Chemistry I – Fall 2004
... 13. Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds? (A) KCl (B) NH4Cl (C) CCl4 (D) CO2 14. Covalent bonds are most likely to be found in the compound represented by the formula (A) NaCl (B) KBr (C) CH4 (D) HI E) CaF2 15. A pure substance melts at 113 °C and does not conduct electricity in ei ...
... 13. Which compound contains both ionic and covalent bonds? (A) KCl (B) NH4Cl (C) CCl4 (D) CO2 14. Covalent bonds are most likely to be found in the compound represented by the formula (A) NaCl (B) KBr (C) CH4 (D) HI E) CaF2 15. A pure substance melts at 113 °C and does not conduct electricity in ei ...
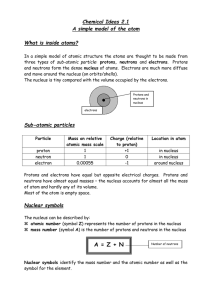
4.1Atoms and Isotopes
... charge is written in the top right if there is a charge 32S2e.g. 16 How many protons, electrons, and neutrons? 16 protons, 16 neutrons, 18 electrons ...
... charge is written in the top right if there is a charge 32S2e.g. 16 How many protons, electrons, and neutrons? 16 protons, 16 neutrons, 18 electrons ...
bands
... The arsenic impurity creates a donor impurity level. Because it takes only a few meV to ionize the As and place the resulting electron in the conduction band, the donor impurity level sits just below the conduction band. A few donor impurities can produce many electrons in the conduction band and g ...
... The arsenic impurity creates a donor impurity level. Because it takes only a few meV to ionize the As and place the resulting electron in the conduction band, the donor impurity level sits just below the conduction band. A few donor impurities can produce many electrons in the conduction band and g ...
File - ARC: Chemistry
... d. Roman numeral following the name ____ 15. How does calcium obey the octet rule when reacting to form compounds? a. It gains electrons. b. It does not change its number of electrons. c. It gives up electrons. d. Calcium does not obey the octet rule. ____ 16. Aluminum is a group 3A metal. Which ion ...
... d. Roman numeral following the name ____ 15. How does calcium obey the octet rule when reacting to form compounds? a. It gains electrons. b. It does not change its number of electrons. c. It gives up electrons. d. Calcium does not obey the octet rule. ____ 16. Aluminum is a group 3A metal. Which ion ...
Chemistry - Delhi Public School, Faridabad
... be stopped by applying the voltage of 0.35 V when the radiation 256.7 nm is used. Calculate the work function for silver metal. 4.48 eV. ...
... be stopped by applying the voltage of 0.35 V when the radiation 256.7 nm is used. Calculate the work function for silver metal. 4.48 eV. ...
Lesson 1 - Working With Chemicals
... For example, hydrogen has one electron and thus it wants to fill that orbit in order to become stable - so it will pair up with another hydrogen atom and they will share the two electrons – covalent bonding. ...
... For example, hydrogen has one electron and thus it wants to fill that orbit in order to become stable - so it will pair up with another hydrogen atom and they will share the two electrons – covalent bonding. ...
Atomic Structure Tick Sheet
... I know that all ATOMS are ELECTRICALLY NEUTRAL because they have EQUAL NUMBERS of positive protons and negative electrons so the charges cancel. I know that all atoms of the same element have the SAME number of protons. I know that atoms of DIFFERENT elements have DIFFERENT numbers of protons. I kno ...
... I know that all ATOMS are ELECTRICALLY NEUTRAL because they have EQUAL NUMBERS of positive protons and negative electrons so the charges cancel. I know that all atoms of the same element have the SAME number of protons. I know that atoms of DIFFERENT elements have DIFFERENT numbers of protons. I kno ...
Metals, Semiconductors, and Insulators
... There are other ways of changing the electrical conductivity in the ceramic which have a far greater effect than temperature. •Doping with an element whose valence is different from the atom it replaces. The doping levels in an insulator are generally greater than the ones used in semiconductors. Tu ...
... There are other ways of changing the electrical conductivity in the ceramic which have a far greater effect than temperature. •Doping with an element whose valence is different from the atom it replaces. The doping levels in an insulator are generally greater than the ones used in semiconductors. Tu ...
