Ionic Bonding - KMChemistryMatters
... • Lattice energies compensate for the loss of up to three electrons. • In general, electrons are removed from orbitals in order of decreasing n (i.e. electrons are removed from 4s before the 3d). Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions are formed when there is an overall charge on a compound containing co ...
... • Lattice energies compensate for the loss of up to three electrons. • In general, electrons are removed from orbitals in order of decreasing n (i.e. electrons are removed from 4s before the 3d). Polyatomic Ions • Polyatomic ions are formed when there is an overall charge on a compound containing co ...
Document
... - Debye assumed that the forces of interaction between a neighboring pair of atoms were roughly equivalent to a linear spring. Pushing the atoms together would have the effect of compressing the spring, and in so doing, a restoring force would be developed that would act to return the atoms to their ...
... - Debye assumed that the forces of interaction between a neighboring pair of atoms were roughly equivalent to a linear spring. Pushing the atoms together would have the effect of compressing the spring, and in so doing, a restoring force would be developed that would act to return the atoms to their ...
Preview Sample 1
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
... D) are always some form of carbohydrate. E) are naturally similar to sugars. 102) Alaska Natives have a lower incidence of heart disease even though their diets are high in fat and cholesterol. This may be due to the large amount of ________ in their diets. A) steroids B) omega-3 fatty acids C) trig ...
Exam 2 Form N - TAMU Chemistry
... a) Light has the characteristics of both a wave and a particle. b) The number of electrons ejected from a metal surface irradiated with visible light does not depend on the color of the light as long as the light is above a certain, minimum energy . c) Electrons in atoms are found in s, p, d, or f o ...
... a) Light has the characteristics of both a wave and a particle. b) The number of electrons ejected from a metal surface irradiated with visible light does not depend on the color of the light as long as the light is above a certain, minimum energy . c) Electrons in atoms are found in s, p, d, or f o ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 4
... Strong and Weak Acids and Bases • Strong acids ionize completely to H+ • HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • In a solution of 1.0 M HCl, there is 1M H+ and 1M Cl• No HCl is left un-ionized • Other strong acids ionize in similar fashion ...
... Strong and Weak Acids and Bases • Strong acids ionize completely to H+ • HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • In a solution of 1.0 M HCl, there is 1M H+ and 1M Cl• No HCl is left un-ionized • Other strong acids ionize in similar fashion ...
Solid State Physics and Semiconductors
... Bloch waves with the same k (each has a different periodic component u). Within a band (i.e., for fixed n), nk varies continuously with k, as does its energy. So if one multiply a plane wave eikr by a periodic function, one get a Bloch wave. The quantity k is the so called crystal momentum, very s ...
... Bloch waves with the same k (each has a different periodic component u). Within a band (i.e., for fixed n), nk varies continuously with k, as does its energy. So if one multiply a plane wave eikr by a periodic function, one get a Bloch wave. The quantity k is the so called crystal momentum, very s ...
File
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
... 20. Element whose atoms lose electrons in chemical reactions to become positive ions. 21. Groups 3-12 on the periodic table. 22. Scientist who performed the gold foil experiment, and concluded that an atom must be composed of mostly empty space with a small, dense, positively-charged nucleus. 23. An ...
Chemistry for BIOS 302
... Atoms are usually neutral in electrical charge, which means that they have the same number of electrons (- charge) as protons (+ charge). Electrons circle the nucleus at defined positions called shells. The innermost shell of every atom holds 2 electrons. The next two shells hold up to 8 electrons. ...
... Atoms are usually neutral in electrical charge, which means that they have the same number of electrons (- charge) as protons (+ charge). Electrons circle the nucleus at defined positions called shells. The innermost shell of every atom holds 2 electrons. The next two shells hold up to 8 electrons. ...
HERE
... grams of water and quickly sealed the bag. The tablet began to fizz and soon disappeared. The bag was filled with gas. If the mass of the liquid after the reaction is completed is still 50 grams, how much gas is produced? A) 30 grams B) 50 grams C) 80 grams D) 90 grams 17) Which piece of lab equipme ...
... grams of water and quickly sealed the bag. The tablet began to fizz and soon disappeared. The bag was filled with gas. If the mass of the liquid after the reaction is completed is still 50 grams, how much gas is produced? A) 30 grams B) 50 grams C) 80 grams D) 90 grams 17) Which piece of lab equipme ...
Atom The smallest part of an element that can exist on its own
... Dibasic acid One which has 2 replaceable H atoms per molecule Isotopes Atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers - As the number of protons increases, the number of neutrons increases relatively faster, so small atoms have proton and neutron numbers which are comparable whereas ...
... Dibasic acid One which has 2 replaceable H atoms per molecule Isotopes Atoms having the same atomic number but different mass numbers - As the number of protons increases, the number of neutrons increases relatively faster, so small atoms have proton and neutron numbers which are comparable whereas ...
Atomic Theories- Part I - Tenafly Public Schools
... chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Example: CO2 ...
... chemically combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. Example: CO2 ...
