Thermodynamics: Spontaneity, Entropy and Free energy
... • 3rd Law: the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero (S =0) ...
... • 3rd Law: the entropy of a pure crystalline substance at absolute zero is zero (S =0) ...
Writing Chemical Equations
... • 2 Al atoms react with 3 Br2 molecules – Amounts in moles of species ...
... • 2 Al atoms react with 3 Br2 molecules – Amounts in moles of species ...
402 - Sydenham High School
... to distinguish between strength and concentration. This takes mental effort The fact that sometimes a chemical can act as an acid in one reaction and as a base in another reaction is interesting. I now see how important empirical evidence is to the study of chemistry. The ultimate way of knowing in ...
... to distinguish between strength and concentration. This takes mental effort The fact that sometimes a chemical can act as an acid in one reaction and as a base in another reaction is interesting. I now see how important empirical evidence is to the study of chemistry. The ultimate way of knowing in ...
Weak Acids and Bases Practice -- Chemistry 121A
... yield. It runs from 0% (all reactants) to 100% (all products). This is simply more convenient than Q, which runs from 0 to infinity. The way I look at it is this for a weak acid: %ionization = [A−]eq/[HA]o x 100% That is, the “final” concentration of A− at equilibrium divided by the “initial” concen ...
... yield. It runs from 0% (all reactants) to 100% (all products). This is simply more convenient than Q, which runs from 0 to infinity. The way I look at it is this for a weak acid: %ionization = [A−]eq/[HA]o x 100% That is, the “final” concentration of A− at equilibrium divided by the “initial” concen ...
Equilibrium
... k=rate constant n=order (not related to coefficient in balanced equation) Integrated Rate Law: describes concentration as a function of time. ...
... k=rate constant n=order (not related to coefficient in balanced equation) Integrated Rate Law: describes concentration as a function of time. ...
Document
... 1.5 Oxalic acid reacts spontaneously with Cerium (IV) to produce CO2 and Cerium (III). a) true ...
... 1.5 Oxalic acid reacts spontaneously with Cerium (IV) to produce CO2 and Cerium (III). a) true ...
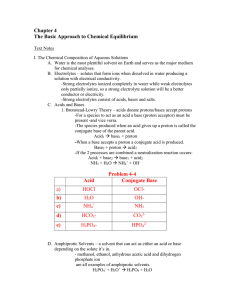
Chapter 4
... - acetic acid can act as a differentiating solvent in which various acids dissociate to different degrees and thus have different strengths, while water acts as a leveling solvent for strong acids because the strong acid will dissociate completely and have no differences in strength. F. Chemical Equ ...
... - acetic acid can act as a differentiating solvent in which various acids dissociate to different degrees and thus have different strengths, while water acts as a leveling solvent for strong acids because the strong acid will dissociate completely and have no differences in strength. F. Chemical Equ ...
Chemistry 3202 Name: Acid-base Theory Problems Assignment 1
... Evidence indicates that the hydrogen carbonate ion is amphoteric. A sodium hydrogen carbonate solution can neutralize a sodium hydroxide spill and also a hydrochloric acid spill. a) ...
... Evidence indicates that the hydrogen carbonate ion is amphoteric. A sodium hydrogen carbonate solution can neutralize a sodium hydroxide spill and also a hydrochloric acid spill. a) ...
Answer on Question #44399 – Chemistry – Other HC2O4 − + HOH
... Answer According to the Brønsted–Lowry theory, an acid is a species able to lose, or "donate" a proton (H+) while a base is a species with the ability to gain, or "accept," a proton. The hydrogen oxalate ion can gain a proton acting as a base towards water, while the latter donates proton acting as ...
... Answer According to the Brønsted–Lowry theory, an acid is a species able to lose, or "donate" a proton (H+) while a base is a species with the ability to gain, or "accept," a proton. The hydrogen oxalate ion can gain a proton acting as a base towards water, while the latter donates proton acting as ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... chemistry. Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
... chemistry. Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
midterm 2 exam for section 3 from 2015
... (e) What sign should S have for the combustion in part (d)? Justify your answer. ...
... (e) What sign should S have for the combustion in part (d)? Justify your answer. ...
4. Which of the following describes how a Keq value is related to the
... What happens when O2 is added to the above system? Equilibrium ...
... What happens when O2 is added to the above system? Equilibrium ...
Review - The University of Texas at Dallas
... Electrolytic Cell Non-spontaneous because E < 0 So external electromotive force (potential) ...
... Electrolytic Cell Non-spontaneous because E < 0 So external electromotive force (potential) ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.