Chem I Review Part 1
... 36. The mineral pyrolusite is a compound of manganese-55 and oxygen-16. If 63% of the mass of pyrolusite is due to manganese, what is the empirical formula of pyrolusite? A. MnO B. Mn2O C. Mn2O2 D. MnO2 E. none of these 37. The total number of electrons present in a sulfate ion is A. 2. B. 26. C. 3 ...
... 36. The mineral pyrolusite is a compound of manganese-55 and oxygen-16. If 63% of the mass of pyrolusite is due to manganese, what is the empirical formula of pyrolusite? A. MnO B. Mn2O C. Mn2O2 D. MnO2 E. none of these 37. The total number of electrons present in a sulfate ion is A. 2. B. 26. C. 3 ...
Chemistry 106: General Chemistry
... What mass of nitrogen dioxide would be contained in a 4.32 L vessel at 48° C and 1062 torr? 5.35 x 104 g 53.5 g 10.5 g 105.0 g none of the above ...
... What mass of nitrogen dioxide would be contained in a 4.32 L vessel at 48° C and 1062 torr? 5.35 x 104 g 53.5 g 10.5 g 105.0 g none of the above ...
Unit 2 Review: Chemistry - Mr. Hoover's Science Classes
... If need be reduce to lowest terms (in other words, if they are the same number, you don’t write those numbers down because you could divide the whole molecule by that number which would = 1) MgI2 (if the number crossed is a 1, the 1 is not shown) ...
... If need be reduce to lowest terms (in other words, if they are the same number, you don’t write those numbers down because you could divide the whole molecule by that number which would = 1) MgI2 (if the number crossed is a 1, the 1 is not shown) ...
1305- practise exam 2
... PART II – Show your work: (8 points each) 21a. Element X has natural isotopes; X-63 (62.940amu) and X-65 (64.928amu). Calculate the atomic mass of element X given the abundance of X-63 is 69.17% b. Which element corresponds to each of the following electron configuration? i. 1S2 2S2 2P5 ii. 1S2 2S2 ...
... PART II – Show your work: (8 points each) 21a. Element X has natural isotopes; X-63 (62.940amu) and X-65 (64.928amu). Calculate the atomic mass of element X given the abundance of X-63 is 69.17% b. Which element corresponds to each of the following electron configuration? i. 1S2 2S2 2P5 ii. 1S2 2S2 ...
Chapter 07 and 08 Chemical Bonding and Molecular
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
... • Pure substance • Made of 2 or more elements in a definite proportion by mass • Physically and chemically different from the elements that make up the compound • All elements (except Noble gases) react to gain a stable octet. (duet-for H through B) • Compounds form to gain a stable valence shell wh ...
chem final review
... A) a law only summarizes observations; a theory A) They are pure substances. attempts to explain observations B) They can be physically separated into their B) a theory only summarizes observations; a law constituent elements. attempts to explain observations C) They have properties similar to those ...
... A) a law only summarizes observations; a theory A) They are pure substances. attempts to explain observations B) They can be physically separated into their B) a theory only summarizes observations; a law constituent elements. attempts to explain observations C) They have properties similar to those ...
CHEM_Review - Kenston Local Schools
... single atom. Such a group of atoms is called a radical. if a radical Is used In a formula more than once, the radical is put in parentheses and the subscdpt appears outside the parentheses. When a subscript appears outside the parentheses, It indicates that all the demerits inside parentheses should ...
... single atom. Such a group of atoms is called a radical. if a radical Is used In a formula more than once, the radical is put in parentheses and the subscdpt appears outside the parentheses. When a subscript appears outside the parentheses, It indicates that all the demerits inside parentheses should ...
Metals without Electrons - Condensed Matter Theory group
... there are only two independent spin states corresponding to opposite spin directions (frequently referred to as “up” and “down”). In a magnetic material, such as iron as found in a bar magnet, these spins align parallel with each other, forming a large total magnetic moment. This is a ferromagnet. T ...
