The Equilibrium Constant
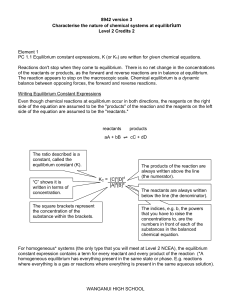
... TIPS FOR SOLVING EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT QUESTIONS 1) If given the initial concentrations of all parts and the change in concentration of 1+ parts (reactants or products), you can use stoichiometry to find the change in the other parts. 2) If not given, let x be the change in concentration of the re ...
... TIPS FOR SOLVING EQUILIBRIUM CONSTANT QUESTIONS 1) If given the initial concentrations of all parts and the change in concentration of 1+ parts (reactants or products), you can use stoichiometry to find the change in the other parts. 2) If not given, let x be the change in concentration of the re ...
Wanganui High School
... For homogeneous* systems (the only type that you will meet at Level 2 NCEA), the equilibrium constant expression contains a term for every reactant and every product of the reaction (*A homogeneous equilibrium has everything present in the same state or phase. E.g. reactions where everything is a ga ...
... For homogeneous* systems (the only type that you will meet at Level 2 NCEA), the equilibrium constant expression contains a term for every reactant and every product of the reaction (*A homogeneous equilibrium has everything present in the same state or phase. E.g. reactions where everything is a ga ...
Chapter 1: The first law of thermodynamics
... and volume we say that the quantity is a function of state. Therefore, for an ideal gas in equilibrium, the system’s temperature is a function of state ( θ = F ( P,V ) ). A quantity, dG, is said to be an exact differential if it only depends on the difference in the function of state between two clo ...
... and volume we say that the quantity is a function of state. Therefore, for an ideal gas in equilibrium, the system’s temperature is a function of state ( θ = F ( P,V ) ). A quantity, dG, is said to be an exact differential if it only depends on the difference in the function of state between two clo ...
topic 1 sol review homework
... 2. The mass of the calcium atom is due primarily to the mass of its a) protons only b) neutrons only c) protons and neutrons d) protons and electrons 3. Which structure represents a nonpolar molecule? a) H – Cl b) H – H c) H – :O: – H d) NaBr 4. In an aqueous solution, which substance yields hydroge ...
... 2. The mass of the calcium atom is due primarily to the mass of its a) protons only b) neutrons only c) protons and neutrons d) protons and electrons 3. Which structure represents a nonpolar molecule? a) H – Cl b) H – H c) H – :O: – H d) NaBr 4. In an aqueous solution, which substance yields hydroge ...
Document
... a. Ice and water exist in equilibrium at 0C or 273K. b. Steam and water exist in equilibrium at one atmosphere at 100C or 373K. 30. Understand that equilibrium occurs in closed systems. Reactions which result in the formation of a solid precipitate, a gas, or water will NOT reach equilibrium. Such ...
... a. Ice and water exist in equilibrium at 0C or 273K. b. Steam and water exist in equilibrium at one atmosphere at 100C or 373K. 30. Understand that equilibrium occurs in closed systems. Reactions which result in the formation of a solid precipitate, a gas, or water will NOT reach equilibrium. Such ...
The following list of topics for an AP Chemistry course is intended to
... Knowledge of specific facts of chemistry is essential for an understanding of principles and concepts. These descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course t ...
... Knowledge of specific facts of chemistry is essential for an understanding of principles and concepts. These descriptive facts, including the chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated from the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course t ...
Unit 8: Equilibrium Content Outline: Shifting Equilibrium and Le
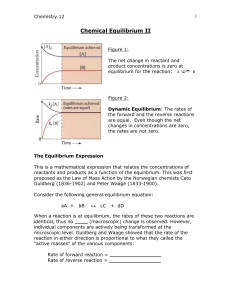
... Dynamic Equilibrium (“Dynamic” means “constant movement”; “equilibrium” means “state of being equal”.) A. This is a “state” where opposite reactions/processes are occurring at the same rate and at the same time in the same space. B. Equilibrium is affected by changes in concentrations, pressure, and ...
