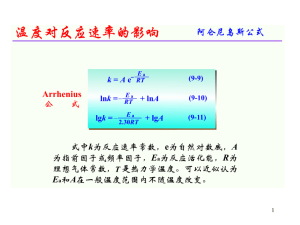
Fall 2008 Blank Exam 1 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... There are six significant figures in this measured quantity. There are five significant figures in this measured quantity. There are four significant figures in this measured quantity. There are three significant figures in this measured quantity. There are two significant figures in this measured q ...
... There are six significant figures in this measured quantity. There are five significant figures in this measured quantity. There are four significant figures in this measured quantity. There are three significant figures in this measured quantity. There are two significant figures in this measured q ...
Document
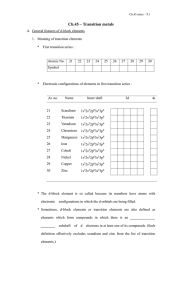
... series, the atomic radii actually ____________again. At the beginning of the series, the increase in __________ _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to th ...
... series, the atomic radii actually ____________again. At the beginning of the series, the increase in __________ _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to th ...
11 myp covalent bonding
... Chemical Bond • But depending on the composition of the substance, the bond between atoms in a compound is classified as either covalent, ionic or metallic. – The chemical bond in compounds made up only of non-metals is referred to as covalent bond. • We will consider covalent bonds, and look at ho ...
... Chemical Bond • But depending on the composition of the substance, the bond between atoms in a compound is classified as either covalent, ionic or metallic. – The chemical bond in compounds made up only of non-metals is referred to as covalent bond. • We will consider covalent bonds, and look at ho ...
Lecture 7
... The greater charge and smaller size of these ions compared to group 1 and the fact that there are twice as many delocalized outer electrons accounts for the greater hardness and higher melting points compared to group 1. Like group 1 compounds, much of the reactivity is due to the reactions of the a ...
... The greater charge and smaller size of these ions compared to group 1 and the fact that there are twice as many delocalized outer electrons accounts for the greater hardness and higher melting points compared to group 1. Like group 1 compounds, much of the reactivity is due to the reactions of the a ...
The Chemical Context of Life
... 鍵, the atoms share the electron equally, ex. H2, O2, CH4. • In a polar covalent bond 極性共價鍵, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally, ex. H2O • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule Copyright © 200 ...
... 鍵, the atoms share the electron equally, ex. H2, O2, CH4. • In a polar covalent bond 極性共價鍵, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally, ex. H2O • Unequal sharing of electrons causes a partial positive or negative charge for each atom or molecule Copyright © 200 ...
Since the electric field intensity (the voltage difference between two
... An electric current results from the motion of electrically charged particles in response to forces that act on them from an externally applied electric field. Positively charged particles are accelerated in the field direction, negatively charged particles in the direction opposite. Within most sol ...
... An electric current results from the motion of electrically charged particles in response to forces that act on them from an externally applied electric field. Positively charged particles are accelerated in the field direction, negatively charged particles in the direction opposite. Within most sol ...
200things2know
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
200 Things to Know to Pass the Chemistry Regents
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
200 Ways to Pass the Chemistry
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
... Which of the following atoms forms a stable ion that does not have an octet structure? Li F Na Cl 98. Covalent bonds form when two atoms share a pair of electrons. How many covalent bonds are found in a nitrogen (N2) molecule? 99. Ionic bonds form when one atom transfers an electron to another atom ...
AP CHEMISTRY SUMMER ASSIGNMENT AP Chemistry is a
... elements tend to lose electrons. They are good conductors, shiny, malleable and ductile. They are solids except for liquid mercury. Nonmetals – elements located to the right of the staircase, plus Hydrogen; they share or gain electrons. Nonmetals can be solids, liquid (Br2) or gases. They are brittl ...
... elements tend to lose electrons. They are good conductors, shiny, malleable and ductile. They are solids except for liquid mercury. Nonmetals – elements located to the right of the staircase, plus Hydrogen; they share or gain electrons. Nonmetals can be solids, liquid (Br2) or gases. They are brittl ...
Lecture 1 - Introduction to Semiconductors - Outline Introductions/Announcements Handouts:
... But, the balance happens on an even finer scale. The Principle of Detailed Balance tells us that each G-R path is in balance: ...
... But, the balance happens on an even finer scale. The Principle of Detailed Balance tells us that each G-R path is in balance: ...
Chapter 2 (Hill/Petrucci/McCreary/Perry This chapter deals with
... 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses and other properties 4. chemical reactions involve the uniting or the separation of atoms of different elements Dalton ...
... 2. in chemical reactions, atoms are neither created nor destroyed 3. atoms of each element have unique properties - all atoms of a given atom are identical and have identical masses and other properties 4. chemical reactions involve the uniting or the separation of atoms of different elements Dalton ...
