What is Thermodynamics?
... • An endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings, so in a scenario where the temperature of a system increases, one would expect such a reaction to be MORE favourable (i.e. the reaction wants heat, and supplying more heat by raising the T is helpful). • In contrast, exothermic reactions ...
... • An endothermic reaction absorbs heat from the surroundings, so in a scenario where the temperature of a system increases, one would expect such a reaction to be MORE favourable (i.e. the reaction wants heat, and supplying more heat by raising the T is helpful). • In contrast, exothermic reactions ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2
... A) Solid sodium carbonate is heated to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. D) Sodium carbonate is heated to give sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. 20) ...
... A) Solid sodium carbonate is heated to give solid sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. B) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. C) Sodium carbonate decomposes to sodium oxide and carbon dioxide gas. D) Sodium carbonate is heated to give sodium oxide and carbon dioxide. 20) ...
WELCOME TO CLASS XII ORIENTATION IN CHEMISTRY SOME
... adding a strong electropositive metal like ...
... adding a strong electropositive metal like ...
BSPH 111 - Refresher Chemistry
... Magnetic Quantum Number (m) Gives the orientation of the orbital in space; in other words, the value of mdescribes whether an orbital lies along the x-, y-, or z-axis on a three-dimensional graph, with the nucleus of the ...
... Magnetic Quantum Number (m) Gives the orientation of the orbital in space; in other words, the value of mdescribes whether an orbital lies along the x-, y-, or z-axis on a three-dimensional graph, with the nucleus of the ...
Get Solutions - Iqraa group of institutes
... 20. Sodium salt of an organic acid ’X’ produces effervescence with conc. H2SO4. ’X’ reacts with the acidified aqueous CaCl2 solution to give a white precipitate which decolourises acidic solution of KmnO4. ’X’ is : ...
... 20. Sodium salt of an organic acid ’X’ produces effervescence with conc. H2SO4. ’X’ reacts with the acidified aqueous CaCl2 solution to give a white precipitate which decolourises acidic solution of KmnO4. ’X’ is : ...
Chemistry I Exams and Keys Corrected 2016 Season
... 21. Which of the following best explains why hydrogen gas emitted light when electrified? A) The electrons turned into photons when subjected to an electric field. B) The electricity caused the gas particles to collide with great kinetic energy, producing photons. C) The ionized gases produced by th ...
... 21. Which of the following best explains why hydrogen gas emitted light when electrified? A) The electrons turned into photons when subjected to an electric field. B) The electricity caused the gas particles to collide with great kinetic energy, producing photons. C) The ionized gases produced by th ...
Notebook - Science
... bond energy: enthalpy required to break a particular bond in 1 mole of gaseous molecules ionic bond: electrostatic force that holds ions together in an ionic compound, forms when the electronegativity difference between the two bonding atoms is 2.0 or more covalent bond: involves the sharing of elec ...
... bond energy: enthalpy required to break a particular bond in 1 mole of gaseous molecules ionic bond: electrostatic force that holds ions together in an ionic compound, forms when the electronegativity difference between the two bonding atoms is 2.0 or more covalent bond: involves the sharing of elec ...
Module 3 -- Lesson 4
... When the volume of the container holding a gaseous system is reduced, the system responds by reducing its own volume. This is done by decreasing the total number of gaseous molecules in the system. Example: In the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g), all substances are gases. Pressure would not shift ...
... When the volume of the container holding a gaseous system is reduced, the system responds by reducing its own volume. This is done by decreasing the total number of gaseous molecules in the system. Example: In the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g), all substances are gases. Pressure would not shift ...
A study of the structure and bonding of small aluminum oxide
... The details of the experimental apparatus have been published elsewhere and will only be given briefly.34 The apparatus is composed of a laser vaporization source, a modified Wiley–McLaren time-of-flight ~TOF! mass spectrometer65 and an improved magnetic-bottle TOF electron analyzer.24,66 A pulsed l ...
