inorganic chemistry iii - National Open University of Nigeria
... of 1871 with the modern periodic table, you will see that it is remarkably similar in its coverage to the modern periodic table, with the exception that the Group VII (18) is missing. Elements of Group 18 were not known at that time and have been discovered only about a hundred years back. Since the ...
... of 1871 with the modern periodic table, you will see that it is remarkably similar in its coverage to the modern periodic table, with the exception that the Group VII (18) is missing. Elements of Group 18 were not known at that time and have been discovered only about a hundred years back. Since the ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... balanced. The next step is to combine the two halfreactions to form an overall equation. 6) Multiply through each half-reactions by appropriate coefficients to match electrons in each half-reaction. (i.e. number of electrons lost by the oxidized species must equal the number gained by the reduced on ...
... balanced. The next step is to combine the two halfreactions to form an overall equation. 6) Multiply through each half-reactions by appropriate coefficients to match electrons in each half-reaction. (i.e. number of electrons lost by the oxidized species must equal the number gained by the reduced on ...
Chemical Bonding - The Free Information Society
... The fall in energy when atoms join together is a measure of the stability of the new aggregate. In order to be regarded as a molecule, the aggregate must be sufficiently stable to resist disruption by thermal motions long enough to enable the observation of whatever distinctive properties and compos ...
... The fall in energy when atoms join together is a measure of the stability of the new aggregate. In order to be regarded as a molecule, the aggregate must be sufficiently stable to resist disruption by thermal motions long enough to enable the observation of whatever distinctive properties and compos ...
Chapter 4: Oxidation and Reduction MH5 4
... Unit 3 Oxidation and Reduction Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin 1 Introduction Another important type of reaction in aqueous solution involves the transfer of electrons between two species. This is called an oxidation-reduction or a redox reaction. What happens when zinc pellets are added to an acid? The ...
... Unit 3 Oxidation and Reduction Chemistry 020, R. R. Martin 1 Introduction Another important type of reaction in aqueous solution involves the transfer of electrons between two species. This is called an oxidation-reduction or a redox reaction. What happens when zinc pellets are added to an acid? The ...
chem481chp
... has the same number of bonds. We can determine which is better by determining which has the least formal charge. It takes energy to get a separation of charge in the molecule (as indicated by the formal charge) so the structure with the least formal charge should be lower in energy and thereby be th ...
... has the same number of bonds. We can determine which is better by determining which has the least formal charge. It takes energy to get a separation of charge in the molecule (as indicated by the formal charge) so the structure with the least formal charge should be lower in energy and thereby be th ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... 1. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scientists to conclude that an atom’s (1) positive charge is evenly distributed throughout its volume (2) negative charge is mainly concentrated in its nucleus (3) mass is evenly distributed throughout its volume (4) volume is mainly unoc ...
... 1. Experiments performed to reveal the structure of atoms led scientists to conclude that an atom’s (1) positive charge is evenly distributed throughout its volume (2) negative charge is mainly concentrated in its nucleus (3) mass is evenly distributed throughout its volume (4) volume is mainly unoc ...
IGCSE SoW 2013
... Describe simple tests for the anions: • Cl-, Br- and I-, using dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate solution • SO42-, using dilute hydrochloric acid and barium chloride solution • CO32-, using dilute hydrochloric acid and identifying the carbon dioxide evolved ...
... Describe simple tests for the anions: • Cl-, Br- and I-, using dilute nitric acid and silver nitrate solution • SO42-, using dilute hydrochloric acid and barium chloride solution • CO32-, using dilute hydrochloric acid and identifying the carbon dioxide evolved ...
Chapter 3
... 33. An anion is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable atom. C. a group of stable atoms. D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 34. An cation is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable a ...
... 33. An anion is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable atom. C. a group of stable atoms. D. an atom or group of atoms with a net positive charge. 34. An cation is defined as A. a charged atom or group of atoms with a net negative charge. B. a stable a ...
