Practice Exam I FR Answers and Explanations
... (a) Predict sign of Eº and explain. The sign of Eº must be positive. The prompt gives a K value of 1.5 × 1011 which means that the products are favored at equilibrium. Since the reaction proceeds as written, the voltage should be positive. (b) Identify reducing agent. Cd changes oxidation states fro ...
... (a) Predict sign of Eº and explain. The sign of Eº must be positive. The prompt gives a K value of 1.5 × 1011 which means that the products are favored at equilibrium. Since the reaction proceeds as written, the voltage should be positive. (b) Identify reducing agent. Cd changes oxidation states fro ...
chemical reactions and stoichiometry chemical reactions and
... In chemical reactions, the amount of each element is always conserved. This is consistent with the statements of Dalton’s atomic theory. In addition, the total amount of electrical charge is always conserved. This is the law of conservation of charge. A balanced chemical equation describes a chemica ...
... In chemical reactions, the amount of each element is always conserved. This is consistent with the statements of Dalton’s atomic theory. In addition, the total amount of electrical charge is always conserved. This is the law of conservation of charge. A balanced chemical equation describes a chemica ...
Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... Thus, although the difluoride CH3CHF2 boils at a higher temperature than CH3CH2F, the trifluoride CH3CF3 boils at a lower temperature than either of them. Even more striking is the observation that the hexafluoride CF3CF3 is the lowest boiling of any of the fluorinated derivatives of ethane. The boi ...
... Thus, although the difluoride CH3CHF2 boils at a higher temperature than CH3CH2F, the trifluoride CH3CF3 boils at a lower temperature than either of them. Even more striking is the observation that the hexafluoride CF3CF3 is the lowest boiling of any of the fluorinated derivatives of ethane. The boi ...
Organic Chemistry - University of California, Riverside
... F attracts electrons more than C in C-F bonds because the electronegativity of F (3.9) is much greater than that of C (2.5). In contrast, C-H bonds are not very polar because the electronegativities of H (2.3) and C (2.5) are about the same. Positive (+) values for the electronegativity differences ...
... F attracts electrons more than C in C-F bonds because the electronegativity of F (3.9) is much greater than that of C (2.5). In contrast, C-H bonds are not very polar because the electronegativities of H (2.3) and C (2.5) are about the same. Positive (+) values for the electronegativity differences ...
Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer in 3
... The excitation spectrum of the tautomer emission (curve a in Figure 2) has its first peak at 356 nm, only slightly blue-shifted from the position at 361 nm in a MCH glass at 77 K." However, it displays more vibrational structure with higher intensities for the higher energy bands, resembling more th ...
... The excitation spectrum of the tautomer emission (curve a in Figure 2) has its first peak at 356 nm, only slightly blue-shifted from the position at 361 nm in a MCH glass at 77 K." However, it displays more vibrational structure with higher intensities for the higher energy bands, resembling more th ...
Chem. 1310 Fall 2005 Final Exam-white ... Name _________________________________ Section Number ___________________
... a. increase the entropy of the universe. b. decrease the energy of the universe. Answer: a 22. Which of the following are generally true? a. Intermolecular forces are weaker than covalent bonds. b. Intermolecular forces are more directional than covalent bonds. c. Any molecule in a gas experiences i ...
... a. increase the entropy of the universe. b. decrease the energy of the universe. Answer: a 22. Which of the following are generally true? a. Intermolecular forces are weaker than covalent bonds. b. Intermolecular forces are more directional than covalent bonds. c. Any molecule in a gas experiences i ...
1.6 Energy changes in chemical reactions
... In the field of renewable energy, dye-sensitized solar cells are being developed that will provide a cheaper alternative to silicon-based products. Light-harvesting dyes containing ruthenium are adsorbed onto a thin film of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in contact with a redox electrolyte. T ...
... In the field of renewable energy, dye-sensitized solar cells are being developed that will provide a cheaper alternative to silicon-based products. Light-harvesting dyes containing ruthenium are adsorbed onto a thin film of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles in contact with a redox electrolyte. T ...
Thermodynamics and Equilibrium
... the spontaneity of a reaction. 1. When Go is a large negative number (more negative than about –10 kJ), the reaction is spontaneous as written, and the reactants transform almost entirely to products when equilibrium is reached. ...
... the spontaneity of a reaction. 1. When Go is a large negative number (more negative than about –10 kJ), the reaction is spontaneous as written, and the reactants transform almost entirely to products when equilibrium is reached. ...
