8.P.1.1 Warm-Up Questions for Website
... B.It can be formed through a physical reaction. C.It can be changed into simpler substances through a physical change. D.It is a pure substance containing elements that are chemically combined. ...
... B.It can be formed through a physical reaction. C.It can be changed into simpler substances through a physical change. D.It is a pure substance containing elements that are chemically combined. ...
Chemical Reactions
... Chemical – stored in the bonds of chemical substances Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Chemical – stored in the bonds of chemical substances Electrical – results from the movement of charged particles Mechanical – directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic – energy traveling in waves (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
Biochemistry-Review of the Basics
... Non-competitive- molecule binds to an allosteric site which causes an shape change in the enzyme so the substrate can't bind ...
... Non-competitive- molecule binds to an allosteric site which causes an shape change in the enzyme so the substrate can't bind ...
Atoms, Ions, and Molecules File
... Atoms of different elements are different. • Atoms are not changed into different atoms in a chemical reaction. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. ...
... Atoms of different elements are different. • Atoms are not changed into different atoms in a chemical reaction. • Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements combine. ...
The Chemical Context of Life by Dr. Ty C.M. Hoffman
... measure of an atom's degree to which it attracts electrons is called its electronegativity. If a covalent bond is formed between two atoms that have drastically different electronegativities, the shared elect ...
... measure of an atom's degree to which it attracts electrons is called its electronegativity. If a covalent bond is formed between two atoms that have drastically different electronegativities, the shared elect ...
Elements, mixtures and compounds lecture
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
... A. exists as only one type of atom: it is, therefore a pure substance (This does not often occur in nature); gold necklace? Oxygen is the most common pure element on Earth (occurs as a dioxide: O2 , what does “di” mean?) B. cannot be broken down by chemical reactions: burning/acids/eating (but nucle ...
Part a
... Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide
... a. Chemists discovered that if two or more different compounds are composed of the same elements, the ratio of the masses of the second element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This example illustrates the law of multiple proportions ...
... a. Chemists discovered that if two or more different compounds are composed of the same elements, the ratio of the masses of the second element is always a ratio of small whole numbers. This example illustrates the law of multiple proportions ...
Semester 2 review questions
... 4. __________What is the valence electron configuration for any element in group 2? 5. __________ What energy level are Bromine’s valence electrons in? 6. Period:__________ Given the following configuration: [Ar]4s23d104p2; what period and block is the last valence electron found in? ...
... 4. __________What is the valence electron configuration for any element in group 2? 5. __________ What energy level are Bromine’s valence electrons in? 6. Period:__________ Given the following configuration: [Ar]4s23d104p2; what period and block is the last valence electron found in? ...
Thermionic phenomena and the laws which govern them O W. R
... It is necessary to say a word or two in parenthesis about the positive ionization which is frequently observed. This is due to an emission of positive ions which arises in various ways. When any ordinary sample of a solid is first heated, it gives rise to a copious emission of positive ions which de ...
... It is necessary to say a word or two in parenthesis about the positive ionization which is frequently observed. This is due to an emission of positive ions which arises in various ways. When any ordinary sample of a solid is first heated, it gives rise to a copious emission of positive ions which de ...
Document
... Brittle, don’t conduct, may be solids, liquids or gases, not ductile, not malleable Right of the zig-zag line Fluorine 14) Name and describe the two main classifications of matter. Pure Substances (elements and compounds) and Mixtures 15) Name any two materials that can be classified as substances a ...
... Brittle, don’t conduct, may be solids, liquids or gases, not ductile, not malleable Right of the zig-zag line Fluorine 14) Name and describe the two main classifications of matter. Pure Substances (elements and compounds) and Mixtures 15) Name any two materials that can be classified as substances a ...
MYP 10 PeriodicityWS
... 5(a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why sodium chloride has a high melting point. (b) Lithium reacts with water. Write an equation for the reaction and state two observations that could be made during the reaction. [SL paper 2, Nov 05] 6 (a) Fo ...
... 5(a) Draw a diagram to show the structure of sodium chloride. Explain, in terms of bonding, why sodium chloride has a high melting point. (b) Lithium reacts with water. Write an equation for the reaction and state two observations that could be made during the reaction. [SL paper 2, Nov 05] 6 (a) Fo ...