Review AGº = -RTlnKº Calculate the equilibrium constant Kc at 25 ºC
... Because changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy are state functions, we can use any pathway to calculate the change in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy of an overall reaction. Hess’s Law: ΔH for a process is equal to the sum of ΔH for any set of steps, i.e., for any path that equals the over ...
... Because changes in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy are state functions, we can use any pathway to calculate the change in enthalpy, entropy, and free energy of an overall reaction. Hess’s Law: ΔH for a process is equal to the sum of ΔH for any set of steps, i.e., for any path that equals the over ...
Chemistry English
... How to illustrate the 2p orbitals that contain 6 electrons? 3.12 Writing Electronic Configurations for Atoms The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which must be f ...
... How to illustrate the 2p orbitals that contain 6 electrons? 3.12 Writing Electronic Configurations for Atoms The electronic configurations for an atom is written by listing the orbitals occupied by electrons in the atom along with the number of electrons in each orbitals. Three Rules which must be f ...
Chapter 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... the attractions between the ions are so large that the water molecule will not separate the ion, and the substance remains mostly ...
... the attractions between the ions are so large that the water molecule will not separate the ion, and the substance remains mostly ...
Lab 1
... Above, when adding we look for the least number of accurate places to the right. So above, all of the numbers are 3 places to the right, so our answer, 53.552, must have 3 places to the right; which makes it a 5 sig fig number. ...
... Above, when adding we look for the least number of accurate places to the right. So above, all of the numbers are 3 places to the right, so our answer, 53.552, must have 3 places to the right; which makes it a 5 sig fig number. ...
urbano, mariajose
... • Usually has an atomic number of 6; therefore, it has 4 valence electrons. • Usually completes its outer energy shell by sharing valence electrons in four covalent bonds. (Not likely to form ionic bonds.) Emergent properties, such as the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form, are determined by ...
... • Usually has an atomic number of 6; therefore, it has 4 valence electrons. • Usually completes its outer energy shell by sharing valence electrons in four covalent bonds. (Not likely to form ionic bonds.) Emergent properties, such as the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form, are determined by ...
Answers to NHSCE 2002 Part A Page 1
... H2S > H2Se > H2Te. This is largely due to the fact that the atoms become larger down the group so that the bonds with hydrogen become weaker. A similar effect might be expected in Group 17 with the acids HCl, HBr and HI, however these are all such strong acids that their pH values in aqueous solutio ...
... H2S > H2Se > H2Te. This is largely due to the fact that the atoms become larger down the group so that the bonds with hydrogen become weaker. A similar effect might be expected in Group 17 with the acids HCl, HBr and HI, however these are all such strong acids that their pH values in aqueous solutio ...
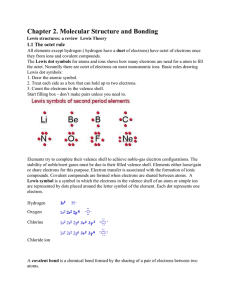
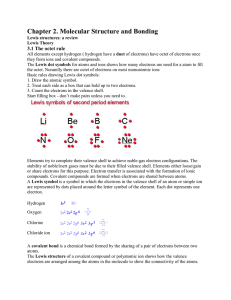
Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding
... has the same number of bonds. We can determine which is better by determining which has the least formal charge. It takes energy to get a separation of charge in the molecule (as indicated by the formal charge) so the structure with the least formal charge should be lower in energy and thereby be th ...
... has the same number of bonds. We can determine which is better by determining which has the least formal charge. It takes energy to get a separation of charge in the molecule (as indicated by the formal charge) so the structure with the least formal charge should be lower in energy and thereby be th ...
Chemistry Notes for the Whole Year Powerpoint
... of electrons in that orbital. For example, 1s1, the first number means energy level one, s is the orbital, and the superscript number means that there is one electron in this orbital. • Start at hydrogen and fill electrons from left to right starting from there. Count how many electrons are in these ...