... The details of the experimental apparatus have been published elsewhere and will only be given briefly.34 The apparatus is composed of a laser vaporization source, a modified Wiley–McLaren time-of-flight ~TOF! mass spectrometer65 and an improved magnetic-bottle TOF electron analyzer.24,66 A pulsed l ...
Fundamentals of Theoretical Organic Chemistry Lecture 1
... Interactions between molecules are important for several reasons. One example is the interaction between the solvent and solute as shown in Figure 1.1.2—4. Such interactions play a key role for certain reactions, which occur in a given polar solvent, but do not take place in apolar solvent. Intermol ...
... Interactions between molecules are important for several reasons. One example is the interaction between the solvent and solute as shown in Figure 1.1.2—4. Such interactions play a key role for certain reactions, which occur in a given polar solvent, but do not take place in apolar solvent. Intermol ...
Final Review 2006
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
... ____ 76. What principle states that atoms tend to form compounds so that each atom can have eight electrons in its outermost energy level? a. rule of eights c. configuration rule b. Avogadro principle d. octet rule ____ 77. Multiple covalent bonds may occur in atoms that contain carbon, nitrogen, or ...
Final Exam Review 2010 UbD
... How does shielding change as you move across a row on the periodic table? ______________________ How does shielding change as you move down a column on the periodic table? ____________________ 35. Define “nuclear charge” _________________________________________________________________ 36. Define “a ...
... How does shielding change as you move across a row on the periodic table? ______________________ How does shielding change as you move down a column on the periodic table? ____________________ 35. Define “nuclear charge” _________________________________________________________________ 36. Define “a ...
GQ2613291336
... shown in the fig. (3) and the summary of findings of k, t1/2, and R2 are given in the table(2), where t1/2 is the half-life of the reaction R2 is the correlation coefficient which is a measure of the goodness-of-fit of the regression and 0 ≤ R2 ≤ 1. Pseudo first order equation was fitted for the dat ...
... shown in the fig. (3) and the summary of findings of k, t1/2, and R2 are given in the table(2), where t1/2 is the half-life of the reaction R2 is the correlation coefficient which is a measure of the goodness-of-fit of the regression and 0 ≤ R2 ≤ 1. Pseudo first order equation was fitted for the dat ...
High-pressure experiments and modeling of methane/air catalytic
... that heterogeneous processes at gas turbine conditions are largely influenced by kinetics. The effectiveness of the modeling tools thus depends strongly on the availability of reliable, heterogeneous, kinetic data, which are necessary for the correct description of the catalytic processes. In gas tu ...
... that heterogeneous processes at gas turbine conditions are largely influenced by kinetics. The effectiveness of the modeling tools thus depends strongly on the availability of reliable, heterogeneous, kinetic data, which are necessary for the correct description of the catalytic processes. In gas tu ...
Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
... quantity of product expected from a reaction. This quantity is known as the predicted yield (which is also known as the theoretical yield). • The predicted yield is calculated on the assumption that all the limiting reactant reacts to make product on the ratio described by the balanced equation. • T ...
... quantity of product expected from a reaction. This quantity is known as the predicted yield (which is also known as the theoretical yield). • The predicted yield is calculated on the assumption that all the limiting reactant reacts to make product on the ratio described by the balanced equation. • T ...
+ NO 2
... FACTORS WHICH AFFECT THE RATE OF A CHEMICAL REACTION (BONDS MUST BREAK) • SURFACE AREA/ CONTACT AREA (OPPORTUNITY FOR COLLISIONS) • CONCENTRATION ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • TEMPERATURE ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • CATALYST ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) • NATURE OF REACTANTS ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) ...
... FACTORS WHICH AFFECT THE RATE OF A CHEMICAL REACTION (BONDS MUST BREAK) • SURFACE AREA/ CONTACT AREA (OPPORTUNITY FOR COLLISIONS) • CONCENTRATION ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • TEMPERATURE ( INCREASE FREQUENCY) • CATALYST ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) • NATURE OF REACTANTS ( EFFECTIVE COLLISIONS) ...
University of Lusaka
... Magnetic Quantum Number (m) Gives the orientation of the orbital in space; in other words, the value of mdescribes whether an orbital lies along the x-, y-, or z-axis on a three-dimensional graph, with the nucleus of the ...
