Chapter 4 The Study of Chemical Reactions
... • To know how well the reaction goes to products, we study its thermodynamics, the energetics of the reaction at equilibrium. • To use a reaction in a realistic time period (and to keep the reaction from becoming violent), we study its kinetics, the variation of reaction rates with different conditi ...
... • To know how well the reaction goes to products, we study its thermodynamics, the energetics of the reaction at equilibrium. • To use a reaction in a realistic time period (and to keep the reaction from becoming violent), we study its kinetics, the variation of reaction rates with different conditi ...
dx cx dx and x - Cameron University
... 16.2 Determine the entropy change in a cyclic process ()S = 0, since S is a state function) 16.3 Determine the entropy change in a reversible adiabatic process 16.4 Determine the entropy change in a reversible phase change at constant temperature and pressure 16.5 Determine the entropy change in a r ...
... 16.2 Determine the entropy change in a cyclic process ()S = 0, since S is a state function) 16.3 Determine the entropy change in a reversible adiabatic process 16.4 Determine the entropy change in a reversible phase change at constant temperature and pressure 16.5 Determine the entropy change in a r ...
VALIDITY OF HENRY`S LAW IN DILUTE SOLUTIONS (l)
... refers to the solvent and L is the Henry-Dalton absorption coefficient) the absorption cocfficient can be approximately constant even in such concentration intervals where the activity coefficient of the gas dissolved is not constant. This is equivalent to the original interpretation of Henry's Law. ...
... refers to the solvent and L is the Henry-Dalton absorption coefficient) the absorption cocfficient can be approximately constant even in such concentration intervals where the activity coefficient of the gas dissolved is not constant. This is equivalent to the original interpretation of Henry's Law. ...
Chapter 12: Chemical Equilibrium • Chemical Equilibrium
... decrease in rate of the forward reaction. • As the reactants are being consumed, the product concentration increases, with a corresponding increase in the rate of the reverse reaction. • When the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, the reaction has reached equilibri ...
... decrease in rate of the forward reaction. • As the reactants are being consumed, the product concentration increases, with a corresponding increase in the rate of the reverse reaction. • When the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction, the reaction has reached equilibri ...
Unit Seven Worksheet – 2
... Ratio of the concentration of the dissociated (or ionized) form of an acid to the concentration of the undissociated acid; symbolized Ka Base that dissociates completely into metal ions and hydroxide ions in aqueous solution Acid that completely ionizes in aqueous solution Base that does not dissoci ...
... Ratio of the concentration of the dissociated (or ionized) form of an acid to the concentration of the undissociated acid; symbolized Ka Base that dissociates completely into metal ions and hydroxide ions in aqueous solution Acid that completely ionizes in aqueous solution Base that does not dissoci ...
Lecture 1
... Gas - a form of matter that fills any container it occupies Physical state - the state of physical properties of a sample such as volume, mole, pressure, and temperature Mole - the number of atoms or molecules equal to Avogradro’s number NA = 6.022137 × 1023, which is defined as the number of atoms ...
... Gas - a form of matter that fills any container it occupies Physical state - the state of physical properties of a sample such as volume, mole, pressure, and temperature Mole - the number of atoms or molecules equal to Avogradro’s number NA = 6.022137 × 1023, which is defined as the number of atoms ...
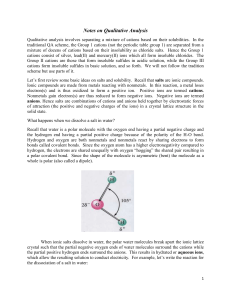
Notes on QA - Scarsdale Public Schools
... To understand what happens in the reaction we need to also review LeChatelier’s principle for systems at equilibrium: If a stress is applied to an equilibrium system, the system moves (shifts) in the direction that relieves the stress. Consider our equilibrium system: Cu(OH)2(s) = Cu2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq ...
... To understand what happens in the reaction we need to also review LeChatelier’s principle for systems at equilibrium: If a stress is applied to an equilibrium system, the system moves (shifts) in the direction that relieves the stress. Consider our equilibrium system: Cu(OH)2(s) = Cu2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq ...
homework
... examinations, students are urged to attend class faithfully. Please keep in mind that the goal is to successfully complete this course and keep in mind, also, that the goal is to prepare you for the comprehensive examination. It is therefore important to organize a self imposed study schedule, disci ...
