Lecture 7
... Because the outer electrons are far from the nucleus and easily lost, they are all strong reducing agents. Going down the group the outer electrons get further from the nucleus and so are more weakly held. This is because of the greater distance between the nucleus and the outer electron and the inc ...
... Because the outer electrons are far from the nucleus and easily lost, they are all strong reducing agents. Going down the group the outer electrons get further from the nucleus and so are more weakly held. This is because of the greater distance between the nucleus and the outer electron and the inc ...
AQA_GCSE_Chemistry_Higher_Unit_2_Notes
... a) The pressure brings the molecules closer together, so that they react faster and also give a greater yield of ammonia since the forward reaction is encouraged. However, pumps to provide high pressure are expensive. b) High temperature makes molecules move faster, so that they collide more often ...
... a) The pressure brings the molecules closer together, so that they react faster and also give a greater yield of ammonia since the forward reaction is encouraged. However, pumps to provide high pressure are expensive. b) High temperature makes molecules move faster, so that they collide more often ...
Final Exam Practice Problems: R = 0.0821 Latm/molK NA = 6.022
... A) Li+ (aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq) B) Li+ (aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq) C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s) D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) ...
... A) Li+ (aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + Li+(aq) + NO3-(aq) B) Li+ (aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq) C) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → Cu2+(aq) + S2-(aq) + 2 LiNO3(s) D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) ...
Tutorial #1 - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... “B” is the fastest reaction because aqueous ions are highly mobile and more concentrated than molecules in a gas. The aqueous ions have a high probability of colliding. Also, when Ag+ and Ireact, there are no bonds to break. They simply collide and bond to form the solid. (The activation energy is v ...
... “B” is the fastest reaction because aqueous ions are highly mobile and more concentrated than molecules in a gas. The aqueous ions have a high probability of colliding. Also, when Ag+ and Ireact, there are no bonds to break. They simply collide and bond to form the solid. (The activation energy is v ...
Second Semester Review Part 1
... relation between solubility and temperature? (A) An increase in temperature increases the solubility of a gas in a liquid. (B) The change of solubility with temperature is the same for all substances. (C) The solubility of a liquid in a liquid is independent of temperature. (D) The solubility of mos ...
... relation between solubility and temperature? (A) An increase in temperature increases the solubility of a gas in a liquid. (B) The change of solubility with temperature is the same for all substances. (C) The solubility of a liquid in a liquid is independent of temperature. (D) The solubility of mos ...
RedOx notes:
... the inner “valley of confusion”) until there is only one left; if the element is last to choose it must have the charge that makes everything else sum to zero. If you don’t choose first you might not get your first choice (you can’t always get what you wanted, but if you try real hard you (might jus ...
... the inner “valley of confusion”) until there is only one left; if the element is last to choose it must have the charge that makes everything else sum to zero. If you don’t choose first you might not get your first choice (you can’t always get what you wanted, but if you try real hard you (might jus ...
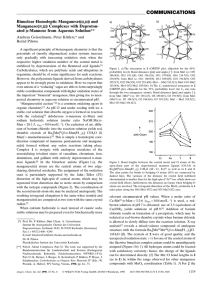
COMMUNICATIONS
... A significant principle of bioinorganic chemistry is that the potentials of (mostly oligonuclear) redox systems increase only gradually with increasing oxidation state when the respective higher oxidation number of the central metal is stabilized by deprotonation of the Brùnsted acid ligands.[1] Car ...
... A significant principle of bioinorganic chemistry is that the potentials of (mostly oligonuclear) redox systems increase only gradually with increasing oxidation state when the respective higher oxidation number of the central metal is stabilized by deprotonation of the Brùnsted acid ligands.[1] Car ...
Chapter 19
... atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the following equation represents the redox reaction used to manufacture ammonia (NH 3). N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) → 2NH 3(g) This process involves neither ions nor any obvious transfer of electrons. The reactants and products are all molecular compoun ...
