3.Redox
... 1. Titration = the controlled addition, from a buret, of the solution of one reactant (titrant) to a solution of another reactant until an “end point” is reached. a. At the end point, one has mixed stoichiometric amounts of the two reactants. b. The end point is signaled by using an indicator. This ...
... 1. Titration = the controlled addition, from a buret, of the solution of one reactant (titrant) to a solution of another reactant until an “end point” is reached. a. At the end point, one has mixed stoichiometric amounts of the two reactants. b. The end point is signaled by using an indicator. This ...
Ryoji Noyori - Nobel Lecture
... intrinsically achiral metal atoms must possess suitable three-dimensional structures and functionality to generate sufficient reactivity and the desired stereoselectivity. Sometimes the properties of achiral ligands are also important. The chiral catalyst can permit kinetically precise discriminatio ...
... intrinsically achiral metal atoms must possess suitable three-dimensional structures and functionality to generate sufficient reactivity and the desired stereoselectivity. Sometimes the properties of achiral ligands are also important. The chiral catalyst can permit kinetically precise discriminatio ...
Solubility and complexes
... Stereoisomers: same atom connectivities but different arrangement of atoms in space Geometric isomerism Optical isomerism ...
... Stereoisomers: same atom connectivities but different arrangement of atoms in space Geometric isomerism Optical isomerism ...
1. What energy changes occur when chemical bonds are formed
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
... The reaction is spontaneous at low temperatures but becomes non-spontaneous at high temperatures. ...
Chemical Reactions
... them out (or give them to your dog.) The rest of the cookies are okay. How many cookies could you have made (theoretical ...
... them out (or give them to your dog.) The rest of the cookies are okay. How many cookies could you have made (theoretical ...
Test bank questions
... 50.0 g of N2O4 is introduced into an evacuated 2.00 L vessel and allowed to come to equilibrium with its decomposition product, N2O4(g) 2NO2(g). For this reaction Kc = 0.133. Once the system has reached equilibrium, 5.00 g of NO 2 is injected into the vessel, and the system is allowed to equilibrate ...
... 50.0 g of N2O4 is introduced into an evacuated 2.00 L vessel and allowed to come to equilibrium with its decomposition product, N2O4(g) 2NO2(g). For this reaction Kc = 0.133. Once the system has reached equilibrium, 5.00 g of NO 2 is injected into the vessel, and the system is allowed to equilibrate ...
08272012BC Science Chem 12 Chapter 1 Answer Key
... significant than the pressure as we are very close to sea level. This means molar volume is likely a bit smaller than 24.5 L/mol (or 26.5 L/mol for trial two). Dividing by a smaller number would lead to a LARGER MASS of zinc expected. 1.2 Review Questions (page 25) 1. Factors affecting heterogeneous ...
... significant than the pressure as we are very close to sea level. This means molar volume is likely a bit smaller than 24.5 L/mol (or 26.5 L/mol for trial two). Dividing by a smaller number would lead to a LARGER MASS of zinc expected. 1.2 Review Questions (page 25) 1. Factors affecting heterogeneous ...
aq - Byron High School
... Metathesis (Exchange) Reactions • Metathesis comes from a Greek word that means “to transpose” • It appears the ions in the reactant compounds exchange, or transpose, ions ...
... Metathesis (Exchange) Reactions • Metathesis comes from a Greek word that means “to transpose” • It appears the ions in the reactant compounds exchange, or transpose, ions ...
Chapter 14 Review
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
... A. Increasing the system volume shifts the equilibrium to the right. B. Increasing the temperature shifts the equilibrium to the right. C. A catalyst speeds up the approach to equilibrium and shifts the position of equilibrium to the right. D. Decreasing the total pressure of the system shifts the e ...
Hydrocarbons and Fuels - Deans Community High School
... 1. Before collecting the alcohol and carboxylic acid set up a water bath using the larger beaker and heat the water until it boils. Turn off the Bunsen. 2. Add the alcohol to a test tube to a depth of about 1 cm. To this add about the same volume of carboxylic acid. If the acid is a solid then use a ...
... 1. Before collecting the alcohol and carboxylic acid set up a water bath using the larger beaker and heat the water until it boils. Turn off the Bunsen. 2. Add the alcohol to a test tube to a depth of about 1 cm. To this add about the same volume of carboxylic acid. If the acid is a solid then use a ...
IChO_Comp_Prob_Answ 1997
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
29th INTERNATIONAL CHEMISTRY OLYMPIAD PREPARATORY
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
... routine material studied in most high schools around the world. But this is how it should be since the competitors involved are among the best that our countries have to offer. However, it is felt that even these topics and the level of expertise expected can be mastered by our students without sign ...
as a PDF
... of irradiation pulses prevents this kind of redox process through electron transfer. It was shown that in the same mixed ion system the metal clusters obtained change with increasing dose rate from a bilayered core/shell structure to an alloyed structure or bimetallic solid solution.10 In the litera ...
... of irradiation pulses prevents this kind of redox process through electron transfer. It was shown that in the same mixed ion system the metal clusters obtained change with increasing dose rate from a bilayered core/shell structure to an alloyed structure or bimetallic solid solution.10 In the litera ...