CHEMISTRY 1 FINAL EXAM REVIEW
... A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a cation in a compound D. a reaction in which two or more su ...
... A. a reaction in which a single compound is broken down into simpler substances B. a reaction in which oxygen reacts with another substance, often producing heat or light C. a reaction in which the atoms of one element replace the atoms of a cation in a compound D. a reaction in which two or more su ...
Grade 10 NSC Chemistry Curriculum
... covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simple ionic compounds. Ionic structure as illustrated by sodium chloride • Revise the writing of names when given the form ...
... covalent molecules, names and formulae of covalent compounds. • Ionic bonding: transfer of electrons in the formation of ionic bonding, cations and anions, electron diagrams of simple ionic compounds. Ionic structure as illustrated by sodium chloride • Revise the writing of names when given the form ...
Chp 1,2 rev
... Give the names of the shapes of molecules below HI BF3 CI4 NH3 H2O SO2 What is hybridization? How many sets of electrons are around the central atom if its sp3 hybridized? Sp2? ...
... Give the names of the shapes of molecules below HI BF3 CI4 NH3 H2O SO2 What is hybridization? How many sets of electrons are around the central atom if its sp3 hybridized? Sp2? ...
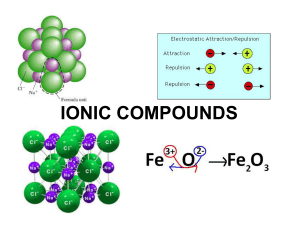
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... ionic compound, the bonds will break. The energy required to separate one mole of the ions of an ionic compound is referred to as the Lattice Energy ...
... ionic compound, the bonds will break. The energy required to separate one mole of the ions of an ionic compound is referred to as the Lattice Energy ...
Unit A Review Questions
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
... The zinc electrode is gaining mass because the copper ions are coming out of the solution and are being reduced by the zinc metal being oxidized. This would also account for the colour change in the copper nitrate solution. As the copper ions come out of the solution, the solution becomes a fainter ...
Chemistry Cram Sheet
... A polyatomic ion and another element…It’s BOTH! (The polyatomic ion is the covalent part, the whole compound will be ionic.) Polarity Covalent bonds are when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. If the electrons are shared equally, it is a nonpolar covalent bond. If the electrons are shared u ...
... A polyatomic ion and another element…It’s BOTH! (The polyatomic ion is the covalent part, the whole compound will be ionic.) Polarity Covalent bonds are when electrons are shared between two nonmetals. If the electrons are shared equally, it is a nonpolar covalent bond. If the electrons are shared u ...
Unit 1 – Physical Science and Chemical Reactions
... Never change the charge on an ion from the Periodic Table - To find the net charge, multiply the charge by using a subscript Never Never Never Never use the prefix system - The first name of the ionic compound stays the same - The second name of the ionic compound changes the last three letters ...
... Never change the charge on an ion from the Periodic Table - To find the net charge, multiply the charge by using a subscript Never Never Never Never use the prefix system - The first name of the ionic compound stays the same - The second name of the ionic compound changes the last three letters ...
Chapter 4 4.1 Defining the Atom • Early Models of the Atom atom
... 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratio ...
... 1) All elements are composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. Atoms of any one element are different from those of any other element 3) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratio ...
Lecture 3 Diode
... Has tightly bound electrons in its outer or Valence ring, they cannot be easily displaced. Semiconductor; Has at least 4 electrons in the outer or Valence ring, it is neither a conductor nor an insulator. In its pure state it makes a better insulator than conductor. 4 electrons allows easy bonding w ...
... Has tightly bound electrons in its outer or Valence ring, they cannot be easily displaced. Semiconductor; Has at least 4 electrons in the outer or Valence ring, it is neither a conductor nor an insulator. In its pure state it makes a better insulator than conductor. 4 electrons allows easy bonding w ...
chapter19_2007
... Note the superposition needed to Note is still the finite large but not large: of both bands: promote an gap Semiconductors between of may have Reason forelectron the highto reasonable bands conductivity the conductivity of metals under certain conditions conduction band ...
... Note the superposition needed to Note is still the finite large but not large: of both bands: promote an gap Semiconductors between of may have Reason forelectron the highto reasonable bands conductivity the conductivity of metals under certain conditions conduction band ...