CHEM 1212 Module Ten-Chapter 16 Name
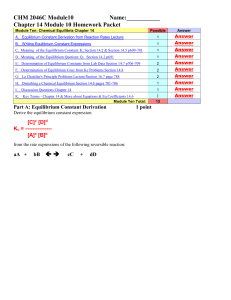
... gases), then the we say the system is in _______________equilibrium. __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in __________________ equilibrium. __________________ 3. The state where the concentrations of the re ...
... gases), then the we say the system is in _______________equilibrium. __________________ 2. If at least one of the reactants or one of the products is not in the same phase, then we say the system is in __________________ equilibrium. __________________ 3. The state where the concentrations of the re ...
Answers - University of Waterloo
... 23 Equal volumes of 0.1 mol L−1 HCl(aq) and 0.1 mol L−1 HF(aq) are titrated in separate experiments with 0.1 mol L−1 NaOH(aq). Which of the following would be equal for both titrations? ...
... 23 Equal volumes of 0.1 mol L−1 HCl(aq) and 0.1 mol L−1 HF(aq) are titrated in separate experiments with 0.1 mol L−1 NaOH(aq). Which of the following would be equal for both titrations? ...
Chapter 10
... A conventional equation plus its associated ∆H term. Thermochemical equations are typically written in one of two different ways, depending on the context for which it is needed. Example: When one mole of acetylene gas reacts with two moles of hydrogen gas, one mole of ethane gas is formed and 311 k ...
... A conventional equation plus its associated ∆H term. Thermochemical equations are typically written in one of two different ways, depending on the context for which it is needed. Example: When one mole of acetylene gas reacts with two moles of hydrogen gas, one mole of ethane gas is formed and 311 k ...
Unit 10: Chemical Reactions
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
... The substances that undergo a chemical reaction are the reactants. The new substances formed are the products. Special symbols are written after formulas in equations to show a substance’s state. The designations for solid, liquid, or gas, are (s), (l), and (g), respectively. A substance dissolv ...
ExamView - 2002 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... When the equation above is correctly balanced and all coefficients are reduced to lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient for H+(aq) is A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 E) 14 50. Which of the following represents acceptable laboratory practice? A) Placing a hot object on a balance pan B) Using distilled water ...
... When the equation above is correctly balanced and all coefficients are reduced to lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient for H+(aq) is A) 2 B) 4 C) 6 D) 8 E) 14 50. Which of the following represents acceptable laboratory practice? A) Placing a hot object on a balance pan B) Using distilled water ...
Lectures on Chapter 4, Part 2 Powerpoint 97 Document
... OH Ag(s) + CN (aq) + O2 (g) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Oxidation: CN-(aq) + Ag(s) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Since we need two cyanide ions to form the complex, add two to the reactant side of the equation. Silver is also oxidized, so it looses an electron, so we add one electron to the product side. 2 CN-(aq) + Ag(s) Ag(CN)2- ...
... OH Ag(s) + CN (aq) + O2 (g) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Oxidation: CN-(aq) + Ag(s) Ag(CN)2-(aq) Since we need two cyanide ions to form the complex, add two to the reactant side of the equation. Silver is also oxidized, so it looses an electron, so we add one electron to the product side. 2 CN-(aq) + Ag(s) Ag(CN)2- ...
Minimum Learning Competencies - Ministry of Education, Ethiopia
... alcohols • Performa an activity of preparing locally distilled alcohol ( Katikalla ) • Explain the chemical reactions of alcohols such as oxidation, reaction with active metals, esterification and dehydration • Write the general structural formulas of aldehydes, Ketones, carboxylic acids and esters ...
... alcohols • Performa an activity of preparing locally distilled alcohol ( Katikalla ) • Explain the chemical reactions of alcohols such as oxidation, reaction with active metals, esterification and dehydration • Write the general structural formulas of aldehydes, Ketones, carboxylic acids and esters ...
Chapter 9 Lota_2 Dæmi A4 Varmafræði
... When each beaker reaches thermal equilibrium, which of the following will be true, and why? You should not need to do any calculations here. (i) Both beakers will be at the same temperature. (ii) The beaker with the copper sample in it will be at a higher temperature. (iii) The beaker with the gold ...
... When each beaker reaches thermal equilibrium, which of the following will be true, and why? You should not need to do any calculations here. (i) Both beakers will be at the same temperature. (ii) The beaker with the copper sample in it will be at a higher temperature. (iii) The beaker with the gold ...
CHEM 1411 – STUDY-GUIDE-for-TEST-2
... 31. Which of the following statements is consistent with Boyle's Law concerning an ideal gas? A) At constant temperature and moles, a plot of volume versus pressure is linear. B) At constant pressure and volume, a plot of temperature versus moles is linear. C) At constant pressure and moles, a plot ...
... 31. Which of the following statements is consistent with Boyle's Law concerning an ideal gas? A) At constant temperature and moles, a plot of volume versus pressure is linear. B) At constant pressure and volume, a plot of temperature versus moles is linear. C) At constant pressure and moles, a plot ...
chemistry (9189)
... describe metallic bonding in terms of a lattice of positive ions surrounded by mobile electrons ...
... describe metallic bonding in terms of a lattice of positive ions surrounded by mobile electrons ...
Document
... Suppose we want DH for the reaction 2C(graphite) + O2(g) 2CO(g) It is difficult to measure directly. However, two other reactions are known: C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g); DH = -393.5 kJ 2CO2(g) 2CO(g) + O2(g); DH = – 566.0 kJ In order for these to add to give the reaction we want, we must multi ...
... Suppose we want DH for the reaction 2C(graphite) + O2(g) 2CO(g) It is difficult to measure directly. However, two other reactions are known: C(graphite) + O2(g) CO2(g); DH = -393.5 kJ 2CO2(g) 2CO(g) + O2(g); DH = – 566.0 kJ In order for these to add to give the reaction we want, we must multi ...
Synthetic Polymers - McQuarrie General Chemistry
... can be increased by increasing the number of crosslinks between chains. High elasticity is found in substances composed of long polymer chains joined by sparsely distributed cross-links, such as the polymer chains found in rubber bands. Natural rubber is composed of chains of cis-1,4-isoprene units ...
... can be increased by increasing the number of crosslinks between chains. High elasticity is found in substances composed of long polymer chains joined by sparsely distributed cross-links, such as the polymer chains found in rubber bands. Natural rubber is composed of chains of cis-1,4-isoprene units ...
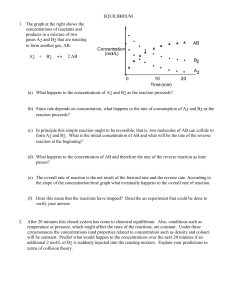
EQUILIBRIUM - SCH4U1-CCVI
... 1. Once a system has reached equilibrium, are the following true or false? a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __________ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. ______________ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. ___________ d. The reaction ...
... 1. Once a system has reached equilibrium, are the following true or false? a. The reaction is finished, no more products are forming. __________ b. The concentrations of the reactants and the products are equal. ______________ c. The concentrations are no longer changing. ___________ d. The reaction ...
Ch 16 Power Point
... and the processes of heat transfer 11C use thermochemical equations to calculate energy changes that occur in chemical reactions and classify reactions as exothermic or ...
... and the processes of heat transfer 11C use thermochemical equations to calculate energy changes that occur in chemical reactions and classify reactions as exothermic or ...
step by step Stoichiometry
... Or 80.3 divided by 55.847, multiplied by 3, divided by 2, multiplied by 28.01015 ...
... Or 80.3 divided by 55.847, multiplied by 3, divided by 2, multiplied by 28.01015 ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.