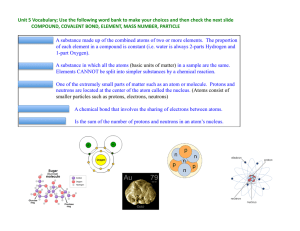
Atoms and bonds in molecules and chemical
... unifies the phenomena better than any other. In the causal model the explanation will trace the causal processes and interactions leading to the event (i.e. the causal history) , or at least a subset of these, as well as describing the processes and interactions that make up the event itself. Except ...
... unifies the phenomena better than any other. In the causal model the explanation will trace the causal processes and interactions leading to the event (i.e. the causal history) , or at least a subset of these, as well as describing the processes and interactions that make up the event itself. Except ...
Final Exam Review 2010 UbD
... 31. What are the properties of metals? ________________________________________________________ 32. What are the properties of metalloids? ____________________________________________________ 33. What are the properties of non-metals? ____________________________________________________ 34. Define “ ...
... 31. What are the properties of metals? ________________________________________________________ 32. What are the properties of metalloids? ____________________________________________________ 33. What are the properties of non-metals? ____________________________________________________ 34. Define “ ...
Chemical Reactions PPT
... type of atom on the reactants side of the chemical equation MUST be equal to the number of each type of atom on the products side of the equation. • Coefficient-represent the number of units of each substance taking part in the reaction ...
... type of atom on the reactants side of the chemical equation MUST be equal to the number of each type of atom on the products side of the equation. • Coefficient-represent the number of units of each substance taking part in the reaction ...
Document
... (a) Match the substances in the boxes on the left with the descriptions in the boxes on the right. The first one has been done for you. ...
... (a) Match the substances in the boxes on the left with the descriptions in the boxes on the right. The first one has been done for you. ...
Utah - Wavefunction, Inc.
... origin. The periodic table is used to organize elements by structure. A relationship exists between the chemical behavior and the structure of atoms. The periodic table reflects this relationship. The nucleus of an atom is a tiny fraction of the volume of the atom. Each proton or neutr ...
... origin. The periodic table is used to organize elements by structure. A relationship exists between the chemical behavior and the structure of atoms. The periodic table reflects this relationship. The nucleus of an atom is a tiny fraction of the volume of the atom. Each proton or neutr ...
Lecture 2 - TCD Chemistry
... Material particles which cannot be divided into smaller particles, but they can react to give other elementary particles Protons, neutron, electrons (valid for nearly all atoms: exception the hydrogen atom) ...
... Material particles which cannot be divided into smaller particles, but they can react to give other elementary particles Protons, neutron, electrons (valid for nearly all atoms: exception the hydrogen atom) ...
r - Purdue Physics
... •Note atomic mass is the actual mass of the nucleus in atomic mass units with Carbon set to be 12 units and atomic mass in general is not an integer •H2O gives the number of atoms required to make a molecule • water = 2 Hydrogen plus 1 Oxygen •In a nuclear reaction energy, charge, and atomic mass ar ...
... •Note atomic mass is the actual mass of the nucleus in atomic mass units with Carbon set to be 12 units and atomic mass in general is not an integer •H2O gives the number of atoms required to make a molecule • water = 2 Hydrogen plus 1 Oxygen •In a nuclear reaction energy, charge, and atomic mass ar ...
AQA Additional Sci C2 Revision Guide
... outer shell of its atoms. Elements in groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table only have 1 or 2 electrons in their outer shells so these form positive ions by losing their outer electrons. Elements in groups 6 and 7 of the periodic table only need 1 or 2 electrons to fill up their outer shells so these ...
... outer shell of its atoms. Elements in groups 1 and 2 of the periodic table only have 1 or 2 electrons in their outer shells so these form positive ions by losing their outer electrons. Elements in groups 6 and 7 of the periodic table only need 1 or 2 electrons to fill up their outer shells so these ...
I, I, I, 4- Measurement Unit Conversions- Kilo
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
... Describe trends in properties (e.g., ionization energy or reactivity as a function of location on the periodic table, boiling point of organic liquids as a function of molecular weight). Atomic radius is one-half of the distance between the center of identical atoms that are not bonded together. Ion ...
Balancing RedOx reactions handout
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to it’s charge. 3. If a group of atoms is ionic, the individual oxidation numbers must add up to its charge. (CO32-, NO3- , etc.) 4. The oxidation numbers of elements in a neutral molecule must add up to zero. (H2O, SO3 , KMnO4 , etc.) 5. Fluorine ...
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is equal to it’s charge. 3. If a group of atoms is ionic, the individual oxidation numbers must add up to its charge. (CO32-, NO3- , etc.) 4. The oxidation numbers of elements in a neutral molecule must add up to zero. (H2O, SO3 , KMnO4 , etc.) 5. Fluorine ...