(MDCAT) 2017 - University Of Health Sciences Lahore
... i) Describe metallic bonding in terms of positive ions surrounded by mobile electrons (sea of electrons). j) Describe, interpret and/or predict the effect of different types of bonding (ionic bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding; Van der Waal’s forces and metallic bonding) on the physical pro ...
... i) Describe metallic bonding in terms of positive ions surrounded by mobile electrons (sea of electrons). j) Describe, interpret and/or predict the effect of different types of bonding (ionic bonding; covalent bonding; hydrogen bonding; Van der Waal’s forces and metallic bonding) on the physical pro ...
Introduction: A Historical Approach to Catalysis
... same way, produce the same crystal forms: the crystal form does not depend on the nature of the atoms, but only on their number and mode of combination” v synthesized benzene F.C. Jentoft Dept. AC / FHI Berlin ...
... same way, produce the same crystal forms: the crystal form does not depend on the nature of the atoms, but only on their number and mode of combination” v synthesized benzene F.C. Jentoft Dept. AC / FHI Berlin ...
20.2 Oxidation Numbers
... oxidation number is the charge that it would have if the electrons in the bond were assigned to the atom of the more electronegative element. An increase in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates oxidation. A decrease in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates reduction. ...
... oxidation number is the charge that it would have if the electrons in the bond were assigned to the atom of the more electronegative element. An increase in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates oxidation. A decrease in the oxidation number of an atom or ion indicates reduction. ...
Chapter 4
... of the two. Nevertheless, some of the earliest insights into the microscopic nature of aqueous solutions came through macroscopic observations on the ability of solutions to conduct electricity. To understand why, let’s first look at some significant early discoveries about electricity. Static elect ...
... of the two. Nevertheless, some of the earliest insights into the microscopic nature of aqueous solutions came through macroscopic observations on the ability of solutions to conduct electricity. To understand why, let’s first look at some significant early discoveries about electricity. Static elect ...
Curriculum Vitae - Université Paris-Sud
... Université Paris-Sud, 91405 Orsay, France For more than two decades, extensive research work has been devoted to the unique properties of clusters. They are made of a small number (or nuclearity) of atoms or molecules only, and therefore constitute a new state of matter, or mesoscopic phase, between ...
... Université Paris-Sud, 91405 Orsay, France For more than two decades, extensive research work has been devoted to the unique properties of clusters. They are made of a small number (or nuclearity) of atoms or molecules only, and therefore constitute a new state of matter, or mesoscopic phase, between ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e. react) during the course of the reaction. ...
... • To form the net ionic equation, cross out anything that does not change from the left side of the equation to the right. • The only things left in the equation are those things that change (i.e. react) during the course of the reaction. ...
Fundamentals Diagnostic Quiz
... 18. All of the following are statements from Daltons atomic hypothesis, except: a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. *c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. d) A compound is a specific combination of atom ...
... 18. All of the following are statements from Daltons atomic hypothesis, except: a) All the atoms of a given element are identical. b) The atoms of different elements have different masses. *c) All atoms are composed of electrons, protons, and neutrons. d) A compound is a specific combination of atom ...
CHEMICAL EQUATIONS - Clayton State University
... BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS - Whole numbers are placed on the left side of the formula (called coefficients) to balance the equation (subscripts remain unchanged) - The coefficients in a chemical equation are the smallest set of whole numbers that balance the equation C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + ...
... BALANCING CHEMICAL EQUATIONS - Whole numbers are placed on the left side of the formula (called coefficients) to balance the equation (subscripts remain unchanged) - The coefficients in a chemical equation are the smallest set of whole numbers that balance the equation C2H5OH(l) + O2(g) → 2CO2(g) + ...
Ionic Liquids Beyond Simple Solvents: Glimpses at the State of the
... not—were performed in IL solvents, and for quite a while, just using an IL for something safely guaranteed a publication in a chemistry journal. These days, ILs are typically applied as solvents for chemical transformations, and the huge choice of different ILs has led to the term “designer solvents ...
... not—were performed in IL solvents, and for quite a while, just using an IL for something safely guaranteed a publication in a chemistry journal. These days, ILs are typically applied as solvents for chemical transformations, and the huge choice of different ILs has led to the term “designer solvents ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Department of Chemistry
... • For a given set of reaction conditions, the equilibrium amounts of reactants and products in a reversible reaction are independent of whether the reaction is homogeneous, heterogeneous or otherwise catalysed. • A catalyst does not change the position of equilibrium. • The catalyst only acts to dec ...
