Sec 5.8 - 5.11 notes
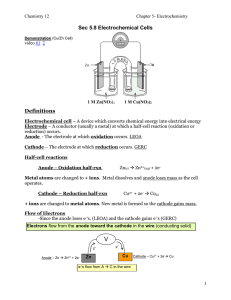
... 1) Electrochemical cells convert __________ energy into ___________ energy. 2) ___________ is the electrode where oxidation occurs. 3) Electrons are ________ at the anode. 4) _________ is the electrode where reduction occurs. 5) In the half-rx at the cathode, e-‘s are on the ______ side of the equat ...
... 1) Electrochemical cells convert __________ energy into ___________ energy. 2) ___________ is the electrode where oxidation occurs. 3) Electrons are ________ at the anode. 4) _________ is the electrode where reduction occurs. 5) In the half-rx at the cathode, e-‘s are on the ______ side of the equat ...
Equilibrium
... The activation energy barrier for a catalyzed reaction is lower than that of a uncatalyzed reaction. With a lower activation energy barrier, more reactants have the energy to form products within a given time. Because a catalyst is not consumed during a reaction, it does not appear as a reactant or ...
... The activation energy barrier for a catalyzed reaction is lower than that of a uncatalyzed reaction. With a lower activation energy barrier, more reactants have the energy to form products within a given time. Because a catalyst is not consumed during a reaction, it does not appear as a reactant or ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of t ...
... energies, electronegativity and melting points for the alkali metals (Li Cs), halogens (F I) and period 3 elements (Na Ar). Cross reference with topics 2, 4 and 5. Data for all these properties are listed in the data booklet. Explanations for the first four trends should be given in terms of t ...
Chemistry Name Mr. Reger Review Guide – Ch. 9
... 12. A student isolates 1.6g of a product after a reaction. If the theoretical yield of the reaction is 2.0g, what is the percent yield? ...
... 12. A student isolates 1.6g of a product after a reaction. If the theoretical yield of the reaction is 2.0g, what is the percent yield? ...
chemical reactions
... One type of redox reactions are single replacement reactions. In these reactions an active metal replace a less active metal. ...
... One type of redox reactions are single replacement reactions. In these reactions an active metal replace a less active metal. ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... 2. The reaction of succinic acid provides energy for the ATP synthesis and is shown below: ...
... 2. The reaction of succinic acid provides energy for the ATP synthesis and is shown below: ...
Ch 17 practice assessment w
... how can this be accomplished if they are traveling in a truck through different weather conditions? Also, when you receive your perishable product, how can you be certain that it has not been exposed to unfavorable conditions? It’s simple. You can use equilibrium. In water solutions, the Co 2 ion i ...
... how can this be accomplished if they are traveling in a truck through different weather conditions? Also, when you receive your perishable product, how can you be certain that it has not been exposed to unfavorable conditions? It’s simple. You can use equilibrium. In water solutions, the Co 2 ion i ...
and Lead Bis(tri-tert-butoxystannate)
... plex 3 of the 1-hydroxycyclobutabenzene is also not obtainable by direct reaction of the ligand with [Cr(CO),] or [Cr(CO),(NH,),].t3b1 Therefore 2 was reduced with lithium aluminum hydride to 3. The withdrawal of electrons by the tricarbonylchromium(0) moiety leads to a noticeable increase in reacti ...
... plex 3 of the 1-hydroxycyclobutabenzene is also not obtainable by direct reaction of the ligand with [Cr(CO),] or [Cr(CO),(NH,),].t3b1 Therefore 2 was reduced with lithium aluminum hydride to 3. The withdrawal of electrons by the tricarbonylchromium(0) moiety leads to a noticeable increase in reacti ...
Basic chemistry - Ross University
... and [Mg2+ ] (3 mM), since these influence the activity of many enzymes. The values chosen simply reflect those that we find in living cells. If a parameter X is measured under chemical standard conditions, we write X 0 , if it was measured under biological standard conditions we write X 00 . In olde ...
... and [Mg2+ ] (3 mM), since these influence the activity of many enzymes. The values chosen simply reflect those that we find in living cells. If a parameter X is measured under chemical standard conditions, we write X 0 , if it was measured under biological standard conditions we write X 00 . In olde ...
