/cognitive functions are produced by neural circuits in the brain. Cognitive neuroscience is a branch of both psychology and neuroscience, overlapping with disciplines such as physiological psychology, cognitive psychology, and neuropsychology. Cognitive neuroscience relies upon theories in cognitive science coupled with evidence from neuropsychology, and computational modeling.Due to its multidisciplinary nature, cognitive neuroscientists may have various backgrounds. Other than the associated disciplines just mentioned, cognitive neuroscientists may have backgrounds in neurobiology, bioengineering, psychiatry, neurology, physics, computer science, linguistics, philosophy, and mathematics.Methods employed in cognitive neuroscience include experimental paradigms from psychophysics and cognitive psychology, functional neuroimaging, electrophysiology, cognitive genomics, and behavioral genetics. Studies of patients with cognitive deficits due to brain lesions constitute an important aspect of cognitive neuroscience. Theoretical approaches include computational neuroscience and cognitive psychology.Cognitive neuroscience can look at the effects of damage to the brain and subsequent changes in the thought processes due to changes in neural circuitry resulting from the ensued damage. Also, cognitive abilities based on brain development is studied and examined under the subfield of developmental cognitive neuroscience.