... Magnetic Quantum Number (m) Gives the orientation of the orbital in space; in other words, the value of mdescribes whether an orbital lies along the x-, y-, or z-axis on a three-dimensional graph, with the nucleus of the ...
DFT Studies of the Zinc Complexes of DNA Bases
... In the present study, as a continuation of our study on the binding of metal cations with DNA bases we report a DFT investigation on the interaction of Zn with DNA bases. We focus in this study our attention on the geometrical structures, association sites and association energies for the Zn complex ...
... In the present study, as a continuation of our study on the binding of metal cations with DNA bases we report a DFT investigation on the interaction of Zn with DNA bases. We focus in this study our attention on the geometrical structures, association sites and association energies for the Zn complex ...
H + H–H H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ H∙∙∙∙∙∙H H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙H
... A + B-C A-B + C During reaction, energies are being redistributed among bonds: old bonds are being ripped apart and new bonds formed. H + H–H H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ H∙∙∙∙∙∙H H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙H (activated state) H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙H H–H + H This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + ...
... A + B-C A-B + C During reaction, energies are being redistributed among bonds: old bonds are being ripped apart and new bonds formed. H + H–H H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙ H∙∙∙∙∙∙H H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙H (activated state) H∙∙∙∙∙∙H∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙∙H H–H + H This process can be generalized as: A + B-C [ABC] A-B + ...
Lecture 3 - Classification and Nomenclature
... of iron-sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked iron centers in ...
... of iron-sulfur clusters containing sulfide-linked iron centers in ...
Future perspectives in catalysis - NRSC
... It was also launched a quest to research and understand the underlying process. In 2007, the German scientist Gerhard Ertl was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry for unraveling the mechanisms of the Haber-Bosch process. In the 1960s, he began using the equipment used in the burgeoning semiconduct ...
... It was also launched a quest to research and understand the underlying process. In 2007, the German scientist Gerhard Ertl was awarded the Nobel Prize for Chemistry for unraveling the mechanisms of the Haber-Bosch process. In the 1960s, he began using the equipment used in the burgeoning semiconduct ...
CHEM 1405 Practice Exam #2 (2015)
... C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 10) How many valence electrons does the representative element with the electron configuration 1s2 ...
... C) Sb and Te D) Po and At C) Ca D) none of the above 8) Which of the following elements are fourth period metalloids? A) Si and Ge B) Ge and As 9) Which of the following is an alkali metal? A) Al B) Fe 10) How many valence electrons does the representative element with the electron configuration 1s2 ...
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Front Nucleation in a Bistable
... CO reaction has been shown to exhibit rate multiplicity, oscillatory behavior, and spatial pattern formation on a Pt( 100) surface.l.2 Propagating reaction fronts, spiral waves, and turbulent patterns have been observed a t temperatures between about 420 and 440 K.3-5 In this parameter range the sur ...
... CO reaction has been shown to exhibit rate multiplicity, oscillatory behavior, and spatial pattern formation on a Pt( 100) surface.l.2 Propagating reaction fronts, spiral waves, and turbulent patterns have been observed a t temperatures between about 420 and 440 K.3-5 In this parameter range the sur ...
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
... equation that shows either the oxidation or the reduction reaction that occurs during a redox reaction. Oxidation: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e− Reduction: S + 2e− → S2− It is important to remember that the two half-reactions occur simultaneously. The resulting ions that are formed are then attracted to one anoth ...
... equation that shows either the oxidation or the reduction reaction that occurs during a redox reaction. Oxidation: Zn → Zn2+ + 2e− Reduction: S + 2e− → S2− It is important to remember that the two half-reactions occur simultaneously. The resulting ions that are formed are then attracted to one anoth ...
Photoredox catalysis
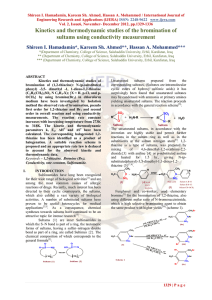
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.