chemical equilibrium
... Adding a catalyst DOES NOT AFFECT THE POSITION OF EQUILIBRIUM. However, it does increase the rate of attainment of equilibrium. This is especially important in reversible, exothermic industrial reactions such as the Haber or Contact Processes where economic factors are paramount. Catalysts provide a ...
... Adding a catalyst DOES NOT AFFECT THE POSITION OF EQUILIBRIUM. However, it does increase the rate of attainment of equilibrium. This is especially important in reversible, exothermic industrial reactions such as the Haber or Contact Processes where economic factors are paramount. Catalysts provide a ...
Chapter 2 Study Guides
... Main Idea: Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. ...
... Main Idea: Enzymes allow chemical reactions to occur under tightly controlled conditions. ...
بسم الله الرحمن الرحيم
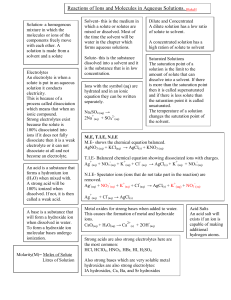
... 1 – A mixture of a gas in a gas can only form a solution 2 – Enthalpy is the heat of reaction at constant pressure 3 – The solute particles can be seperated from colloides by filtration 4 – Potential energy equals m . g . h 5 – Molarity is an intensive property. 6 – There are 3 significant figures i ...
... 1 – A mixture of a gas in a gas can only form a solution 2 – Enthalpy is the heat of reaction at constant pressure 3 – The solute particles can be seperated from colloides by filtration 4 – Potential energy equals m . g . h 5 – Molarity is an intensive property. 6 – There are 3 significant figures i ...
2. Covalent network
... 1. When the rate of the forward reaction is equivalent to the rate of the reverse reaction the system is at equilibrium. 2. jA+kB<-->lC+mD a. j, j, l, and m are coefficient. b.A and B are the concentrations of the reactants c. C and D are the concentrations of the products k= [C]^l x [D]^m [A]^j x [ ...
... 1. When the rate of the forward reaction is equivalent to the rate of the reverse reaction the system is at equilibrium. 2. jA+kB<-->lC+mD a. j, j, l, and m are coefficient. b.A and B are the concentrations of the reactants c. C and D are the concentrations of the products k= [C]^l x [D]^m [A]^j x [ ...
Solution chemistry and reaction mechanism taking place during the
... In(OH)xSy contain InCl3, acetic acid and thioacetamide. As it was stated in a previous work [4], the chemical species present in the solution and the rate of thioacetamide hydrolysis, depend on the solution pH. Therefore, the pH of solutions containing thioacetamide, acetic acid and InCl3 was measur ...
... In(OH)xSy contain InCl3, acetic acid and thioacetamide. As it was stated in a previous work [4], the chemical species present in the solution and the rate of thioacetamide hydrolysis, depend on the solution pH. Therefore, the pH of solutions containing thioacetamide, acetic acid and InCl3 was measur ...
Rate and Equilibrium
... Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a change is imposed on a system at equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to reduce that change. Effect of concentration change on equilibrium: If the concentration of a substance involved in equilibrium is artificial ...
... Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a change is imposed on a system at equilibrium, the position of the equilibrium will shift in a direction that tends to reduce that change. Effect of concentration change on equilibrium: If the concentration of a substance involved in equilibrium is artificial ...
Review Sheet Exam 2 3.4-4.7
... 15. Which one of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte? a. NaOH b. HBr c. KF d. HF 16. Which of the following is a weak electrolyte, circle all that apply. a. C2H6 b. CH3OH c. NH3 d. HNO3 e. CH3CO2H 17. Label the following with Strong, Weak, or Non- electrolyte. a. KOH b. H2SO4 c. C6H12O6(glucos ...
... 15. Which one of the following is NOT a strong electrolyte? a. NaOH b. HBr c. KF d. HF 16. Which of the following is a weak electrolyte, circle all that apply. a. C2H6 b. CH3OH c. NH3 d. HNO3 e. CH3CO2H 17. Label the following with Strong, Weak, or Non- electrolyte. a. KOH b. H2SO4 c. C6H12O6(glucos ...
ap chemistry – 2013-2014
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
... AP CHEMISTRY – 2013-2014 Course Description: This AP Chemistry course is designed to be the equivalent of the general chemistry course usually taken during the first year of college. This course is structured around six big ideas that include: Structure of matter, properties of matter-characteristic ...
BH - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... to a known amount of another substance. An indicator is most commonly used to signal when a reaction is complete. Endpoint- the volume of the added reactant (titrant) required to complete the reaction. ...
... to a known amount of another substance. An indicator is most commonly used to signal when a reaction is complete. Endpoint- the volume of the added reactant (titrant) required to complete the reaction. ...
Ch. 20 study questions
... A copper-zinc voltaic cell is constructed using100 mL solutions of 1M solutions of copper sulfate and zinc sulfate with a sodium sulfate salt bridge. After some time, t, had passed at 25C, the concentration of the Zn2+ ions in the anode half cell had increased to 1.50M and the concentration of the ...
... A copper-zinc voltaic cell is constructed using100 mL solutions of 1M solutions of copper sulfate and zinc sulfate with a sodium sulfate salt bridge. After some time, t, had passed at 25C, the concentration of the Zn2+ ions in the anode half cell had increased to 1.50M and the concentration of the ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.