U3 Student Workbook - The Connected Chemistry Curriculum
... of Mass to chemical equations by learning how to balance them. Following a teacher demonstration of the simulation and procedures, students will use the simulations to look at ten different reactions. In each of the reactions, students will create submicroscopic sketches and balance the chemical for ...
... of Mass to chemical equations by learning how to balance them. Following a teacher demonstration of the simulation and procedures, students will use the simulations to look at ten different reactions. In each of the reactions, students will create submicroscopic sketches and balance the chemical for ...
advanced placement chemistry workbook and note set
... three electrons to fill its valence shell and form the nitrogen ion, which has a charge of 3-. The charge is due to the difference between positive charges (protons) and negative charges (electrons): an atom of nitrogen contains 7 protons and 7 electrons; an ion of nitrogen contains 7 protons and 10 ...
... three electrons to fill its valence shell and form the nitrogen ion, which has a charge of 3-. The charge is due to the difference between positive charges (protons) and negative charges (electrons): an atom of nitrogen contains 7 protons and 7 electrons; an ion of nitrogen contains 7 protons and 10 ...
BASIC CONCEPTS OF CHEMISTRY
... The study of chemical processes should be approached through a series of successive approximations. The first stage is expedient to consider only the initial and final states of the interacting bodies without considering the way in which the process takes place, and the development of the process in ...
... The study of chemical processes should be approached through a series of successive approximations. The first stage is expedient to consider only the initial and final states of the interacting bodies without considering the way in which the process takes place, and the development of the process in ...
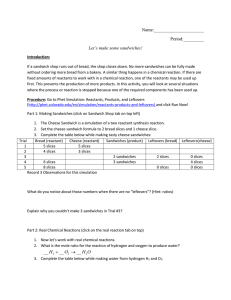
Name: Period:______ Let`s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If
... Name:______________________ Period:_________ Let’s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If a sandwich shop runs out of bread, the shop closes down. No more sandwiches can be fully made without ordering more bread from a bakery. A similar thing happens in a chemical reaction. If there are fixed amount ...
... Name:______________________ Period:_________ Let’s make some sandwiches! Introduction: If a sandwich shop runs out of bread, the shop closes down. No more sandwiches can be fully made without ordering more bread from a bakery. A similar thing happens in a chemical reaction. If there are fixed amount ...
Chemical bonding and structure
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
... as protons and electrons. This is because the number of protons (+) is equal to the number of electrons (−), and so their charges cancel each other out. The positively charged protons, located within the nucleus of the atom, are not transferred during chemical reactions. Electrons, however, position ...
Mechanochemistry: the varied applications of mechanical bond
... were cracked by breaking of intermolecular cohesive ligations producing very high surface area for the solid-solid reaction with equally micronized reagent crystallites or with liquids. A fair reactivity comparison for solid-liquid reactions would be the use of pre-milled C60 for the reaction with t ...
... were cracked by breaking of intermolecular cohesive ligations producing very high surface area for the solid-solid reaction with equally micronized reagent crystallites or with liquids. A fair reactivity comparison for solid-liquid reactions would be the use of pre-milled C60 for the reaction with t ...
CHEM 1212 Principles of Chemistry II Course Study Guide
... to know from previous material: element names and symbols, parts of the periodic table whether referred to by section name or group name, how ions are made and predict the charges…just as a start. Naming is one of the more difficult topics because of all the skills it requires. This means that you w ...
... to know from previous material: element names and symbols, parts of the periodic table whether referred to by section name or group name, how ions are made and predict the charges…just as a start. Naming is one of the more difficult topics because of all the skills it requires. This means that you w ...
NICKEL(II) PINCER COMPLEXES SUPPORTED BY 2,6
... The starting material of the ligand synthesis, 2,6-dicarboxaldehye was prepared from 2,6-dimethanol pyridine through oxidation with SeO2/Dioxane (Figure 9). Then, tolualdehyde was stirred at room temperature for 5 h with 4-methylacetophenone and NaOH in EtOH/H2O to form 1,3-bis(4-tolyl)-2-propen-1-o ...
... The starting material of the ligand synthesis, 2,6-dicarboxaldehye was prepared from 2,6-dimethanol pyridine through oxidation with SeO2/Dioxane (Figure 9). Then, tolualdehyde was stirred at room temperature for 5 h with 4-methylacetophenone and NaOH in EtOH/H2O to form 1,3-bis(4-tolyl)-2-propen-1-o ...
Introduction to Kinetics and Equilibrium
... Introduction to Kinetics and Equilibrium Kinetics and equilibrium are two of the most important areas in chemistry Entire books and important areas in chemistry. Entire books and courses at the undergraduate and graduate level are devoted to them. Chemical kinetics – the study of the rates of ...
... Introduction to Kinetics and Equilibrium Kinetics and equilibrium are two of the most important areas in chemistry Entire books and important areas in chemistry. Entire books and courses at the undergraduate and graduate level are devoted to them. Chemical kinetics – the study of the rates of ...
Equilibrium - Clayton State University
... - Such reactions are known as reversible reactions - Forward reaction rate decreases with time as reactants are used up - Reverse reaction rate increases with time as products are being formed - Concentrations are reached when both forward and reverse rates become equal ...
... - Such reactions are known as reversible reactions - Forward reaction rate decreases with time as reactants are used up - Reverse reaction rate increases with time as products are being formed - Concentrations are reached when both forward and reverse rates become equal ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.