... examinations, students are urged to attend class faithfully. Please keep in mind that the goal is to successfully complete this course and keep in mind, also, that the goal is to prepare you for the comprehensive examination. It is therefore important to organize a self imposed study schedule, disci ...
Regents Chemistry Review Questions
... Under what conditions of temperature and pressure are real gases most like ideal gases? Under what conditions of temperature and pressure do gases deviate most from ideal? When an air bag in an automobile inflates, the nitrogen gas inside of it is at a pressure of 1.30 atmospheres, a temperature of ...
... Under what conditions of temperature and pressure are real gases most like ideal gases? Under what conditions of temperature and pressure do gases deviate most from ideal? When an air bag in an automobile inflates, the nitrogen gas inside of it is at a pressure of 1.30 atmospheres, a temperature of ...
Name - cloudfront.net
... 43. What would likely happen (how would it feel) if you were to touch the flask in which an endothermic reaction were occurring? 44. Standard conditions of temperature and pressure for a thermochemical equation are __ and __kPa. 45. If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat w ...
... 43. What would likely happen (how would it feel) if you were to touch the flask in which an endothermic reaction were occurring? 44. Standard conditions of temperature and pressure for a thermochemical equation are __ and __kPa. 45. If heat is released by a chemical system, an equal amount of heat w ...
AP® Chemistry 2009 Free-Response Questions Form B
... Answer Question 4 below. The Section II score weighting for this question is 10 percent. 4. For each of the following three reactions, write a balanced equation in part (i) and answer the question in part (ii). In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutio ...
... Answer Question 4 below. The Section II score weighting for this question is 10 percent. 4. For each of the following three reactions, write a balanced equation in part (i) and answer the question in part (ii). In part (i), coefficients should be in terms of lowest whole numbers. Assume that solutio ...
simulating fritz haber`s ammonia synthesis with thermodynamic
... results is given in Figure 1 (page 116). Ammonia synthesis is an exothermic equilibrium reaction. ...
... results is given in Figure 1 (page 116). Ammonia synthesis is an exothermic equilibrium reaction. ...
Chemical Reactions
... – same number of atoms of each element appear on each side of the equation – stoichiometric coefficients - needed to balance the equations ...
... – same number of atoms of each element appear on each side of the equation – stoichiometric coefficients - needed to balance the equations ...
File
... Using the average bond enthalpy values in Table 10 of the Data Booklet, determine the standard enthalpy change for this reaction. ...
... Using the average bond enthalpy values in Table 10 of the Data Booklet, determine the standard enthalpy change for this reaction. ...
Ion Exchange
... Ion Exchange Ion-exchange chromatography retains analyte molecules on the column based on coulombic (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insolu ...
... Ion Exchange Ion-exchange chromatography retains analyte molecules on the column based on coulombic (ionic) interactions. The stationary phase surface displays ionic functional groups (R-X) that interact with analyte ions of opposite charge. An ion-exchange resin or ion-exchange polymer is an insolu ...
1 - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... 1. Define the following: a. energy b. kinetic energy c. potential energy d. first law of thermodynamics e. work f. heat g. system vs surroundings h. open system, closed system and isolated system i. enthalpy j. Cv k. Cp 2. Predict whether q, w, and ΔE are positive, negative or zero for: a. heating 2 ...
... 1. Define the following: a. energy b. kinetic energy c. potential energy d. first law of thermodynamics e. work f. heat g. system vs surroundings h. open system, closed system and isolated system i. enthalpy j. Cv k. Cp 2. Predict whether q, w, and ΔE are positive, negative or zero for: a. heating 2 ...
K b
... bases are added or when dilution occurs. • The buffer is a mixture of an acid and its conjugate base. There must be comparable amounts of the conjugate acid and base (say, within a factor of 10) to exert significant buffering. ...
... bases are added or when dilution occurs. • The buffer is a mixture of an acid and its conjugate base. There must be comparable amounts of the conjugate acid and base (say, within a factor of 10) to exert significant buffering. ...
Word - The University of British Columbia
... processes. At the end of the semester, students are expected to: ...
... processes. At the end of the semester, students are expected to: ...
Equilibrium chemistry
Equilibrium chemistry is a concerned with systems in chemical equilibrium. The unifying principle is that the free energy of a system at equilibrium is the minimum possible, so that the slope of the free energy with respect to the reaction coordinate is zero. This principle, applied to mixtures at equilibrium provides a definition of an equilibrium constant. Applications include acid-base, host-guest, metal-complex, solubility, partition, chromatography and redox equilibria.