2002 local exam - Virginia Section
... the lettered choice that best fits the statement for each question and fill in the corresponding block on the answer sheet. You may use a choice more than once, once, or not at all. (A) density (B) equilibrium constant (C) freezing point (D) molarity (E) molecular mass 4. Can be expressed in moles p ...
... the lettered choice that best fits the statement for each question and fill in the corresponding block on the answer sheet. You may use a choice more than once, once, or not at all. (A) density (B) equilibrium constant (C) freezing point (D) molarity (E) molecular mass 4. Can be expressed in moles p ...
Higher Chemistry - Mobile Resource
... a reaction. At first we might think this is because there is an increase in the number of collisions at the higher temperature. However it can be shown that a 10°C rise in temperature hardly increases the number of collisions yet we know that the rate roughly doubles. It can also be shown that rates ...
... a reaction. At first we might think this is because there is an increase in the number of collisions at the higher temperature. However it can be shown that a 10°C rise in temperature hardly increases the number of collisions yet we know that the rate roughly doubles. It can also be shown that rates ...
General and Organic Chemistry Review Primer
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
... the number of protons and neutrons. Calculating an element’s mass number is complicated by the existence of isotopes, atoms of an element with the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. Many naturally occurring elements exist as a mixture of isotopes. For example, carbon has three ...
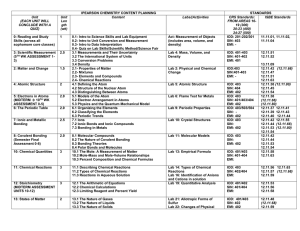
System International Base Units
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions - electrons transferred from reducing agent to oxidizing agent Combination Reaction A + B AB o Example: 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition Reaction AB A + B o Example: 2H2O2 H2O + O2 Combustion Reaction Reactant + O2 Products, (one of the reactants is always ...
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions - electrons transferred from reducing agent to oxidizing agent Combination Reaction A + B AB o Example: 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition Reaction AB A + B o Example: 2H2O2 H2O + O2 Combustion Reaction Reactant + O2 Products, (one of the reactants is always ...
System International Base Units
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions - electrons transferred from reducing agent to oxidizing agent Combination Reaction A + B AB o Example: 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition Reaction AB A + B o Example: 2H2O2 H2O + O2 Combustion Reaction Reactant + O2 Products, (one of the reactants is always ...
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions - electrons transferred from reducing agent to oxidizing agent Combination Reaction A + B AB o Example: 2Na + Cl2 2NaCl Decomposition Reaction AB A + B o Example: 2H2O2 H2O + O2 Combustion Reaction Reactant + O2 Products, (one of the reactants is always ...
Final Exam Practice Problems: R = 0.0821 Latm/molK NA = 6.022
... A) Increase heat or reduce pressure B) Increase heat or increase pressure C) Cool or reduce pressure D) Cool or increase pressure E) None of the above 36. Draw the best Lewis structure for the free radical, NO2- What is the formal charge on the N? A) 0 B) +1 C) -1 D) +2 E) -2 37. What element is und ...
... A) Increase heat or reduce pressure B) Increase heat or increase pressure C) Cool or reduce pressure D) Cool or increase pressure E) None of the above 36. Draw the best Lewis structure for the free radical, NO2- What is the formal charge on the N? A) 0 B) +1 C) -1 D) +2 E) -2 37. What element is und ...
Fundamental of Organic chemistry
... The hybrid orbitals are in tetravalent arrangement in order to minimize the repulsion among them. For such sp3 orbitals overlapping with is orbitals from four hydrogen atoms, methane is formed. ...
... The hybrid orbitals are in tetravalent arrangement in order to minimize the repulsion among them. For such sp3 orbitals overlapping with is orbitals from four hydrogen atoms, methane is formed. ...
Summaries of Review Topics for AP Chemistry
... (1) The simplest ratio of the ions represented in an ionic compound is called a formula unit. (2) If an ion consists of only one atom, it’s called a monatomic ion. The charge (or oxidation number/state) of a monatomic ion is equal to the number of electrons that were transferred from an atom. Ex: Ca ...
