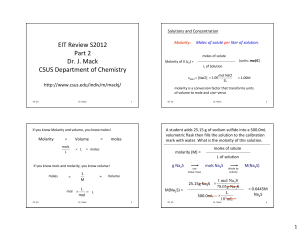
EIT Review S2012 Part 2 Dr. J. Mack CSUS Department of Chemistry
... The rate of effusion of a gas is proportional to its uRMS. over time, the mixture becomes homogeneous. ...
... The rate of effusion of a gas is proportional to its uRMS. over time, the mixture becomes homogeneous. ...
2 - Scheikundeolympiade
... For substituted oxiranes the direction of ring opening (which C–O bond is cleaved) depends on the stability of the intermediate carbenium ion. The more stable the intermediate carbenium ion the more probable its formation. However, an open carbenium ion (with a planar structure) only forms if it is ...
... For substituted oxiranes the direction of ring opening (which C–O bond is cleaved) depends on the stability of the intermediate carbenium ion. The more stable the intermediate carbenium ion the more probable its formation. However, an open carbenium ion (with a planar structure) only forms if it is ...
File
... oxidation state of a species tells you if it has undergone oxidation or reduction. The usual Oxidation Numbers for common elements in their compounds ...
... oxidation state of a species tells you if it has undergone oxidation or reduction. The usual Oxidation Numbers for common elements in their compounds ...
CHAPTER 19
... Combining the half reactions gives a full picture of what occurs. Metallic copper reacts in nitric acid and in so doing one copper atom is oxidized from Cu to C u 2+as two nitrogen atoms are reduced from a +5 oxidation state to a +4 oxidation state. Both atoms and electrons are conserved. This b ...
... Combining the half reactions gives a full picture of what occurs. Metallic copper reacts in nitric acid and in so doing one copper atom is oxidized from Cu to C u 2+as two nitrogen atoms are reduced from a +5 oxidation state to a +4 oxidation state. Both atoms and electrons are conserved. This b ...
MALTA
... Programme of Study in Chemistry for the BSc(Hons)degree (Bye-Laws of 2003) ACADEMIC YEAR 2005-2006 The following programme of study is offered within the framework of the B.Sc (Hons) degree regulated by the Bye-Laws of 2003 and applies only to students registering for the first year of the degree on ...
... Programme of Study in Chemistry for the BSc(Hons)degree (Bye-Laws of 2003) ACADEMIC YEAR 2005-2006 The following programme of study is offered within the framework of the B.Sc (Hons) degree regulated by the Bye-Laws of 2003 and applies only to students registering for the first year of the degree on ...
Organic - NUS Chemistry
... Furthermore, they are also trained with essential chemistry laboratory skills, as a key to their success in their higher year education and future work. In Experiment 1, the thermodynamic property Ksp of an organic salt is measured at different temperatures and the enthalpy and entropy change of the ...
... Furthermore, they are also trained with essential chemistry laboratory skills, as a key to their success in their higher year education and future work. In Experiment 1, the thermodynamic property Ksp of an organic salt is measured at different temperatures and the enthalpy and entropy change of the ...
Reaction Dynamics of Zr and Nb with Ethylene
... interaction is optimized for doubly occupied d orbitals. Ab initio calculations indicate that sd hybridization of the transition metal center promotes bond formation in the DCD mechanism.21 However, only certain electron configurations on the metal allow for sd hybridization, namely, s1dn-1 configur ...
... interaction is optimized for doubly occupied d orbitals. Ab initio calculations indicate that sd hybridization of the transition metal center promotes bond formation in the DCD mechanism.21 However, only certain electron configurations on the metal allow for sd hybridization, namely, s1dn-1 configur ...
2.3 ThermoChemistry - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... the enthalpy change which occurs when one mole of an ionic crystal is formed from the ions in their gaseous states under standard conditions. ...
... the enthalpy change which occurs when one mole of an ionic crystal is formed from the ions in their gaseous states under standard conditions. ...