Sub Unit Plan 1 Chem Periodic Table
... II.3 Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. (3.1v) II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, ...
... II.3 Elements can be classified by their properties and located on the Periodic Table as metals, nonmetals, metalloids (B, Si, Ge, As, Sb, Te), and noble gases. (3.1v) II.4 Elements can be differentiated by their physical properties. Physical properties of substances, such as density, conductivity, ...
CHAPTER 10
... Valence bond theory states that a stable molecule forms from reacting atoms when the potential energy of the system has decreased to a minimum. As the Cl atoms approach to form the Cl2 molecule, an electron in a p orbital of each atom is attracted to the nucleus of the other atom. As the atoms get c ...
... Valence bond theory states that a stable molecule forms from reacting atoms when the potential energy of the system has decreased to a minimum. As the Cl atoms approach to form the Cl2 molecule, an electron in a p orbital of each atom is attracted to the nucleus of the other atom. As the atoms get c ...
Review Unit 5
... CHEMICALLY STABLE: Elements that are nonreactive because their last electron shell is completely filled with 8 electrons. (e.g. Neon, Argon, Krypton.) ISOTOPE: ...
... CHEMICALLY STABLE: Elements that are nonreactive because their last electron shell is completely filled with 8 electrons. (e.g. Neon, Argon, Krypton.) ISOTOPE: ...
Final Exam - W09
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
Covalent Bonding and Molecular Structure
... between two charged species is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge on the particles (qA and qB in Equation 8.1) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two particles (r in Equation 8.1). ...
... between two charged species is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge on the particles (qA and qB in Equation 8.1) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two particles (r in Equation 8.1). ...
© NCERT not to be republished
... solution is formed and when H+ ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen? 46. A solution of KMnO4 on reduction yields either a colourless solution or a brown precipitate or a green solution depending on pH of the solution. What different stages o ...
... solution is formed and when H+ ions are added to yellow solution, an orange solution is obtained. Explain why does this happen? 46. A solution of KMnO4 on reduction yields either a colourless solution or a brown precipitate or a green solution depending on pH of the solution. What different stages o ...
Year 9 Chemical Sciences Program Term 3 Course 2 2017
... modelling chemical reactions in terms of rearrangement of atoms describing observed reactions using word equations considering the role of energy in chemical reactions recognising that the conservation of mass in a chemical reaction can be demonstrated by simple chemical equations ...
... modelling chemical reactions in terms of rearrangement of atoms describing observed reactions using word equations considering the role of energy in chemical reactions recognising that the conservation of mass in a chemical reaction can be demonstrated by simple chemical equations ...
lewis dot diagrams (structures) for atoms and ions predicting
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
... 2. Chemical bonding is the process of atoms combining to form new __________________________. 3. Matter tends to exist in its ______________________________ energy state. 4. A(n) __________________________ bond is a bond in which one atom donates electrons to another atom. 5. When the number of prot ...
CHAPTER 10 CHEMICAL BONDING II: MOLECULAR GEOMETRY
... The Lewis structure of PCl3 is shown below. Since in the VSEPR method the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom (phosphorus, in this case) is important in determining the structure, the lone pairs of electrons around the chlorine atoms have been omitted for simp ...
... The Lewis structure of PCl3 is shown below. Since in the VSEPR method the number of bonding pairs and lone pairs of electrons around the central atom (phosphorus, in this case) is important in determining the structure, the lone pairs of electrons around the chlorine atoms have been omitted for simp ...
Lecture 2
... Chatt’s explanation: soft metals ACIDS have d electrons available for p-bonding Model: Base donates electron density to metal acceptor. Back donation, from acid to base, may occur from the metal d electrons into vacant orbitals on the base. ...
... Chatt’s explanation: soft metals ACIDS have d electrons available for p-bonding Model: Base donates electron density to metal acceptor. Back donation, from acid to base, may occur from the metal d electrons into vacant orbitals on the base. ...
Nonlocal Effects in the Plasmons of Strongly Interacting
... on extended planar surfaces,18 ωp and η are the valence-electrongas plasma frequency and the plasmon width of the bulk metal, respectively, VF is the Fermi velocity, and a is the particle radius. In other words, the damping rate η in the conduction electron motion is increased by the rate of collisi ...
... on extended planar surfaces,18 ωp and η are the valence-electrongas plasma frequency and the plasmon width of the bulk metal, respectively, VF is the Fermi velocity, and a is the particle radius. In other words, the damping rate η in the conduction electron motion is increased by the rate of collisi ...
Redox
... Before metallurgy, humans discovered fire. The technology of fire has been crucial in the development of human cultures, but only relatively recently (18th century) have we come to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burnin ...
... Before metallurgy, humans discovered fire. The technology of fire has been crucial in the development of human cultures, but only relatively recently (18th century) have we come to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burnin ...