... • For a given set of reaction conditions, the equilibrium amounts of reactants and products in a reversible reaction are independent of whether the reaction is homogeneous, heterogeneous or otherwise catalysed. • A catalyst does not change the position of equilibrium. • The catalyst only acts to dec ...
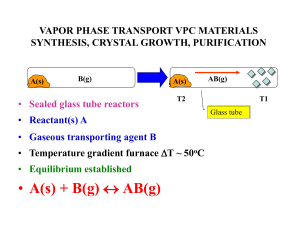
vapor phase transport vpc materials synthesis, crystal growth
... The Meissner effect is one of the defining features of superconductivity, and its discovery served to establish that the onset of superconductivity is a phase transition between uncoupled and phonon coupled electrons ...
... The Meissner effect is one of the defining features of superconductivity, and its discovery served to establish that the onset of superconductivity is a phase transition between uncoupled and phonon coupled electrons ...
Follow Along Notes - Jackson County School System
... Given the equilibrium reaction ZnCO3(s) ZnO(s) + CO2(g). Which one of the following statements is true? a. Equal concentrations of ZnO(s) and CO2(g) would result from the decomposition of a given amount of ZnCO3(s). b. The same equilibrium condition would result if we started with only pure ZnCO3(s) ...
... Given the equilibrium reaction ZnCO3(s) ZnO(s) + CO2(g). Which one of the following statements is true? a. Equal concentrations of ZnO(s) and CO2(g) would result from the decomposition of a given amount of ZnCO3(s). b. The same equilibrium condition would result if we started with only pure ZnCO3(s) ...
CLASSES AND NOMENCLATURE OF INORGANIC COMPOUNDS
... 9. Speed of what reactions increases if the 10. The law of mass action describes the temperature is increased? dependence of rate of chemical reaction on: A endothermic A the concentration of reactans B exothermic B areas of surface of clashing of reactive C anyone compounds D red-ox reaction C the ...
... 9. Speed of what reactions increases if the 10. The law of mass action describes the temperature is increased? dependence of rate of chemical reaction on: A endothermic A the concentration of reactans B exothermic B areas of surface of clashing of reactive C anyone compounds D red-ox reaction C the ...
Solids Chemistry XII - The Gurukul Institute
... Explains why ionic and metallic crystals have higher heat of vaporization than do covalent molecular solids? [ Hint : electrostatic forces of attraction act between the ions in ionic compounds and between the lattice of metal cations and delocalized electrons in metallic which are stronger than the ...
... Explains why ionic and metallic crystals have higher heat of vaporization than do covalent molecular solids? [ Hint : electrostatic forces of attraction act between the ions in ionic compounds and between the lattice of metal cations and delocalized electrons in metallic which are stronger than the ...
B - eko.olunet.org
... Purity Grade of Compounds 3. In chemical experiments, the purity of the starting material and the composition of impurities/additives are of great importance. For his experiments, Thomas needed KBr with at least 95.0% purity. In order to determine the purity of an available inorganic compound, he w ...
... Purity Grade of Compounds 3. In chemical experiments, the purity of the starting material and the composition of impurities/additives are of great importance. For his experiments, Thomas needed KBr with at least 95.0% purity. In order to determine the purity of an available inorganic compound, he w ...
Chemical Equilibrium - Request a Spot account
... Notice the arrow in this reaction is pointing only to the right. This reaction is not an equilibrium system. The reaction is said to go to completion. Consequently, the number of chloride ions and hydronium ions formed by this reaction are equal to the number HCl molecules dissolved in water. That i ...
... Notice the arrow in this reaction is pointing only to the right. This reaction is not an equilibrium system. The reaction is said to go to completion. Consequently, the number of chloride ions and hydronium ions formed by this reaction are equal to the number HCl molecules dissolved in water. That i ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Analyze: Our task is to write a net ionic equation for a precipitation reaction, given the names of the reactants present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular ...
... Analyze: Our task is to write a net ionic equation for a precipitation reaction, given the names of the reactants present in solution. Plan: We first need to write the chemical formulas of the reactants and products and to determine which product is insoluble. Then we write and balance the molecular ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.