Carbon dioxide capture and utilization in petrochemical industry
... CO2 cryogenic distillation involves separation of gas mixture by fractional condensation and distillation at low temperature. Cryogenic temperatures are obtained by a closed-cycle operated refrigeration system consisting of a compressor, a Joule-Thompson valve (JTV), multi-stage heat exchangers and ...
... CO2 cryogenic distillation involves separation of gas mixture by fractional condensation and distillation at low temperature. Cryogenic temperatures are obtained by a closed-cycle operated refrigeration system consisting of a compressor, a Joule-Thompson valve (JTV), multi-stage heat exchangers and ...
Thermodynamics of Combustion
... (or bond) energy contained in a fuel as thermal energy). The most common combustion processes encountered in engineering are those which convert a hydrocarbon fuel (which might range from pure hydrogen to almost pure carbon, e.g. coal) into carbon dioxide and water. This combustion is usually perfor ...
... (or bond) energy contained in a fuel as thermal energy). The most common combustion processes encountered in engineering are those which convert a hydrocarbon fuel (which might range from pure hydrogen to almost pure carbon, e.g. coal) into carbon dioxide and water. This combustion is usually perfor ...
Manual Physical Chemistry III
... The molecules of liquids attract each other by cohesive forces resulting into small distances between the molecules (on the order of 0.1 nm). Thus the compressibility of liquids is lower than that of gas, while the density is much higher. On the other hand, these cohesive forces are not strong enoug ...
... The molecules of liquids attract each other by cohesive forces resulting into small distances between the molecules (on the order of 0.1 nm). Thus the compressibility of liquids is lower than that of gas, while the density is much higher. On the other hand, these cohesive forces are not strong enoug ...
g - mrnicholsscience
... • 25.0 g sucrose, C12H22O11 (FM=342g/mol), is burned, but only 30.0 g CO2 is recovered. • What is the percent yield? Do the mass-to-mass problem to find the expected yield. Divide the actual/expected, convert to a % ...
... • 25.0 g sucrose, C12H22O11 (FM=342g/mol), is burned, but only 30.0 g CO2 is recovered. • What is the percent yield? Do the mass-to-mass problem to find the expected yield. Divide the actual/expected, convert to a % ...
AP Chemistry Lab Manual
... 5. If you make a mistake, DO NOT ERASE OR SCRIBBLE. Just draw ONE LINE through your error, and continue. It is expected that some errors will occur. A lab notebook is a working document, not a perfect, error-free, polished product. Errors should be corrected by drawing one line through the mistake, ...
... 5. If you make a mistake, DO NOT ERASE OR SCRIBBLE. Just draw ONE LINE through your error, and continue. It is expected that some errors will occur. A lab notebook is a working document, not a perfect, error-free, polished product. Errors should be corrected by drawing one line through the mistake, ...
NEW MONO- AND DINUCLEAR RUTHENIUM COMPLEXES CONTAINING THE 3,5-BIS(2- PYRIDYL)PYRAZOLE LIGAND. SYNTHESIS,
... synthesized and characterized by means of structural, spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques. These complexes have the formula [Ru2(µ-X)(bpp)(trpy)2]2+, where X = Cl, 1, and acetate, 2. The chloro and acetato bridges can be hydrolyzed in basic and acidic media, respectively, to generate the di ...
... synthesized and characterized by means of structural, spectroscopic and electrochemical techniques. These complexes have the formula [Ru2(µ-X)(bpp)(trpy)2]2+, where X = Cl, 1, and acetate, 2. The chloro and acetato bridges can be hydrolyzed in basic and acidic media, respectively, to generate the di ...
Computational Study of Structure and Reactivity
... efficient and economical way. One promising way is the catalytic oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of light alkanes and alcohols to the corresponding alkenes and aldehydes. The advantages of ODH over conventional nonoxidative routes rely on the fact that the ODH reaction is (i) exothermic and can operat ...
... efficient and economical way. One promising way is the catalytic oxidative dehydrogenation (ODH) of light alkanes and alcohols to the corresponding alkenes and aldehydes. The advantages of ODH over conventional nonoxidative routes rely on the fact that the ODH reaction is (i) exothermic and can operat ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.