... atoms are covalently bonded to other atoms. For example, the following equation represents the redox reaction used to manufacture ammonia (NH 3). N 2(g) + 3H 2(g) → 2NH 3(g) This process involves neither ions nor any obvious transfer of electrons. The reactants and products are all molecular compoun ...
Photosynthesis in Bacteria By Emmy Muscan
... -light reactions- light energy absorbed & converted to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) -dark reactions-carbohydrates made from CO2 using energy stored in ATP & NADPH ...
... -light reactions- light energy absorbed & converted to chemical energy (ATP, NADPH) -dark reactions-carbohydrates made from CO2 using energy stored in ATP & NADPH ...
24. The following reaction is at equilibrium
... 22. The following statements refer to a mixture (reaction quotient Q) that is prepared and then allowed to come to equilibrium. Which statement is NOT CORRECT? (A) A reaction will proceed to make the value of Q approach that of K. (B) If Q = K there is no change. (C) If Q > K, the reaction goes to ...
... 22. The following statements refer to a mixture (reaction quotient Q) that is prepared and then allowed to come to equilibrium. Which statement is NOT CORRECT? (A) A reaction will proceed to make the value of Q approach that of K. (B) If Q = K there is no change. (C) If Q > K, the reaction goes to ...
Entering and leaving group effects in Oh ligand substitutions
... Ligands trans-to each other compete for electron density because both M-L bonds use the same metal orbitals, e.g. dz2 or pz See p. 831 in Ch.22, Box 22.8: Very strong -donors (e.g. H– and alkyl– ligands) compete for orbital overlap at the metal with the leaving group: this weakens the M-L bond in t ...
... Ligands trans-to each other compete for electron density because both M-L bonds use the same metal orbitals, e.g. dz2 or pz See p. 831 in Ch.22, Box 22.8: Very strong -donors (e.g. H– and alkyl– ligands) compete for orbital overlap at the metal with the leaving group: this weakens the M-L bond in t ...
3. Chemical changes and Structure Unit Questions
... 24. (a) Atoms of different elements have different attractions for bonded electrons. What term is used as a measure of the attraction an atom involved in a bond has for the electrons of the bond? (1) (b) Atoms of different elements are different sizes. What is the trend in atomic size across the per ...
... 24. (a) Atoms of different elements have different attractions for bonded electrons. What term is used as a measure of the attraction an atom involved in a bond has for the electrons of the bond? (1) (b) Atoms of different elements are different sizes. What is the trend in atomic size across the per ...
File - Science With BLT
... a. coefficients of the reactants equal the coefficients of the products. b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the subscripts of the products. ...
... a. coefficients of the reactants equal the coefficients of the products. b. same number of each kind of atom appears in the reactants and in the products. c. products and reactants are the same chemicals. d. subscripts of the reactants equal the subscripts of the products. ...
Theoretical Study of Atomic Layer Deposition Reaction Mechanism
... The theoretical predicted result is compared with the available experimental data. 2. Computational Methods Quantum chemical density functional theory is employed to investigate the model reaction mechanism for the ALD of Al2O3 formation on graphene edges. The geometric parameters of the reactants, ...
... The theoretical predicted result is compared with the available experimental data. 2. Computational Methods Quantum chemical density functional theory is employed to investigate the model reaction mechanism for the ALD of Al2O3 formation on graphene edges. The geometric parameters of the reactants, ...
1 Unit 11-12: Equilibrium and Acid/Bases Notes Colligative
... endothermic reactions means Ea is being absorbed into the reaction to make it happen, “+” value, therefore add value to reactants side exothermic reactions means Ea is being released from the reaction; “‐” value, therefore add value to products side ...
... endothermic reactions means Ea is being absorbed into the reaction to make it happen, “+” value, therefore add value to reactants side exothermic reactions means Ea is being released from the reaction; “‐” value, therefore add value to products side ...
AP Chemistry - cloudfront.net
... 9.29 Using the periodic table only arrange the members of each of the following sets in order of increasing bond strength. (a) Br-Br, Cl-Cl, I-I; (b) S-H, S-Br, S-Cl; (c) C== N, C-N, C==N. 9.41 Using EN values, indicate the polarity of the following bonds with polar arrows, and determine the more po ...