June review January 2012 part A
... (l) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (2) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more positively charged electrons. (3) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (4) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded ...
... (l) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (2) A neutral nucleus is surrounded by one or more positively charged electrons. (3) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded by one or more negatively charged electrons. (4) A positively charged nucleus is surrounded ...
Unit 10
... Determine the types of reactants involved and the products formed in the reaction. Write down the correct formulae of reactants on the left hand side of the arrow. Write down the correct formulae of products on the right hand side of the arrow. Balance the equation with simple whole numbers such tha ...
... Determine the types of reactants involved and the products formed in the reaction. Write down the correct formulae of reactants on the left hand side of the arrow. Write down the correct formulae of products on the right hand side of the arrow. Balance the equation with simple whole numbers such tha ...
Exam 1 Review Sheet Honors Biology This is to be used for
... 38. Compare a covalent bond to an ionic bond. Give an example of a covalent bond. Show, using valence shell diagrams, how two oxygen atoms come together to form a double bond. 39. Arrange the terms single, double and triple covalent bonds from strongest to weakest. Which would require the most energ ...
... 38. Compare a covalent bond to an ionic bond. Give an example of a covalent bond. Show, using valence shell diagrams, how two oxygen atoms come together to form a double bond. 39. Arrange the terms single, double and triple covalent bonds from strongest to weakest. Which would require the most energ ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... Amount of energy that must be absorbed by reactants in 53. their ground states to reach the transition state so that a reaction can occur (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 54. Energy change associated with a mole of gas and ions reacting with water (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 55. The energy change whe ...
... Amount of energy that must be absorbed by reactants in 53. their ground states to reach the transition state so that a reaction can occur (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 54. Energy change associated with a mole of gas and ions reacting with water (A) A (D) D (B) B (E) E (C) C 55. The energy change whe ...
HIGHER TIER CHEMISTRY MINI-MOCK UNIT 2
... The graph below shows the results of four experiments, 1 to 4. In each experiment the amount of calcium carbonate, the volume of acid and the concentration of the acid were kept the same but the temperature of the acid was changed each time. The calcium carbonate was in the form of small lumps of ma ...
... The graph below shows the results of four experiments, 1 to 4. In each experiment the amount of calcium carbonate, the volume of acid and the concentration of the acid were kept the same but the temperature of the acid was changed each time. The calcium carbonate was in the form of small lumps of ma ...
Chemistry Final Review 2017 1. List a set of elements
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
objectives chm 1025 - Miami Dade College
... problems involving the Rydberg equation for hydrogen-like species. [OPTIONAL] c. Comparing and contrasting the particle and wave description of light. d. Relating important advances made in atomic theory to electronic emission and absorption spectra. e. Giving some of the very basic tenants involved ...
... problems involving the Rydberg equation for hydrogen-like species. [OPTIONAL] c. Comparing and contrasting the particle and wave description of light. d. Relating important advances made in atomic theory to electronic emission and absorption spectra. e. Giving some of the very basic tenants involved ...
Molecular Geometry and Chemical Bonding Theory
... According to the valence bond theory, a bond forms when two electrons (usually one from each of two atoms) with opposite spins are present in a region of higher probability formed by overlapping orbitals between the nuclei of the two atoms. For molecules involving more than two atoms, bond formation ...
... According to the valence bond theory, a bond forms when two electrons (usually one from each of two atoms) with opposite spins are present in a region of higher probability formed by overlapping orbitals between the nuclei of the two atoms. For molecules involving more than two atoms, bond formation ...
OKEMOS PUBLIC SCHOOLS
... As the size of an atom increases its attraction for outer electrons (increases/decreases) making the atom have (high/lower) ionization energy ...
... As the size of an atom increases its attraction for outer electrons (increases/decreases) making the atom have (high/lower) ionization energy ...
KEY Midterm Exam 1 Sept.14, 1999 Chemistry 211 PAGE 1 0f 5
... where 1 marg = 4.8648 grams (exactly). Their scale of atomic masses is based on the isotope 3 2S (atomic mass on earth = 31.972 g/mole), so they define one "elom" of 3 2S as the amount of sulfur atoms in exactly 32 margs of 3 2S. Furthermore, they define Nor, or "Ordagova's number" (after their well ...
... where 1 marg = 4.8648 grams (exactly). Their scale of atomic masses is based on the isotope 3 2S (atomic mass on earth = 31.972 g/mole), so they define one "elom" of 3 2S as the amount of sulfur atoms in exactly 32 margs of 3 2S. Furthermore, they define Nor, or "Ordagova's number" (after their well ...
2003
... Distinguish between structures C and D by drawing a diagram showing the arrangement and type of particles in each structure. OUTCOME – P 13 (2 marks) ...
... Distinguish between structures C and D by drawing a diagram showing the arrangement and type of particles in each structure. OUTCOME – P 13 (2 marks) ...