Exercise II
... This is known as a symmetrical or identity reaction since both the reactants (Cl, + CH3 Cl) and products (CH3 Cl + Cl, ) are identical. However, more general reactions involving different attacking and leaving groups form the basis of this reaction. The restriction of having identical attacking and ...
... This is known as a symmetrical or identity reaction since both the reactants (Cl, + CH3 Cl) and products (CH3 Cl + Cl, ) are identical. However, more general reactions involving different attacking and leaving groups form the basis of this reaction. The restriction of having identical attacking and ...
Asymmetry of Electron Transmission through Monolayers of Helical
... one-electron redox process of the Fc/Fc+ couple. The relationship between peak currents and the scan rates was linear, which indicated that electron transfer originates from the surface-bound redox center. The surface coverage of polyalanine derivative molecules was estimated from the area of the cy ...
... one-electron redox process of the Fc/Fc+ couple. The relationship between peak currents and the scan rates was linear, which indicated that electron transfer originates from the surface-bound redox center. The surface coverage of polyalanine derivative molecules was estimated from the area of the cy ...
Theory of Coordination Chemistry
... Aconitase - aconitate hydratase; is an enzyme that catalyses the stereospecific isomerization of citrate to isocitrate via cis-aconitate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, a non-redox-active process. ...
... Aconitase - aconitate hydratase; is an enzyme that catalyses the stereospecific isomerization of citrate to isocitrate via cis-aconitate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle, a non-redox-active process. ...
Test 8 Review
... Ideal Gases. In order to study gases, chemists have devised a model. The model is called an ideal gas (a gas which explains the behavior of all gases). This Ideal Gas Kinetic theory of gases (under ideal circumstances) model is based on the assumptions to the right, and can be 1. Gas are composed of ...
... Ideal Gases. In order to study gases, chemists have devised a model. The model is called an ideal gas (a gas which explains the behavior of all gases). This Ideal Gas Kinetic theory of gases (under ideal circumstances) model is based on the assumptions to the right, and can be 1. Gas are composed of ...
Document
... _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to the primary ______________ and ___________________ of the 3d subshell, so that the effective nuclear charge increa ...
... _______________ with atomic number pulls in the electron cloud, resulting in a reduction of atomic size. Since electrons are added to an inner d subshell across the series, this adds to the primary ______________ and ___________________ of the 3d subshell, so that the effective nuclear charge increa ...
Unit 4
... In an electron-transfer reaction, by definition, one substance must gain electrons while another substance must lose electrons. Oxidation is the loss of electrons by a substance (alternatively, it is an increase in the oxidation number of a substance.) Reduction is the gain of electrons by a substan ...
... In an electron-transfer reaction, by definition, one substance must gain electrons while another substance must lose electrons. Oxidation is the loss of electrons by a substance (alternatively, it is an increase in the oxidation number of a substance.) Reduction is the gain of electrons by a substan ...
unit (4) calculations and chemical reactions
... In an electron-transfer reaction, by definition, one substance must gain electrons while another substance must lose electrons. Oxidation is the loss of electrons by a substance (alternatively, it is an increase in the oxidation number of a substance.) Reduction is the gain of electrons by a substan ...
... In an electron-transfer reaction, by definition, one substance must gain electrons while another substance must lose electrons. Oxidation is the loss of electrons by a substance (alternatively, it is an increase in the oxidation number of a substance.) Reduction is the gain of electrons by a substan ...
Equilibrium and Kinetic Studies of Ligand
... buffer or bis-tris (bis-[2-hydroxyethyl]iminotris [hydroxy ethyl]methane) buffer are used (9). The chromatograms of other metal-HQS complexes exhibited single peaks even when the eluents contained a phosphate buffer. We have shown that this anomalous behavior of the alu minum complex can be explain ...
... buffer or bis-tris (bis-[2-hydroxyethyl]iminotris [hydroxy ethyl]methane) buffer are used (9). The chromatograms of other metal-HQS complexes exhibited single peaks even when the eluents contained a phosphate buffer. We have shown that this anomalous behavior of the alu minum complex can be explain ...
Title Photochemical chlorination of methane Author(s) Tamura, Mikio
... suns of partial pressures of Cl and Cls as will be explained later), for in the reaction mechanism I the partial reaction (3) will be fast in comparison with the reaction (2), and hence the mean life of the chlorine atom will be longer than that of CIT,. As the reaction velocity is proportional to a ...