... there are only two independent spin states corresponding to opposite spin directions (frequently referred to as “up” and “down”). In a magnetic material, such as iron as found in a bar magnet, these spins align parallel with each other, forming a large total magnetic moment. This is a ferromagnet. T ...
atomic number - geraldinescience
... • Based on similarities in their chemical properties, elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called groups. • An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined by the number of the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud. These electrons are called valence elect ...
... • Based on similarities in their chemical properties, elements on the periodic table are arranged in columns, which are called groups. • An atom’s chemical properties are largely determined by the number of the outermost electrons in an atom’s electron cloud. These electrons are called valence elect ...
Chemistry B2A Chapter 18 Oxidation
... Note: When the oxidizing or reducing agent is named, the whole compound is specified, not just the element that undergoes the change. Oxidation states (oxidation numbers): it lets us keep track of electrons in oxidationreduction reactions by assigning charges to the various atoms in a compound. Howe ...
... Note: When the oxidizing or reducing agent is named, the whole compound is specified, not just the element that undergoes the change. Oxidation states (oxidation numbers): it lets us keep track of electrons in oxidationreduction reactions by assigning charges to the various atoms in a compound. Howe ...
chapter43
... The quantum-based free-electron theory of electrical conduction in metals takes into account the wave nature of the electrons The model is that the outer-shell electrons are free to move through the metal, but are trapped within a three-dimensional box formed by the metal surfaces Each electron can ...
... The quantum-based free-electron theory of electrical conduction in metals takes into account the wave nature of the electrons The model is that the outer-shell electrons are free to move through the metal, but are trapped within a three-dimensional box formed by the metal surfaces Each electron can ...
Final Exam Review Guide
... Rotation (spinning in place) – all phases Vibration (shaking in place) – all phases Translation (moving from place to place) – Liquid and Gas only Describe the “Kinetic Theory of Gases” and list the three assumptions associated with it. What volume does one mole of any gas occupy at STP? 22.4 L Kine ...
... Rotation (spinning in place) – all phases Vibration (shaking in place) – all phases Translation (moving from place to place) – Liquid and Gas only Describe the “Kinetic Theory of Gases” and list the three assumptions associated with it. What volume does one mole of any gas occupy at STP? 22.4 L Kine ...
Document
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
... In this reaction two light atomic nuclei, when they are very close to each other, fuse together to form a single heavier nucleus of a new element. The process is exothermic (release of energy). The nuclear fusions occur at only very high temperatures. When 2 hydrogen nuclei fuse together by nuclear ...
eBook AQA GCSE Chemistry Unit C2 Part 1
... made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. In ammonia, each molecule consists of one atom of nitrogen joined to three atoms of hydrogen. The atoms are held together by covalent bonds. A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonds form so that atoms can achieve stable el ...
... made up of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. In ammonia, each molecule consists of one atom of nitrogen joined to three atoms of hydrogen. The atoms are held together by covalent bonds. A covalent bond is a shared pair of electrons. Covalent bonds form so that atoms can achieve stable el ...
FREE Sample Here
... 78) How would the lack of a cofactor for an enzyme affect that enzyme's function? A) The enzyme would cease to function after reaching a maximum rate. B) The enzyme would function more slowly. C) The enzyme's function would not be altered. D) The enzyme would not be able to function. E) The enzyme w ...
... 78) How would the lack of a cofactor for an enzyme affect that enzyme's function? A) The enzyme would cease to function after reaching a maximum rate. B) The enzyme would function more slowly. C) The enzyme's function would not be altered. D) The enzyme would not be able to function. E) The enzyme w ...
2014MSC(ORGANIC(CHEMISTRY!
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
... ! Polar!covalent!bonds!are!formed!through!the!sharing!of!electrons!between!neutral!atoms!–! it!is!polar!where!the!electrons!are!attracted!stronger!to!one!atom!over!the!other.!! ! Therefore,!the!electron!distribution!between!the!atoms!is!not!symmetrical,!and!atoms!have! a!partial!negative!or!positive ...
apbio ch 2 study guide
... injected into the blood, and its rate of excretion in the urine can be measured. o Radioactive tracers can be used with imaging instruments such as PET scanners to monitor chemical processes in the body. ...
... injected into the blood, and its rate of excretion in the urine can be measured. o Radioactive tracers can be used with imaging instruments such as PET scanners to monitor chemical processes in the body. ...