Integrated Coordinated Science Framework - Ms
... speed of 3 × 10 m/s (or 186,000 miles per second). In a medium the speed of an electromagnetic wave depends on the medium’s properties and on the frequency of the wave. The ratio of the speed of a wave of a given frequency in a vacuum to its speed in a medium is called that medium’s index of refract ...
... speed of 3 × 10 m/s (or 186,000 miles per second). In a medium the speed of an electromagnetic wave depends on the medium’s properties and on the frequency of the wave. The ratio of the speed of a wave of a given frequency in a vacuum to its speed in a medium is called that medium’s index of refract ...
Grade 11 Chemistry Exam Review
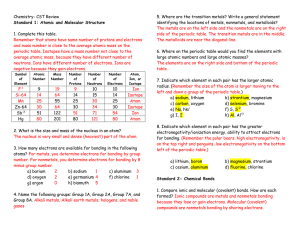
... Which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius? a) sulfur b) selenium c) oxygen d) tellurium ...
... Which of the following elements has the smallest atomic radius? a) sulfur b) selenium c) oxygen d) tellurium ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 73. The relationship in which the physical and chemical properties of elements show a periodic pattern when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number is called a. the periodic law b. the law of octaves c. Mendeleev’s law d. Meyer’s periodicity 74. The elements in group 1 (1A) of the peri ...
... 73. The relationship in which the physical and chemical properties of elements show a periodic pattern when the elements are arranged by increasing atomic number is called a. the periodic law b. the law of octaves c. Mendeleev’s law d. Meyer’s periodicity 74. The elements in group 1 (1A) of the peri ...
FINAL EXAM Review Sheet / Study Guide Honors Chemistry
... 18) A gas occupies 5.50 m3 at -53.0°C, exerting a pressure of 400.0 kPa. What volume (in liters) would the gas occupy at 272.0°C if the pressure is increased to 5.91 atm. ...
... 18) A gas occupies 5.50 m3 at -53.0°C, exerting a pressure of 400.0 kPa. What volume (in liters) would the gas occupy at 272.0°C if the pressure is increased to 5.91 atm. ...
Chapter 2
... Dalton proposed a theory of matter based on it having ultimate, indivisible particles to explain these (and other) laws. 1) Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of a given element has the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from atoms ...
... Dalton proposed a theory of matter based on it having ultimate, indivisible particles to explain these (and other) laws. 1) Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms. 2) All atoms of a given element has the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from atoms ...
Group 2 Elements
... cancels the increased nuclear charge down the group, the increase in atomic radius results in a decrease in the attractive force between the outer electrons and the nucleus. ...
... cancels the increased nuclear charge down the group, the increase in atomic radius results in a decrease in the attractive force between the outer electrons and the nucleus. ...
IPC Semester Exam Review – Chemistry Topics
... The Nature of Science Identify each of the following examples as PURE or APPLIED sciences. 1. Development of the computer chip. 3. SONAR mapping of the ocean floor. 2. Study of sound waves. 4. Investigating the properties of silicon. After reading cooking instructions that said to add salt to water ...
... The Nature of Science Identify each of the following examples as PURE or APPLIED sciences. 1. Development of the computer chip. 3. SONAR mapping of the ocean floor. 2. Study of sound waves. 4. Investigating the properties of silicon. After reading cooking instructions that said to add salt to water ...
Chemistry- CST Review
... 1. What causes gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory? Gas pressure is caused by the random motion of the gas molecules. 2. If someone sprays perfume at the front of the room, will the people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. Yes, the perfume will be s ...
... 1. What causes gas pressure in terms of kinetic theory? Gas pressure is caused by the random motion of the gas molecules. 2. If someone sprays perfume at the front of the room, will the people in the back of the room eventually be able to smell it? Why? Explain completely. Yes, the perfume will be s ...
7 Periodic Properties of the Elements
... A billiard ball is an imperfect model for an atom. The ball has a definite “hard” boundary, while an atom has no definite edge and can be reshaped by interactions with other atoms. That said, the billiard ball is a more appropriate analogy for the nonbonding radius of a fluorine atom. The ball’s rad ...
... A billiard ball is an imperfect model for an atom. The ball has a definite “hard” boundary, while an atom has no definite edge and can be reshaped by interactions with other atoms. That said, the billiard ball is a more appropriate analogy for the nonbonding radius of a fluorine atom. The ball’s rad ...
Chapter 2 - Molecules of Life (Biochemistry) Periodic Table of
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
... • Electrons not shared equally! • One atom “hogs” the electrons! • This leads to the formation of hydrogen bonds.! ...
Prerequisite Knowledge for Chemistry
... The periodic table is ordered from left to right and down by increasing atomic number. ...
... The periodic table is ordered from left to right and down by increasing atomic number. ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of
... Work out the following problems and record your answers on the cover sheet. Hand in cover sheet. 1) An unknown acid reacts with NaOH according to the equation, H2X(s) + 2 NaOH(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Na2X(aq). What is the molar mass of the acid if 22.4 mL of 0.0848 M NaOH is needed to neutralize 0.1846 g o ...