... (1) The simplest ratio of the ions represented in an ionic compound is called a formula unit. (2) If an ion consists of only one atom, it’s called a monatomic ion. The charge (or oxidation number/state) of a monatomic ion is equal to the number of electrons that were transferred from an atom. Ex: Ca ...
- Catalyst
... Step 1) Assign oxidation numbers to all elements in the equation. Step 2) From the changes in oxidation numbers, identify the oxidized and reduced species. Step 3) Compute the number of electrons lost in the oxidation and gained in the reduction from the oxidation number changes. Draw tie-lines betw ...
... Step 1) Assign oxidation numbers to all elements in the equation. Step 2) From the changes in oxidation numbers, identify the oxidized and reduced species. Step 3) Compute the number of electrons lost in the oxidation and gained in the reduction from the oxidation number changes. Draw tie-lines betw ...
1. The compound which could act both as oxidising as well as
... (d) adenine and guanine : thymine and cytosine The equivalent mass of iron in the reaction, 2 Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3 is (a) half of its atomic mass (b)one third of its atomic mass (c) same as its atomic mass (d)one fourth of its atomic mass In the reaction, 4NH3+ 5O24NO + 6H2O. When one mole of ammonia ...
... (d) adenine and guanine : thymine and cytosine The equivalent mass of iron in the reaction, 2 Fe + 3Cl2 → 2FeCl3 is (a) half of its atomic mass (b)one third of its atomic mass (c) same as its atomic mass (d)one fourth of its atomic mass In the reaction, 4NH3+ 5O24NO + 6H2O. When one mole of ammonia ...
Course Map_2011-2012 - Kenwood Academy High School
... 12.11.74 Understand that the magnitude of a force F is defined as F = ma (Force equals Mass times Acceleration). Know how to perform such calculations. Understand that whenever one object exerts force on another, a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted on the first object. Un ...
... 12.11.74 Understand that the magnitude of a force F is defined as F = ma (Force equals Mass times Acceleration). Know how to perform such calculations. Understand that whenever one object exerts force on another, a force equal in magnitude and opposite in direction is exerted on the first object. Un ...
Nanostructures and Nanomaterials Characterization and Properties
... worry how electrons are accelerated, when you apply an electrical field. How this electrical conductivity is actually going to change with temperature, as we shall see soon. Many aspects of this response, that means the response is the material to external stimuli. These external stimuli could invol ...
... worry how electrons are accelerated, when you apply an electrical field. How this electrical conductivity is actually going to change with temperature, as we shall see soon. Many aspects of this response, that means the response is the material to external stimuli. These external stimuli could invol ...
Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... bonding) 30. know which metals need Roman numerals in the names for their ionic compounds and be able to work from a formula back to a name containing a Roman numeral 31. understand the nature of covalent bonding that holds together non-metal atoms 32. be able to name covalent compounds given a name ...
... bonding) 30. know which metals need Roman numerals in the names for their ionic compounds and be able to work from a formula back to a name containing a Roman numeral 31. understand the nature of covalent bonding that holds together non-metal atoms 32. be able to name covalent compounds given a name ...
2. CHEMICAL ACTIVITY of the METALS 3. PATTERNS of the
... • brass, a mixture of z).................... and ................... • aa)...................................., with a very low melting point, is an alloy of ab).................................. and .................................... and is used in ac)..................................... and ... ...
... • brass, a mixture of z).................... and ................... • aa)...................................., with a very low melting point, is an alloy of ab).................................. and .................................... and is used in ac)..................................... and ... ...
Definition of a Mineral
... • Describes how light reflects off the surface • Main categories are “metallic” and “nonmetallic” • Non-metallic includes “dull,” glassy,” waxy,” “pearly,” and others ...
... • Describes how light reflects off the surface • Main categories are “metallic” and “nonmetallic” • Non-metallic includes “dull,” glassy,” waxy,” “pearly,” and others ...
GCE Getting Started - Edexcel
... Atoms of metallic elements in Groups 1,2 and 3 can form positive ions when they take part in reactions since they are readily able to lose electrons. Atoms of Group 1 metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge, e.g. Na+ Atoms of Group 2 metals lose two electrons and form ions with a 2+ ...