... 9.29 Using the periodic table only arrange the members of each of the following sets in order of increasing bond strength. (a) Br-Br, Cl-Cl, I-I; (b) S-H, S-Br, S-Cl; (c) C== N, C-N, C==N. 9.41 Using EN values, indicate the polarity of the following bonds with polar arrows, and determine the more po ...
Fe(H2O)63+ + H2O → ← H3O+ + Fe(H2O)5(OH)2+
... 51. If a reaction proceeding by the mechanism A + B → C + D occurs at a rate x, and if the concentrations of A and B are both doubled, what will be the new rate of reaction? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
... 51. If a reaction proceeding by the mechanism A + B → C + D occurs at a rate x, and if the concentrations of A and B are both doubled, what will be the new rate of reaction? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) ...
Quiz Samples
... Gas occupies all the volume available T F Calculate the final pressure formed after the containers 1 and 2 were connected: Total volume= 1L+2L=3L; total amount of gas Container 1, 1L under 2 atm of gas Container 2, 2L under 1 atm of gas at normal pressure= 4L*atm (2 L in Container 1 and 2 L in Conta ...
... Gas occupies all the volume available T F Calculate the final pressure formed after the containers 1 and 2 were connected: Total volume= 1L+2L=3L; total amount of gas Container 1, 1L under 2 atm of gas Container 2, 2L under 1 atm of gas at normal pressure= 4L*atm (2 L in Container 1 and 2 L in Conta ...
MOLECULAR FORMULAS N C H H C N H HHH HH
... 4. (9 points) Gold, Au, is dissolved from rock by treating the rock with NaCN in the presence of oxygen. 4 Au(s) + 8 NaCN(aq) + O2(g) + 2 H2O(l) → 4 NaAu(CN)2(aq) + 4 NaOH(aq) (a) If you have 0.050 mol of gold, the number of moles of NaCN required is __________ mol and the number of moles of O2 requ ...
... 4. (9 points) Gold, Au, is dissolved from rock by treating the rock with NaCN in the presence of oxygen. 4 Au(s) + 8 NaCN(aq) + O2(g) + 2 H2O(l) → 4 NaAu(CN)2(aq) + 4 NaOH(aq) (a) If you have 0.050 mol of gold, the number of moles of NaCN required is __________ mol and the number of moles of O2 requ ...
Week 1 - School of Chemical Sciences
... Starting with a well-characterized transition metal complex from the inorganic literature, propose its development into a viable catalytic system for application towards a synthetically useful process. NIH postdoctoral fellowship style recommended. Length may not exceed 4 pages (including all figure ...
... Starting with a well-characterized transition metal complex from the inorganic literature, propose its development into a viable catalytic system for application towards a synthetically useful process. NIH postdoctoral fellowship style recommended. Length may not exceed 4 pages (including all figure ...
1. Explain electrophile and nucleophile. 2. Explain
... 68 Why alkyl groups act as donors when attached to a π System? 69. Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the electron shift using curved arrow rotation. (i) C6H5OH (2) C6H5NO2 (3) C6H5C+H2 (4) CH3CH=CHCHO (5) CH3CH=CHC+H2 (6)C6H5CHO (7) CH2=CHOCH3. 70. Write chemical equat ...
... 68 Why alkyl groups act as donors when attached to a π System? 69. Draw the resonance structures for the following compounds. Show the electron shift using curved arrow rotation. (i) C6H5OH (2) C6H5NO2 (3) C6H5C+H2 (4) CH3CH=CHCHO (5) CH3CH=CHC+H2 (6)C6H5CHO (7) CH2=CHOCH3. 70. Write chemical equat ...
Syracuse University
... courses intended for students with an interest or background in science. No prior chemistry instruction is required or assumed. A general, basic understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to succ ...
... courses intended for students with an interest or background in science. No prior chemistry instruction is required or assumed. A general, basic understanding of math and algebra, including an understanding of decimals, exponents, logarithms, quadratics, and algebraic equations, is essential to succ ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.