... Work out the following problems and record your answers on the cover sheet. Hand in cover sheet. 1) An unknown acid reacts with NaOH according to the equation, H2X(s) + 2 NaOH(aq) → 2 H2O(l) + Na2X(aq). What is the molar mass of the acid if 22.4 mL of 0.0848 M NaOH is needed to neutralize 0.1846 g o ...
chemistry final - Madison Public Schools
... 16. A substance whose mass is 48.00 grams occupies a volume of 12.0 cm3. What is the density of the substance? A. 0.25 g ...
... 16. A substance whose mass is 48.00 grams occupies a volume of 12.0 cm3. What is the density of the substance? A. 0.25 g ...
1. Select the correct statement about subatomic particles. a
... 81. How many moles of glucose, C6H12O6, can be “burned” biologically when 10.0 moles of oxygen are available? a. 0.938 mol d. 60.0 mol b. 1.67 mol e. 301 mol c. 53.3 mol 82. Hydrogen gas can be produced by reacting aluminum with sulfuric acid. How many moles of sulfuric acid are needed to completely ...
... 81. How many moles of glucose, C6H12O6, can be “burned” biologically when 10.0 moles of oxygen are available? a. 0.938 mol d. 60.0 mol b. 1.67 mol e. 301 mol c. 53.3 mol 82. Hydrogen gas can be produced by reacting aluminum with sulfuric acid. How many moles of sulfuric acid are needed to completely ...
Chemistry Test Review - Greenslime Home Page
... What is the difference between physical properties, physical changes & chemical changes? a. Physical properties are what you see, feel hear from objects and can be used to describe it. b. Physical changes occur when you alter the shape or size of an object, but it is still made of the same “stuff” a ...
... What is the difference between physical properties, physical changes & chemical changes? a. Physical properties are what you see, feel hear from objects and can be used to describe it. b. Physical changes occur when you alter the shape or size of an object, but it is still made of the same “stuff” a ...
Chemical Equations
... the arrow) and the products (on the right of the arrow). C. The law of conservation of mass and energy must be satisfied. Therefore the same number of atoms of each element must appear on each side of a correct chemical equation. ...
... the arrow) and the products (on the right of the arrow). C. The law of conservation of mass and energy must be satisfied. Therefore the same number of atoms of each element must appear on each side of a correct chemical equation. ...
High School Chemistry
... b. Using the periodic table, predict the charge an atom will acquire when it forms an ion by gaining or losing electrons. c. Compare covalent and ionic bonds with respect to electron behavior and relative bond strengths. d. Diagram a model of a metallic bond and explain how it differs from ionic an ...
... b. Using the periodic table, predict the charge an atom will acquire when it forms an ion by gaining or losing electrons. c. Compare covalent and ionic bonds with respect to electron behavior and relative bond strengths. d. Diagram a model of a metallic bond and explain how it differs from ionic an ...
CHEM 1211K Test IV MULTIPLE CHOICE. (3 points each) 1) The
... 10) Which of the following statements about gases is false? A) All gases are colorless and odorless at room temperature. B) Distances between molecules of gas are very large compared to bond distances within molecules. C) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. D) Gases expand spontaneously to f ...
... 10) Which of the following statements about gases is false? A) All gases are colorless and odorless at room temperature. B) Distances between molecules of gas are very large compared to bond distances within molecules. C) Non-reacting gas mixtures are homogeneous. D) Gases expand spontaneously to f ...
N5 Chemistry Summary notes 2017
... Atoms are mostly empty space made up of smaller sub-atomic particles. At the centre of the atom is the nucleus. This contains two types of particles, called protons and neutrons. Spinning around the nucleus are very fast moving particles called electrons. They move in different levels, called shells ...
... Atoms are mostly empty space made up of smaller sub-atomic particles. At the centre of the atom is the nucleus. This contains two types of particles, called protons and neutrons. Spinning around the nucleus are very fast moving particles called electrons. They move in different levels, called shells ...
Metric Unit – Chapter 1
... To break a compound apart, you must apply _________ (usually heat / electricity) ...
... To break a compound apart, you must apply _________ (usually heat / electricity) ...
Unit 10: Structure and Bonding
... The properties of isotopes The chemical properties of isotopes are identical, this is because isotopes of the same element have the same number of outer electrons. It is the outer electrons that determine the reactivity. The physical properties such as density, melting and boiling points can differ ...
... The properties of isotopes The chemical properties of isotopes are identical, this is because isotopes of the same element have the same number of outer electrons. It is the outer electrons that determine the reactivity. The physical properties such as density, melting and boiling points can differ ...
The Periodic table and subatomic particles
... 1. Read over notes in this package. 2. Redo these worksheets as well as extra practice sheets that have been provided. 3. Go through your grade 9 and 10 notes (should you still have them). 4. Topics to be covered include: Periodic table and its organization, subatomic particles, Bohr-Rutherford diag ...
... 1. Read over notes in this package. 2. Redo these worksheets as well as extra practice sheets that have been provided. 3. Go through your grade 9 and 10 notes (should you still have them). 4. Topics to be covered include: Periodic table and its organization, subatomic particles, Bohr-Rutherford diag ...