... Atoms of metallic elements in Groups 1,2 and 3 can form positive ions when they take part in reactions since they are readily able to lose electrons. Atoms of Group 1 metals lose one electron and form ions with a 1+ charge, e.g. Na+ Atoms of Group 2 metals lose two electrons and form ions with a 2+ ...
An element is a fundamental substance that cannot be chemically
... • Chemical combination of elements to make different substances occurs when atoms join together in small whole-number ratios. • Chemical reactions only rearrange the way that atoms are combined; the atoms themselves are unchanged. ...
... • Chemical combination of elements to make different substances occurs when atoms join together in small whole-number ratios. • Chemical reactions only rearrange the way that atoms are combined; the atoms themselves are unchanged. ...
Chemistry 201 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State University
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
... calculator, and your University ID Card. If you have notes with you, place them in a sealed backpack and place the backpack OUT OF SIGHT or place the notes directly on the table at the front of the room. Fill in the front page of the Scantron answer sheet with your test form number (listed above), l ...
Redox - edl.io
... 5. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation state of -2. Exceptions to this rule include peroxides (compound containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of -1, as in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and OF2 in which oxygen is assigned a +2 oxidation state. 6. In its covalent ...
... 5. Oxygen is usually assigned an oxidation state of -2. Exceptions to this rule include peroxides (compound containing the O22- group), where each oxygen is assigned an oxidation state of -1, as in hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and OF2 in which oxygen is assigned a +2 oxidation state. 6. In its covalent ...
Ch 4 Types of Chemical Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Hydrogen is almost always +1; metal hydrides are an exception, where it is -1 (in these situations, hydrogen is placed at the end of a chemical formula like LiH) The sum of the oxidation states must be zero for a neutral compound; for polyatomic ions, the sum of the oxidation states must equal t ...
... Hydrogen is almost always +1; metal hydrides are an exception, where it is -1 (in these situations, hydrogen is placed at the end of a chemical formula like LiH) The sum of the oxidation states must be zero for a neutral compound; for polyatomic ions, the sum of the oxidation states must equal t ...
Chemistry - Onslow College
... 3. use the relationship n = cv, and use a mole ratio from a given chemical equation 4. Use the relationship m = nMr and use a mole ratio from a given equation 5. determine the concentration of an unknown solution ...
... 3. use the relationship n = cv, and use a mole ratio from a given chemical equation 4. Use the relationship m = nMr and use a mole ratio from a given equation 5. determine the concentration of an unknown solution ...
Examination
... Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry. Carbon dioxide, CO2, changes from the solid phase to the gas phase at 1 atm and 194.5 K. In the solid phase, CO2 is often called dry ice. When dry ice sublimes in air at 298 K, the water vapor i ...
... Base your answers to questions 66 through 68 on the information below and on your knowledge of chemistry. Carbon dioxide, CO2, changes from the solid phase to the gas phase at 1 atm and 194.5 K. In the solid phase, CO2 is often called dry ice. When dry ice sublimes in air at 298 K, the water vapor i ...
9.1 Electron Transfer Reactions
... 5. O is usually – 2 (except for peroxides where it is – 1) 6. H is usually +1 (except for hydrides where it is – 1) 7. The periodic table can used as a guide for an atom’s oxidation number in a compound (ex: F is usually – 1, alkali metals are usually +1) ...
... 5. O is usually – 2 (except for peroxides where it is – 1) 6. H is usually +1 (except for hydrides where it is – 1) 7. The periodic table can used as a guide for an atom’s oxidation number in a compound (ex: F is usually – 1, alkali metals are usually +1) ...
- TestbankU
... 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. A) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water C) two polar covalent bonds react D) a hydrogen atom loses an electron Answer: A Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 ...
... 36) Van der Waals interactions may result when _____. A) electrons are not symmetrically distributed in a molecule B) molecules held by ionic bonds react with water C) two polar covalent bonds react D) a hydrogen atom loses an electron Answer: A Bloom's Taxonomy: Knowledge/Comprehension Section: 2.3 ...