Chemical Equations and Reactions notes File
... Solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide. Word Equation: sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide Formula ...
... Solid sodium oxide is added to water at room temperature and forms sodium hydroxide. Word Equation: sodium oxide + water sodium hydroxide Formula ...
Biology Fall Semester Test 1 Study Guide
... In the metric system, the basic unit of length is the How many centimeters are in 2.4 km? The basic unit of mass in SI is the The three particles that make up atoms are ...
... In the metric system, the basic unit of length is the How many centimeters are in 2.4 km? The basic unit of mass in SI is the The three particles that make up atoms are ...
The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occured is
... 13. Which reaction requires a continuous supply of energy in order to continue? ...
... 13. Which reaction requires a continuous supply of energy in order to continue? ...
1 ChE 505 WORKSHOP 1 1. Why are chemical reactions important
... Relate molar extent of reaction to the fractional conversion of the limiting reactant. What is the limiting reactant? ...
... Relate molar extent of reaction to the fractional conversion of the limiting reactant. What is the limiting reactant? ...
Chemistry Review for End of year final honors
... form water? 2H2 + O2 2H2O 3.) Calculate the number of moles of Al2O3 that are produced when 0.60 mol of Fe is produce in the following reaction: 2Al + 3FeO 3Fe + Al2O3 4.) When two substances react to form products, the reactant, which is used up in the reaction, is called ______________________ ...
... form water? 2H2 + O2 2H2O 3.) Calculate the number of moles of Al2O3 that are produced when 0.60 mol of Fe is produce in the following reaction: 2Al + 3FeO 3Fe + Al2O3 4.) When two substances react to form products, the reactant, which is used up in the reaction, is called ______________________ ...
II. BIOPHYSICAL CHEMISTRY*
... The reaction progress is followed through changes either in optical ...
... The reaction progress is followed through changes either in optical ...
Unit 6 Jeopardy review - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... Amount of energy needed to start a ...
... Amount of energy needed to start a ...
CHAPTER 8
... and energy concentrating on chemical kinetics, thermodynamics, electrochemistry, organic nomenclature, and chemical equilibrium (acid- base, solubility, complexa- tion, and redox). Laboratory experiments emphasizing quan- titative chemical measurements. Prerequisite: Grade of C or better in CHGN121. ...
... and energy concentrating on chemical kinetics, thermodynamics, electrochemistry, organic nomenclature, and chemical equilibrium (acid- base, solubility, complexa- tion, and redox). Laboratory experiments emphasizing quan- titative chemical measurements. Prerequisite: Grade of C or better in CHGN121. ...
PowerPoint
... and the isobaric water-gas shift reaction proceeds to equilibrium, what is the CO conversion if the temperature is (a) 150 °C, (b) 250 °C and (c) 350 °C? ‣ Noting that the water-gas shift reaction is exothermic; predict whether the equilibrium conversion will increase or decrease as the temperature ...
... and the isobaric water-gas shift reaction proceeds to equilibrium, what is the CO conversion if the temperature is (a) 150 °C, (b) 250 °C and (c) 350 °C? ‣ Noting that the water-gas shift reaction is exothermic; predict whether the equilibrium conversion will increase or decrease as the temperature ...
CHM 101
... the energy versus the reaction progress for this exothermic reaction. Indicate how you would calculate the activation energy and ∆H for the reaction. ...
... the energy versus the reaction progress for this exothermic reaction. Indicate how you would calculate the activation energy and ∆H for the reaction. ...
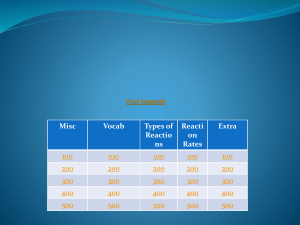
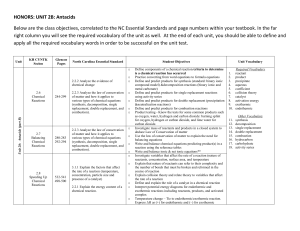
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... as oxygen, water, hydrogen and carbon dioxide: burning splint for oxygen, hydrogen or carbon dioxide, and lime water for carbon dioxide. Investigate mass of reactants and products in a closed system to deduce Law of Conservation of matter Use the law of conservation of matter to explain the need for ...
... as oxygen, water, hydrogen and carbon dioxide: burning splint for oxygen, hydrogen or carbon dioxide, and lime water for carbon dioxide. Investigate mass of reactants and products in a closed system to deduce Law of Conservation of matter Use the law of conservation of matter to explain the need for ...
Chemical Reactions
... number of atoms on each side of the equation. • This is due to the Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter cannot be created or ...
... number of atoms on each side of the equation. • This is due to the Law of Conservation of Matter: Matter cannot be created or ...
View flyer - Tufts University School of Engineering
... The catalytic semi-hydrogenation of acetylene to produce ethylene is a common method for the removal of trace acetylene (~1%) in ethylene feed streams destined for ethylene polymerization. An effective catalyst for this reaction converts all of the acetylene to ethylene without further conversion of ...
... The catalytic semi-hydrogenation of acetylene to produce ethylene is a common method for the removal of trace acetylene (~1%) in ethylene feed streams destined for ethylene polymerization. An effective catalyst for this reaction converts all of the acetylene to ethylene without further conversion of ...
Chemical Kinetics - Review
... Hydrogen peroxide reacts with hydrogen ions and iodide ions according to the reaction mechanism shown below: a. Determine the overall reaction described by this mechanism b. If you wanted to increase the rate of the overall reaction, would it be better to increase the concentration of H+ or I–. Why? ...
... Hydrogen peroxide reacts with hydrogen ions and iodide ions according to the reaction mechanism shown below: a. Determine the overall reaction described by this mechanism b. If you wanted to increase the rate of the overall reaction, would it be better to increase the concentration of H+ or I–. Why? ...
Topic 16 IB Chemistry Definitions
... Created during a bimolecular process. Not a chemical substance which can be isolated, but consists of reacting particles in which bonds are in the process of being broken and formed. Can break down to form either the products or back to the original reactants. ...
... Created during a bimolecular process. Not a chemical substance which can be isolated, but consists of reacting particles in which bonds are in the process of being broken and formed. Can break down to form either the products or back to the original reactants. ...
Catalysis

Catalysis is the increase in the rate of a chemical reaction due to the participation of an additional substance called a catalyst. With a catalyst, reactions occur faster and require less activation energy. Because catalysts are not consumed in the catalyzed reaction, they can continue to catalyze the reaction of further quantities of reactant. Often only tiny amounts are required.