... of electrons in that orbital. For example, 1s1, the first number means energy level one, s is the orbital, and the superscript number means that there is one electron in this orbital. • Start at hydrogen and fill electrons from left to right starting from there. Count how many electrons are in these ...
3.091 Summary Lecture Notes, Fall 2009
... o It’s a defining equation for quantum mechanics o Think of it as equivalent to Newton’s equation: F=ma o Complex equation that allows us to calculate measurable quantities, such as position, momentum, energy of microscopic systems. o Well beyond the scope of this class… ...
... o It’s a defining equation for quantum mechanics o Think of it as equivalent to Newton’s equation: F=ma o Complex equation that allows us to calculate measurable quantities, such as position, momentum, energy of microscopic systems. o Well beyond the scope of this class… ...
Metals
... exist as an array of ions or atoms bound to each other but with no recognisable molecules. The formula NaCl instead tells us that throughout a sample of NaCl sodium and chlorine atoms are present in the ratio 1:1. Because ionic compounds do not contain molecules the sum of the relative atomic masses ...
... exist as an array of ions or atoms bound to each other but with no recognisable molecules. The formula NaCl instead tells us that throughout a sample of NaCl sodium and chlorine atoms are present in the ratio 1:1. Because ionic compounds do not contain molecules the sum of the relative atomic masses ...
Chemistry General v. 2016
... compounds as pure substances. Explain the law of definite proportions to classify elements and compounds as pure substances. Interpret and apply the law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of mass, constant composition (definite proportions), and multiple proportions. Explain why compound ...
... compounds as pure substances. Explain the law of definite proportions to classify elements and compounds as pure substances. Interpret and apply the law of conservation of energy, law of conservation of mass, constant composition (definite proportions), and multiple proportions. Explain why compound ...
Bohr, Niels Henrik David
... their atoms and that only the atomic weight and possible radioactive behaviour are determined by the small but massive nucleus itself. Rutherford's nuclear atom was both mechanically and electromagnetically unstable, but Bohr imposed stability on it by introducing the new and not yet clarified idea ...
... their atoms and that only the atomic weight and possible radioactive behaviour are determined by the small but massive nucleus itself. Rutherford's nuclear atom was both mechanically and electromagnetically unstable, but Bohr imposed stability on it by introducing the new and not yet clarified idea ...
Electrochemistry Oxidation – Reduction and Oxidation Numbers
... state of –2. (Peroxides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 6. Hydrogen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of +1. (Hydrides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 7. For covalently bonded substances, shared electrons are assigned to t ...
... state of –2. (Peroxides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 6. Hydrogen in a compound or ion usually has an oxidation state of +1. (Hydrides are the exception, in which case the oxidation number is –1.) 7. For covalently bonded substances, shared electrons are assigned to t ...
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on top of another one, as with jewelry, or exhaust pipes. a. To make something look more expensive or shinier b. To improve corrosion resistance ...
... A car battery powers the car through a spontaneous reaction, but what can you do if the battery dies? (c) To coat one metal on top of another one, as with jewelry, or exhaust pipes. a. To make something look more expensive or shinier b. To improve corrosion resistance ...
Avogadro`s Law is relation between
... 11-SF6 is a gas used in modification of eyes. If 2.5 g of this gas introduced in evacuated 500ml container at 83°C What is the pressure in atmosphere? a-992atm ...
... 11-SF6 is a gas used in modification of eyes. If 2.5 g of this gas introduced in evacuated 500ml container at 83°C What is the pressure in atmosphere? a-992atm ...
Basic chemistry - Ross University
... educts, rather than the products. By artificially increasing the pressure further we can shift the equilibrium even more to the educts, by applying a vacuum on the other hand we can shift it to the products. Many reactions cause a change in the temperature of the reaction system. Some salts for exam ...
... educts, rather than the products. By artificially increasing the pressure further we can shift the equilibrium even more to the educts, by applying a vacuum on the other hand we can shift it to the products. Many reactions cause a change in the temperature of the reaction system. Some salts for exam ...