... suns of partial pressures of Cl and Cls as will be explained later), for in the reaction mechanism I the partial reaction (3) will be fast in comparison with the reaction (2), and hence the mean life of the chlorine atom will be longer than that of CIT,. As the reaction velocity is proportional to a ...
Final "I Can Statements" Answer Key
... are theoretical although some gases are close. Hydrogen and helium are the closest to ideal gases at all temperatures and pressures. A gas will act most “ideally” under the conditions of __low___ pressure and ___high_____ temperature. The two elements that act ideally most of the time are ___hydroge ...
... are theoretical although some gases are close. Hydrogen and helium are the closest to ideal gases at all temperatures and pressures. A gas will act most “ideally” under the conditions of __low___ pressure and ___high_____ temperature. The two elements that act ideally most of the time are ___hydroge ...
Topic 6 Kinetics File
... Average bond enthalpy: The average enthalpy change of breaking one mole of a bond in a gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indic ...
... Average bond enthalpy: The average enthalpy change of breaking one mole of a bond in a gaseous atom into its constituent gaseous atoms. Born-Haber cycle: Energy cycles for the formation of ionic compounds. If there is little agreement between the theoretical and experimental values, this could indic ...
Chapter 7 Review
... Using the equation: 2 NH3(g) <---> N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 4.00 mol of ammonia gas are introduced into a 2.00 L container and heated. At equilibrium, 2.50 mol of ammonia remain in the container. a) Use an ICE table to determine the equilibrium concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen gas. (3) b) Plot the con ...
... Using the equation: 2 NH3(g) <---> N2(g) + 3 H2(g) 4.00 mol of ammonia gas are introduced into a 2.00 L container and heated. At equilibrium, 2.50 mol of ammonia remain in the container. a) Use an ICE table to determine the equilibrium concentrations of nitrogen and hydrogen gas. (3) b) Plot the con ...
Lab #4: Chemical Reactions
... Dispose of the solution and solid from this part of the experiment in your waste beaker. Rinse the test tube using deionized water from your squirt bottle; pour the rinse water into the waste beaker. Part C-2. In this single replacement reaction, magnesium replaces the hydrogen in HCl. Place 3 mL of ...
... Dispose of the solution and solid from this part of the experiment in your waste beaker. Rinse the test tube using deionized water from your squirt bottle; pour the rinse water into the waste beaker. Part C-2. In this single replacement reaction, magnesium replaces the hydrogen in HCl. Place 3 mL of ...
MASS-INDEPENDENT ISOTOPE FRACTIONATION OF CHROMIUM
... [δ50Cr=1.49±0.05, δ53Cr=−0.85±0.03]), all results showed similar trends as shown in Fig. 3. (Scaling factors A and B in Eq. 3 are variables which strongly depend on the experimental condition. In this study, concentrated HCl may have strengthened the complexation of Cr-Cl, which may have shifted A a ...
... [δ50Cr=1.49±0.05, δ53Cr=−0.85±0.03]), all results showed similar trends as shown in Fig. 3. (Scaling factors A and B in Eq. 3 are variables which strongly depend on the experimental condition. In this study, concentrated HCl may have strengthened the complexation of Cr-Cl, which may have shifted A a ...
Theoretical Enthalpy
... of a reaction experimentally by calorimetry, and for violent reactions by applying Hess’s Law to a series of reactions carried out separately in a calorimeter. These methods have lead to extensive tables listing the enthalpies of vaporization (∆Hvap), enthalpies of fusion (∆Hfus), enthalpies of redu ...
... of a reaction experimentally by calorimetry, and for violent reactions by applying Hess’s Law to a series of reactions carried out separately in a calorimeter. These methods have lead to extensive tables listing the enthalpies of vaporization (∆Hvap), enthalpies of fusion (∆Hfus), enthalpies of redu ...
Syllabus of Medical / Dental Colleges Entrance Test 2016
... equation; order of reaction; rate constant; half-life of a reaction; rate-determining step b) Explain qualitatively, in terms of collisions, the effect of concentration changes on the rate of a reaction c) Explain that, in the presence of a catalyst, a reaction has a different mechanism, i.e. one of ...
... equation; order of reaction; rate constant; half-life of a reaction; rate-determining step b) Explain qualitatively, in terms of collisions, the effect of concentration changes on the rate of a reaction c) Explain that, in the presence of a catalyst, a reaction has a different mechanism, i.e. one of ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.