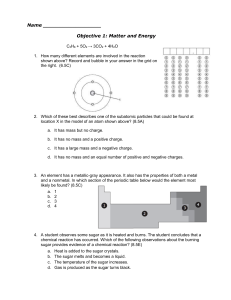
Name Objective 1: Matter and Energy C3H8 + 5O2 → 3CO2 + 4H2O
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
... 16. Which two compounds contain the same total number of atoms? (8.5D) a. C3H8 and C2H6 b. NO2 and KCl c. 2Li2S and Be4Cl2 d. 2CO and CO2 17. All of the following are indicators of a chemical change except — (8.5E) a. formation of a gas b. change in temperature c. change in the state of matter d. fo ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... 13. The prefix mono-‐ means “one,” and the prefix poly-‐ means “many.” How are these meanings related to the terms monomer and polymer? ...
... 13. The prefix mono-‐ means “one,” and the prefix poly-‐ means “many.” How are these meanings related to the terms monomer and polymer? ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2013
... a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to form different compounds. 2. Which best describes the current atomic theory? a. Atoms ...
... a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to form different compounds. 2. Which best describes the current atomic theory? a. Atoms ...
Final review free response ch 1-4
... electrolytes versus nonelectrolytes, strond versus weak, strong acids and bases Molarity, dilution Precipitate Acid/Base (neutralizations) titrations, limiting reagents for aqueous solutions. REDOX oxidation numbers, LEO goes GER (OIL RIG) 1. Complete the molecular and write the complete i ...
... electrolytes versus nonelectrolytes, strond versus weak, strong acids and bases Molarity, dilution Precipitate Acid/Base (neutralizations) titrations, limiting reagents for aqueous solutions. REDOX oxidation numbers, LEO goes GER (OIL RIG) 1. Complete the molecular and write the complete i ...
the electron - QuarkPhysics.ca
... The different numbers of electrons in atoms and the different energy levels for the electrons around the atomic nucleus are the only things that produce the fundamental distinctions between helium, lead, titanium, oxygen, and other elements. The number of protons is important only in that it determi ...
... The different numbers of electrons in atoms and the different energy levels for the electrons around the atomic nucleus are the only things that produce the fundamental distinctions between helium, lead, titanium, oxygen, and other elements. The number of protons is important only in that it determi ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 17-20
... a. Atoms that make up your body were formed in ancient stars. b. Atoms that make up your body were previously a part of your ...
... a. Atoms that make up your body were formed in ancient stars. b. Atoms that make up your body were previously a part of your ...
Final Exam - Seattle Central College
... • Know that hydrogen bonds are the strongest type of intermolecular force, dipole-dipole forces are the next strongest, and London forces are generally the weakest. – Recognize that London forces increase with more electrons—use size to determine relative number of electrons for different molecules. ...
... • Know that hydrogen bonds are the strongest type of intermolecular force, dipole-dipole forces are the next strongest, and London forces are generally the weakest. – Recognize that London forces increase with more electrons—use size to determine relative number of electrons for different molecules. ...
Pretest 4.3 2008
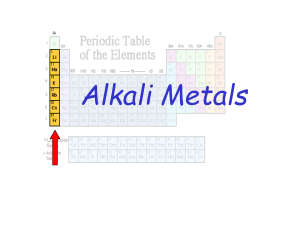
... a. In Period 2, electronegativity increases as the atomic number increases. b. In Period 2, ionization energy decreases as the atomic number increases. c. In Period 2, atomic radius does not change as the atomic number increases. d. In group 1 (alkali metals), boiling points decrease and then increa ...
... a. In Period 2, electronegativity increases as the atomic number increases. b. In Period 2, ionization energy decreases as the atomic number increases. c. In Period 2, atomic radius does not change as the atomic number increases. d. In group 1 (alkali metals), boiling points decrease and then increa ...
Notes matter energy
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
... number and type of atoms in a molecule. For example, H2SO4 (sulfuric acid) is the formula for a molecule because it consists of only nonmetals. The molecule is made up of 2 hydrogen atoms, 1 sulfur atom, and 4 oxygen atoms (and 7 total atoms). Subscripts indicate the number of atoms in the formula ( ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... 1. Which element has the smallest atomic number? F 2. Which element has the largest atomic number? H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductor ...
... 1. Which element has the smallest atomic number? F 2. Which element has the largest atomic number? H 3. Which non-metal has the smallest atomic mass? F 4. Which metal has the largest atomic mass? D 5. Which elements are considered good conductors? C,E,D, 6. Which element is considered semi-conductor ...
Atoms, Molecules, and Ions
... Chemistry 106 and 116 are general chemistry courses intended for students with an interest or background in science. No prior chemistry instruction is required or assumed. A general, basic understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, a ...
... Chemistry 106 and 116 are general chemistry courses intended for students with an interest or background in science. No prior chemistry instruction is required or assumed. A general, basic understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, a ...
CMC Chapter 5
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...
... The Atom and Unanswered Questions • Recall that in Rutherford's model, the atom’s mass is concentrated in the nucleus and electrons move around it. • The model doesn’t explain how the electrons were arranged around the nucleus. • The model doesn’t explain why negatively charged electrons aren’t pul ...