... Dynamic Equilibrium (“Dynamic” means “constant movement”; “equilibrium” means “state of being equal”.) A. This is a “state” where opposite reactions/processes are occurring at the same rate and at the same time in the same space. B. Equilibrium is affected by changes in concentrations, pressure, and ...
Chemical Equilibrium
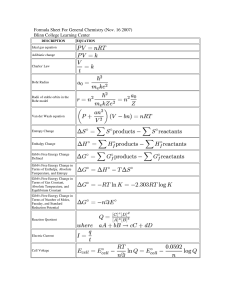
... The equilibrium constant is the reaction quotient value for a system when it is in it’s equilibrium state. Every system of equilibrium has a unique equilibrium constant (K) that is determined experimentally initially. ◦ To do this, you must let the reaction run to its equilibrium state, then figure ...
... The equilibrium constant is the reaction quotient value for a system when it is in it’s equilibrium state. Every system of equilibrium has a unique equilibrium constant (K) that is determined experimentally initially. ◦ To do this, you must let the reaction run to its equilibrium state, then figure ...
Faculty of Science Department of chemistry Practical Physical
... 7. Effect of ionic strength on solubility ...
... 7. Effect of ionic strength on solubility ...
General Equilibrium
... In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can be substituted for activities. (This assumption isn’t always good!) ...
... In dilute solutions, the activity coefficient approaches unity. Often, experimental conditions allow us to assume activity coefficients of one so that concentrations can be substituted for activities. (This assumption isn’t always good!) ...
Subject:
... affects the progression of equilibrium in a reversible reaction Learning Targets: (“I can” or “I will” statements) I will understand the factors that affect the rate of reactions I will be able to define catalyst and understand their role in the rate of chemical reactions. I will be able to interpre ...
... affects the progression of equilibrium in a reversible reaction Learning Targets: (“I can” or “I will” statements) I will understand the factors that affect the rate of reactions I will be able to define catalyst and understand their role in the rate of chemical reactions. I will be able to interpre ...
blood - SCH4U1-02-2010
... 5. pH effects on blood -We are interested in the change in the pH of the blood; therefore, we want an ...
... 5. pH effects on blood -We are interested in the change in the pH of the blood; therefore, we want an ...
Exercises Chem Eqm
... 7.1(a) K = 2.85 x 10-6; (b) ∆rGo = +240 kJ mol-1; (c) ∆rG = 0 7.4(a) Mole fractions A: 0.087, B: 0.370, C: 0.196, D: 0.348, Total: 1.001; (b) Kx – 0.33; (c) p = 0.33; (d) ∆rGo = + 2.8 x 103 J mol-1. 7.6(a) ∆rHo = +2.77 kJ mol-1, ∆rSo = -16.5 J K-1 mol-1 7.9(a) χB = 0.904, χI = 0.096 7.11(a) ∆rGo = – ...
... 7.1(a) K = 2.85 x 10-6; (b) ∆rGo = +240 kJ mol-1; (c) ∆rG = 0 7.4(a) Mole fractions A: 0.087, B: 0.370, C: 0.196, D: 0.348, Total: 1.001; (b) Kx – 0.33; (c) p = 0.33; (d) ∆rGo = + 2.8 x 103 J mol-1. 7.6(a) ∆rHo = +2.77 kJ mol-1, ∆rSo = -16.5 J K-1 mol-1 7.9(a) χB = 0.904, χI = 0.096 7.11(a) ∆rGo = – ...
Big Idea 6
... • Common ion effect: presence of an ion at the start of the “reaction”. Alters the solubility (think Le Chatelier) • pH and solubility: role of pH may impact the solubility of an insoluble salt based on the common ion effect (ex. Mg(OH)2 enhances by the presence of H+ ions/acidic) ...
... • Common ion effect: presence of an ion at the start of the “reaction”. Alters the solubility (think Le Chatelier) • pH and solubility: role of pH may impact the solubility of an insoluble salt based on the common ion effect (ex. Mg(OH)2 enhances by the presence of H+ ions/acidic) ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.